About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 191 results decision clear search
Agent based modeling of the effects of carbon payments and forest owner cooperatives on carbon storage and revenue in Pacific Northwest forestlands.
Dan Brown Pranab Roy Chowdhury | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The Olympic Peninsula ABM works as a virtual laboratory to simulate the existing forestland management practices as followed by different forestland owner groups in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, and explore how they could shape the future provisions of multifunctional ecosystem services such as Carbon storage and revenue generation under the business-as-usual scenario as well as by their adaptation to interventions. Forestlands are socio-ecological systems that interact with economic, socio-cultural, and policy systems. Two intervention scenarios were introduced in this model to simulate the adaptation of landowner behavior and test the efficacy of policy instruments in promoting sustainable forest practices and fostering Carbon storage and revenue generation. (1) A market-linked carbon offset scheme that pays the forestland owners a financial incentive in the form of a yearly carbon rent. (2) An institutional intervention policy that allows small forest owners (SFLO) to cooperate for increased market access and benefits under carbon rent scenario. The model incorporates the heterogeneous contexts within which the forestland owners operate and make their forest management decisions by parameterizing relevant agent attributes and contextualizing their unique decision-making processes.
Agent-based model of team decision-making in hidden profile situations
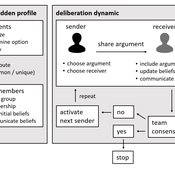
Andreas Flache Jonas Stein Vincenz Frey | Published Thursday, April 20, 2023 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2023The model presented here is extensively described in the paper ‘Talk less to strangers: How homophily can improve collective decision-making in diverse teams’ (forthcoming at JASSS). A full replication package reproducing all results presented in the paper is accessible at https://osf.io/76hfm/.
Narrative documentation includes a detailed description of the model, including a schematic figure and an extensive representation of the model in pseudocode.
The model develops a formal representation of a diverse work team facing a decision problem as implemented in the experimental setup of the hidden-profile paradigm. We implement a setup where a group seeks to identify the best out of a set of possible decision options. Individuals are equipped with different pieces of information that need to be combined to identify the best option. To this end, we assume a team of N agents. Each agent belongs to one of M groups where each group consists of agents who share a common identity.
The virtual teams in our model face a decision problem, in that the best option out of a set of J discrete options needs to be identified. Every team member forms her own belief about which decision option is best but is open to influence by other team members. Influence is implemented as a sequence of communication events. Agents choose an interaction partner according to homophily h and take turns in sharing an argument with an interaction partner. Every time an argument is emitted, the recipient updates her beliefs and tells her team what option she currently believes to be best. This influence process continues until all agents prefer the same option. This option is the team’s decision.
Direct versus Connect
Steven Kimbrough | Published Sunday, January 15, 2023This NetLogo model is an implementation of the mostly verbal (and graphic) model in Jarret Walker’s Human Transit: How Clearer Thinking about Public Transit Can Enrich Our Communities and Our Lives (2011). Walker’s discussion is in the chapter “Connections or Complexity?”. See especially figure 12-2, which is on page 151.
In “Connections or Complexity?”, Walker frames the matter as involving a choice between two conflicting goals. The first goal is to minimize connections, the need to make transfers, in a transit system. People naturally prefer direct routes. The second goal is to minimize complexity. Why? Well, read the chapter, but as a general proposition we want to avoid unnecessary complexity with its attendant operating characteristics (confusing route plans in the case of transit) and management and maintenance challenges. With complexity general comes degraded robustness and resilience.
How do we, how can we, choose between these conflicting goals? The grand suggestion here is that we only choose indirectly, implicitly. In the present example of connections versus complexity we model various alternatives and compare them on measures of performance (MoP) other than complexity or connections per se. The suggestion is that connections and complexity are indicators of, heuristics for, other MoPs that are more fundamental, such as cost, robustness, energy use, etc., and it is these that we at bottom care most about. (Alternatively, and not inconsistently, we can view connections and complexity as two of many MoPs, with the larger issue to be resolve in light of many MoPs, including but not limited to complexity and connections.) We employ modeling to get a handle on these MoPs. Typically, there will be several, taking us thus to a multiple criteria decision making (MCDM) situation. That’s the big picture.
