About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 132 results evolution clear search
Leviathan group model and its approximation
Thibaut Roubin Guillaume Deffuant | Published Tuesday, July 26, 2022The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) with the addition of group idenetity. We aim at better explaining some patterns generated by this model, using a derived mathematical approximation of the evolution of the opinions averaged.
We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other, and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. Moreover, each agent belongs to a single group and the opinions within the group are attracted to their average.
We show that a group hierarchy can emerges from this model, and that the inequality of reputations among groups have a negative effect on the opinions about the groups of low status. The mathematical analysis of the opinion dynamic shows that the lower the status of the group, the more detrimental the interactions with the agents of other groups are for the opinions about this group, especially when gossip is activated. However, the interactions between agents of the same group tend to have a positive effect on the opinions about this group.
Peer reviewed A Simple Agent-Based Spatial Model of the Economy: Tools for Policy
Bernardo Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Tuesday, July 05, 2022This study simulates the evolution of artificial economies in order to understand the tax relevance of administrative boundaries in the quality of life of its citizens. The modeling involves the construction of a computational algorithm, which includes citizens, bounded into families; firms and governments; all of them interacting in markets for goods, labor and real estate. The real estate market allows families to move to dwellings with higher quality or lower price when the families capitalize property values. The goods market allows consumers to search on a flexible number of firms choosing by price and proximity. The labor market entails a matching process between firms (given its location) and candidates, according to their qualification. The government may be configured into one, four or seven distinct sub-national governments, which are all economically conurbated. The role of government is to collect taxes on the value added of firms in its territory and invest the taxes into higher levels of quality of life for residents. The results suggest that the configuration of administrative boundaries is relevant to the levels of quality of life arising from the reversal of taxes. The model with seven regions is more dynamic, but more unequal and heterogeneous across regions. The simulation with only one region is more homogeneously poor. The study seeks to contribute to a theoretical and methodological framework as well as to describe, operationalize and test computer models of public finance analysis, with explicitly spatial and dynamic emphasis. Several alternatives of expansion of the model for future research are described. Moreover, this study adds to the existing literature in the realm of simple microeconomic computational models, specifying structural relationships between local governments and firms, consumers and dwellings mediated by distance.
The conditional defector strategy can violate the most crucial supporting mechanisms of cooperation.
Ahmed Ibrahim | Published Tuesday, June 07, 2022Cooperation is essential for all domains of life. Yet, ironically, it is intrinsically vulnerable to exploitation by cheats. Hence, an explanatory necessity spurs many evolutionary biologists to search for mechanisms that could support cooperation. In general, cooperation can emerge and be maintained when cooperators are sufficiently interacting with themselves. This communication provides a kind of assortment and reciprocity. The most crucial and common mechanisms to achieve that task are kin selection, spatial structure, and enforcement (punishment). Here, we used agent-based simulation models to investigate these pivotal mechanisms against conditional defector strategies. We concluded that the latter could easily violate the former and take over the population. This surprising outcome may urge us to rethink the evolution of cooperation, as it illustrates that maintaining cooperation may be more difficult than previously thought. Moreover, empirical applications may support these theoretical findings, such as invading the cooperator population of pathogens by genetically engineered conditional defectors, which could be a potential therapy for many incurable diseases.
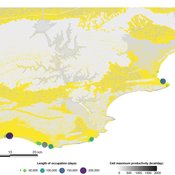
PaleoscapeABM: coastal occupation and shellfish discard
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Tuesday, February 08, 2022This model builds on the Armature distribution within the PaleoscapeABM model, which is itself a variant of the PaleoscapeABM available here written by Wren and Janssen, and.
This model aims to explore where and how much shellfish is discarded at coastal and non-coastal locations by daily coastal foraging. We use this model’s output to test the idea that we can confidently use the archaeological record to evaluate the importance of shellfish in prehistoric people’s diets.
The recognition that aquatic adaptations likely had significant impacts on human evolution triggered an explosion of research on that topic. Recognizing coastal foraging in the past relies on the archaeological signature of that behavior. We use this model to explore why some coastal sites are very intensely occupied and see if it is due to the shellfish productivity of the coast.
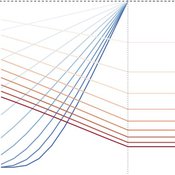
Viability analysis of a population submitted to floods
Sophie Martin | Published Wednesday, September 22, 2021This model computes the guaranteed viability kernel of a model describing the evolution of a population submitted to successive floods.
The population is described by its wealth and its adaptation rate to floods, the control are information campaigns that have a cost but increase the adaptation rate and the expected successive floods belong to given set defined by the maximal high and the minimal time between two floods.
