About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 60 results land use clear search
Coastal Coupled Housing and Land Markets (C-CHALMS)
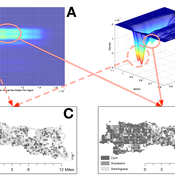
Nicholas Magliocca | Published Thursday, May 18, 2017Next generation of the CHALMS model applied to a coastal setting to investigate the effects of subjective risk perception and salience decision-making on adaptive behavior by residents.
TERRoir level Organic matter Interactions and Recycling model
Myriam Grillot | Published Wednesday, April 19, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, June 17, 2020The TERROIR agent-based model was built for the multi-level analysis of biomass and nutrient flows within agro-sylvo-pastoral villages in West Africa. It explicitly takes into account both human organization and spatial extension of such flows.
Managing ecological disturbances: Learning and the structure of social-ecological networks
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018The aim of this model is to explore and understand the factors driving adoption of treatment strategies for ecological disturbances, considering payoff signals, learning strategies and social-ecological network structure
TREELIM
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Wednesday, November 30, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 10, 2017The model simulates the spatial patterns of secondary forest succession above the current alpine tree line in the context of land use and climate change. Three scenarios are offered: (1) climate change, (2) land use change, (3) species composition.
Irrigation Equity and Efficiency
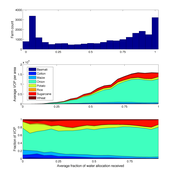
Andrew Bell | Published Tuesday, August 30, 2016The purpose of this model is to examine equity and efficiency in crop production across a system of irrigated farms, as a function of maintenance costs, assessed water fees, and the capacity of farmers to trade water rights among themselves.
Stylized agricultural land-use model for resilience exploration
Patrick Bitterman | Published Tuesday, June 14, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model is a highly stylized land use model in the Clear Creek Watershed in Eastern Iowa, designed to illustrate the construction of stability landscapes within resilience theory.
FEARLUS-SPOMM
Dawn Parker Gary Polhill Nick Gotts Alistair Law Luis Izquierdio Alessandro Gimona Lee-Ann Sutherland | Published Friday, March 25, 2016This is a coupled conceptual model of agricultural land decision-making and incentivisation and species metacommunities.
Nice Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Friday, February 05, 2016 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2017The Nice Musical Chairs (NMC) model represent the competition for space between groups of stakeholders of farming and herding activities in the arid Afro-Eurasia.
Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Wednesday, February 03, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 11, 2016This Agent-Based model intends to explore the conditions for the emergence and change of land use patterns in Central Asian oases and similar contexts.
SugarscapeCW
Christopher Watts | Published Saturday, August 01, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, April 12, 2023A replication in Netlogo 5.2 of the classic model, Sugarscape (Epstein & Axtell, 1996).
Displaying 10 of 60 results land use clear search