DINO model - Dynamics of Internalization and Dissemination of Norms
Marlene Batzke | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2023 | Last modified Saturday, August 19, 2023The DINO model (Dynamics of Internalization and Dissemimnation of Norms) simulates a conceptual model on the dynamics of norm internalization in the decision-making framework of a 3-person prisoner’s dilemma game.
Peer reviewed SIM-VOLATILE: Adoption of emerging circular technologies in the waste-treatment sector
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Wednesday, December 14, 2022The SIM-VOLATILE model is a technology adoption model at the population level. The technology, in this model, is called Volatile Fatty Acid Platform (VFAP) and it is in the frame of the circular economy. The technology is considered an emerging technology and it is in the optimization phase. Through the adoption of VFAP, waste-treatment plants will be able to convert organic waste into high-end products rather than focusing on the production of biogas. Moreover, there are three adoption/investment scenarios as the technology enables the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), single-cell oils (SCO), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). However, due to differences in the processing related to the products, waste-treatment plants need to choose one adoption scenario.
In this simulation, there are several parameters and variables. Agents are heterogeneous waste-treatment plants that face the problem of circular economy technology adoption. Since the technology is emerging, the adoption decision is associated with high risks. In this regard, first, agents evaluate the economic feasibility of the emerging technology for each product (investment scenarios). Second, they will check on the trend of adoption in their social environment (i.e. local pressure for each scenario). Third, they combine these two economic and social assessments with an environmental assessment which is their environmental decision-value (i.e. their status on green technology). This combination gives the agent an overall adaptability fitness value (detailed for each scenario). If this value is above a certain threshold, agents may decide to adopt the emerging technology, which is ultimately depending on their predominant adoption probabilities and market gaps.
The purpose of the study is to unpack and explore a potentially beneficial role of sharing metacognitive information within a group when making repeated decisions about common pool resource (CPR) use.
We explore the explanatory power of sharing metacognition by varying (a) the individual errors in judgement (myside-bias); (b) the ways of reaching a collective judgement (metacognition-dependent), (c) individual knowledge updating (metacognition- dependent) and d) the decision making context.
The model (AgentEx-Meta) represents an extension to an existing and validated model reflecting behavioural CPR laboratory experiments (Schill, Lindahl & Crépin, 2015; Lindahl, Crépin & Schill, 2016). AgentEx-Meta allows us to systematically vary the extent to which metacognitive information is available to agents, and to explore the boundary conditions of group benefits of metacognitive information.
Peer reviewed TRANSOPE: a multi-agent model to simulate outsourcing networks in road freight transport.
Aitor Salas-Peña Blanca Rosa Cases Gutiérrez | Published Friday, October 21, 2022A road freight transport (RFT) operation involves the participation of several types of companies in its execution. The TRANSOPE model simulates the subcontracting process between 3 types of companies: Freight Forwarders (FF), Transport Companies (TC) and self-employed carriers (CA). These companies (agents) form transport outsourcing chains (TOCs) by making decisions based on supplier selection criteria and transaction acceptance criteria. Through their participation in TOCs, companies are able to learn and exchange information, so that knowledge becomes another important factor in new collaborations. The model can replicate multiple subcontracting situations at a local and regional geographic level.
The succession of n operations over d days provides two types of results: 1) Social Complex Networks, and 2) Spatial knowledge accumulation environments. The combination of these results is used to identify the emergence of new logistics clusters. The types of actors involved as well as the variables and parameters used have their justification in a survey of transport experts and in the existing literature on the subject.
As a result of a preferential selection process, the distribution of activity among agents shows to be highly uneven. The cumulative network resulting from the self-organisation of the system suggests a structure similar to scale-free networks (Albert & Barabási, 2001). In this sense, new agents join the network according to the needs of the market. Similarly, the network of preferential relationships persists over time. Here, knowledge transfer plays a key role in the assignment of central connector roles, whose participation in the outsourcing network is even more decisive in situations of scarcity of transport contracts.