Peer reviewed Price Evolution with Expectations
J M Applegate Gesine Steudel Armin Haas Carlo Jaeger | Published Friday, September 10, 2021The Price Evolution with Expectations model provides the opportunity to explore the question of non-equilibrium market dynamics, and how and under which conditions an economic system converges to the classically defined economic equilibrium. To accomplish this, we bring together two points of view of the economy; the classical perspective of general equilibrium theory and an evolutionary perspective, in which the current development of the economic system determines the possibilities for further evolution.
The Price Evolution with Expectations model consists of a representative firm producing no profit but producing a single good, which we call sugar, and a representative household which provides labour to the firm and purchases sugar.The model explores the evolutionary dynamics whereby the firm does not initially know the household demand but eventually this demand and thus the correct price for sugar given the household’s optimal labour.
The model can be run in one of two ways; the first does not include money and the second uses money such that the firm and/or the household have an endowment that can be spent or saved. In either case, the household has preferences for leisure and consumption and a demand function relating sugar and price, and the firm has a production function and learns the household demand over a set number of time steps using either an endogenous or exogenous learning algorithm. The resulting equilibria, or fixed points of the system, may or may not match the classical economic equilibrium.
EMMIT (Extendable Model for Malaria Intervention Testing)
Jacob Heintzelman Greg R Madey | Published Thursday, May 27, 2021EMMIT is an end-user developed agent-based simulation of malaria transmission. The simulation’s development is a case study demonstrating an approach for non-technical investigators to easily develop useful simulations of complex public health problems. We focused on malaria transmission, a major global public health problem, and insecticide resistance (IR), a major problem affecting malaria control. Insecticides are used to reduce transmission of malaria caused by the Plasmodium parasite that is spread by the Anopheles mosquito. However, the emergence and spread of IR in a mosquito population can diminish the insecticide’s effectiveness. IR results from mutations that produce behavioral changes or biochemical changes (such as detoxification enhancement, target site alterations) in the mosquito population that provide resistance to the insecticide. Evolutionary selection for the IR traits reduces the effectiveness of an insecticide favoring the resistant mosquito population. It has been suggested that biopesticides, and specifically those that are Late Life Acting (LLA), could address this problem. LLA insecticides exploit Plasmodium’s approximate 10-day extrinsic incubation period in the mosquito vector, a delay that limits malaria transmission to older infected mosquitoes. Since the proposed LLA insecticide delays mosquito death until after the exposed mosquito has a chance to produce several broods of offspring, reducing the selective pressure for resistance, it delays IR development and gives the insecticide longer effectivity. Such insecticides are designed to slow the evolution of IR thus maintaining their effectiveness for malaria control. For the IR problem, EMMIT shows that an LLA insecticide could work as intended, but its operational characteristics are critical, primarily the mean-time-to-death after exposure and the associated standard deviation. We also demonstrate the simulation’s extensibility to other malaria control measures, including larval source control and policies to mitigate the spread of IR. The simulation was developed using NetLogo as a case study of a simple but useful approach to public health research.
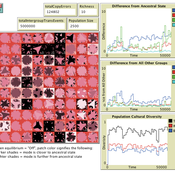
Local extinctions, connectedness, and cultural evolution in structured populations
Luke Premo | Published Tuesday, May 25, 2021This model is designed to address the following research question: How does the amount and topology of intergroup cultural transmission modulate the effect of local group extinction on selectively neutral cultural diversity in a geographically structured population? The experimental design varies group extinction rate, the amount of intergroup cultural transmission, and the topology of intergroup cultural transmission while measuring the effects of local group extinction on long-term cultural change and regional cultural differentiation in a constant-size, spatially structured population. The results show that for most of the intergroup social network topologies tested here, increasing the amount of intergroup cultural transmission (similar to increasing gene flow in a genetic model) erases the negative effect of local group extinction on selectively neutral cultural diversity. The stochastic (i.e., preference attachment) network seems to stand out as an exception.
Dynamics of Public Opinion with Diverse Media and Audiences' Choice
Zhongtian Chen | Published Sunday, April 25, 2021Studies on the fundamental role of diverse media in the evolution of public opinion can protect us from the spreading brainwashing, extremism, and terrorism. Many fear the information cocoon may result in polarization of the public opinion. The model of opinion dynamics that considers different influences and horizons for every individual, and the simulations are based on a real-world social network.
A model of opinion dynamics based on formal argumentation: application to the diffusion of the vegetarian diet
Patrick Taillandier Nicolas Salliou Rallou Thomopoulos | Published Monday, March 15, 2021This generic agent-based model simulates the evolution of agent’s opinions through their exchange of arguments.
The idea behind this model is to explicitly represent the process of mental deliberation of agents from arguments to an opinion, through the use of Dung’s argumentation framework complemented by a structured description of arguments. An application of the model on the diffusion of vegetarian diets is proposed.
Displaying 10 of 132 results evolution clear search