About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 134 results evolution clear search
Evolution of cooperation, punishment and retaliation
Marco Janssen | Published Friday, September 06, 2013Cultural group selection model of agents playing public good games and who are able to punish and punish back.
Evolution of Conditional Cooperation
M Manning Marco Janssen Oyita Udiani | Published Thursday, August 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, May 13, 2022Cultural group selection model used to evaluate the conditions for agents to evolve who have other-regarding preferences in making decisions in public good games.
The Pampas Model: An agent-based model of agricultural systems in the Argentinean Pampas
Michael North Federico Bert Guillermo P Podestá Santiago L Rovere Charles Macal | Published Tuesday, July 16, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 17, 2015The Pampas Model is an Agent-Based Model intended to explore the dynamics of structural and land use changes in agricultural systems of the Argentine Pampas in response to climatic, technological economic, and political drivers.
We propose here a computational model of school segregation that is aligned with a corresponding Schelling-type model of residential segregation. To adapt the model for application to school segregation, we move beyond previous work by combining two preference arguments in modeling parents’ school choice, preferences for the ethnic composition of a school and preferences for minimizing the travelling distance to the school.
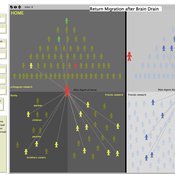
RETURN MIGRATION AFTER BRAIN DRAIN: A SIMULATION APPROACH
Alessandro Pluchino Alessio Emanuele Biondo Andrea Rapisarda | Published Friday, June 21, 2013This model, realized on the NetLogo platform, compares utility levels at home and abroad to simulate agents’ migration and their eventual return. Our model is based on two fundamental individual features, i.e. risk aversion and initial expectation, which characterize the dynamics of different agents according to the evolution of their social contacts.
MoPAgrIB: simulating savannah landscape mosaic under shifting cultivation
Nicolas Becu Marc Deconchat Eric Garine Kouami Kokou Christine Raimond | Published Monday, May 27, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2014MoPAgrIB model simulates the movement of cultivated patches in a savannah vegetation mosaic ; how they move and relocate through the landscape, depending on farming practices, population growth, social rules and vegetation growth.
A simple emulation-based computational model
Carlos M Fernández-Márquez Francisco J Vázquez | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 05, 2019Emulation is one of the simplest and most common mechanisms of social interaction. In this paper we introduce a descriptive computational model that attempts to capture the underlying dynamics of social processes led by emulation.
Variations on the Ethnocentrism Model of Hammond and Axelrod
Fredrik Jansson | Published Saturday, November 10, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Agents co-operate or defect towards other agents in a prisoner’s dilemma, with strategy choice depending on whether agents share tags or are kin in different social structures.
The Evolution of Cooperation in an Ecological Context
Oyita Udiani | Published Saturday, November 03, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a replication of the altruistic trait selection model described in Pepper & Smuts (2000, 2002).
Evolution of indirect reciprocity by social information
Yunhwan Kim | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Indirect reciprocity can be evolved by the shared information among the people of small subgroups in the population.
Displaying 10 of 134 results evolution clear search