About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 55 results economy clear search
An Agent-based model of the economy with consumer credit
Paola D'Orazio Gianfranco Giulioni | Published Friday, April 15, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, March 07, 2019The model was built to study the links between consumer credit, wealth distribution and aggregate demand in a complex macroeconomics system.
A simple agent-based spatial model of the economy
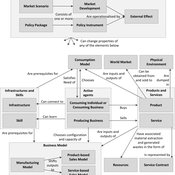
Bernardo Alves Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Thursday, March 10, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 22, 2016The modeling includes citizens, bounded into families; firms and governments; all of them interacting in markets for goods, labor and real estate. The model is spatial and dynamic.
MixFarm ABM Model
Leigh Anderson | Published Thursday, March 03, 2016MixFarmABM Model examines the competitiveness of second-generation biofuel crops with existing crops and beef cows at the farm level and their impact on the farm structure.
Long Term Impacts of Bank Behavior on Financial Stability An Agent Based Modeling Approach
Ilker Arslan | Published Tuesday, October 13, 2015 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model simulates a bank - firm credit network.
SimDrink: An agent-based NetLogo model of young, heavy drinkers for conducting alcohol policy experiments
Nick Scott James Wilson Michael Livingston Aaron Hart David Moore Paul Dietze | Published Friday, September 25, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, October 15, 2015A proof-of-concept agent-based model ‘SimDrink’, which simulates a population of 18-25 year old heavy alcohol drinkers on a night out in Melbourne to provide a means for conducting policy experiments to inform policy decisions.
Generic servicising model (SPREE project)
Igor Nikolic Reinier Van Der Veen Kasper H Kisjes | Published Wednesday, August 26, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, September 28, 2016This generic agent-based model allows the user to simulate and explore the influence of servicising policies on the uptake of servicising and on economic, environmental and social effects, notably absolute decoupling.
06 EiLab V1.36 – Entropic Index Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 14, 2017EiLab explores the role of entropy in simple economic models. EiLab is one of several models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, and CmLab.
Peer reviewed Umwelten Ants
Kit Martin | Published Thursday, January 15, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, August 27, 2015Simulates impacts of ants killing colony mates when in conflict with another nest. The murder rate is adjustable, and the environmental change is variable. The colonies employ social learning so knowledge diffusion proceeds if interactions occur.
Peer reviewed Hohokam Trade Networks Model
Joshua Watts | Published Sunday, October 26, 2014The Hohokam Trade Networks Model focuses on key features of the Hohokam economy to explore how differences in trade network topologies may show up in the archaeological record. The model is set in the Phoenix Basin of central Arizona, AD 200-1450.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
Displaying 10 of 55 results economy clear search