WATER REUSE ADOPTION BY FARMERS (WRAF)
Farshid Shoushtarian | Published Tuesday, September 27, 2022Agriculture is the largest water-consuming sector worldwide, responsible for almost 70% of the world’s total freshwater consumption. Agricultural water reuse is one of the most sustainable and reliable methods to alleviate water shortages worldwide. However, the dynamics of agricultural water reuse adoption by farmers and its impacts on local water resources are still unknown to the scientific community, according to the literature. Therefore, the primary purpose of the WRAF model is to investigate the micro-level dynamics of agricultural water reuse adoption by farmers and its impacts on local water resources. The WRAF was developed using agent-based modeling as an exploratory tool for scenario analysis. The model was specifically designed for researchers and water resources decision-makers, especially those interested in natural resources management and water reuse.
WRAF simulates a virtual agricultural area in which several autonomous farms operate. It also simulates these farms’ water consumption dynamics. The developed model includes two types of agents: farmers and wastewater treatment plants. In general, farmer agents are the main water-consuming agents, and wastewater treatment plant agents are recycled water providers in the WRAF model. Dynamic simulation of agricultural water supply and demand in the area allows the user to observe the results of various irrigation water management scenarios, including recycled water. The models also enable the user to apply multiple climate change scenarios, including normal, moderate drought, severe drought, and wet weather conditions.
An integrated socio-economic Agent-Based Modeling framework towards assessing farmers’ decision making under water scarcity and varying utility function
Ghinwa Harik | Published Tuesday, September 13, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, November 23, 2022A spatio-temporal Agent Based Modeling (ABM) framework is developed to probabilistically predict farmers’ decisions in the context of climate-induced water scarcity under varying utility optimization functions. The proposed framework forecasts farmers’ behavior assuming varying utility functions. The framework allows decision makers to forecast the behavior of farmers through a user-friendly platform with clear output visualization. The functionality of the proposed ABM is illustrated in an agriculturally dominated plain along the Eastern Mediterranean coastline.
Study area GIS data available upon request to [email protected]
Peer reviewed Personnel decisions in the hierarchy
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Friday, August 19, 2022This is a model of organizational behavior in the hierarchy in which personnel decisions are made.
The idea of the model is that the hierarchy, busy with operations, is described by such characteristics as structure (number and interrelation of positions) and material, filling these positions (persons with their individual performance). A particular hierarchy is under certain external pressure (performance level requirement) and is characterized by the internal state of the material (the distribution of the perceptions of others over the ensemble of persons).
The World of the model is a four-level hierarchical structure, consisting of shuff positions of the top manager (zero level of the hierarchy), first-level managers who are subordinate to the top manager, second-level managers (subordinate to the first-level managers) and positions of employees (the third level of the hierarchy). ) subordinated to the second-level managers. Such a hierarchy is a tree, i.e. each position, with the exception of the position of top manager, has a single boss.
Agents in the model are persons occupying the specified positions, the number of persons is set by the slider (HumansQty). Personas have some operational performance (harisma, an unfortunate attribute name left over from the first edition of the model)) and a sense of other personas’ own perceptions. Performance values are distributed over the ensemble of persons according to the normal law with some mean value and variance.
The value of perception by agents of each other is positive or negative (implemented in the model as numerical values equal to +1 and -1). The distribution of perceptions over an ensemble of persons is implemented as a random variable specified by the probability of negative perception, the value of which is set by the control elements of the model interface. The numerical value of the probability equal to 0 corresponds to the case in which all persons positively perceive each other (the numerical value of the random variable is equal to 1, which corresponds to the positive perception of the other person by the individual).
The hierarchy is occupied with operational activity, the degree of intensity of which is set by the external parameter Difficulty. The level of productivity of each manager OAIndex is equal to the level of productivity of the department he leads and is the ratio of the sum of productivity of employees subordinate to the head to the level of complexity of the work Difficulty. An increase in the numerical value of Difficulty leads to a decrease in the OAIndex for all subdivisions of the hierarchy. The managerial meaning of the OAIndex indicator is the percentage of completion of the load specified for the hierarchy as a whole, i.e. the ratio of the actual performance of the structural subdivisions of the hierarchy to the required performance, the level of which is specified by the value of the Difficulty parameter.
…
Displaying 10 of 191 results decision clear search