About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 61 results control clear search
Peer reviewed The Andean Resource Management Model (ARMM)
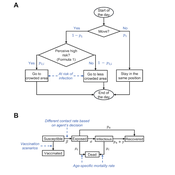
Olga Palacios | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2026ARMM is a theoretical agent-based model that formalizes Murra’s Theory of Verticality (Murra, 1972) to explore how multi-zonal resource management systems emerge in mountain landscapes. The model identifies the social, political, and economic mechanisms that enable vertical complementarity across ecological gradients.
Built in NetLogo, ARMM employs an abstract 111×111 grid divided into four Andean ecological zones (Altiplano, Highland, Lowland, Coast), each containing up to 18 resource types distributed according to ecological suitability. To test general theoretical principles rather than replicate specific geography, resource locations are randomized at each model initialization.
Settlement agents pursue one of two economic strategies: diversification (seeking resource variety, maximum 2 units per type) or accumulation (maximising total quantity, maximum 30 units). Agents move between adjacent zones through hierarchical decision-making, first attempting peaceful interactions—coexistence (governed by tolerance) and trading (governed by cooperation)—before resorting to conflict (theft or takeover, governed by belligerence).
The model demonstrates that vertical complementarity can emerge through fundamentally different mechanisms: either through autonomous mobility under political decentralization or through state-coordinated redistribution under centralization. Sensitivity analysis reveals that belligerence and economic strategy explain approximately 25% of outcome variance, confirming that structural inequalities between zones result from political-economic organization rather than environmental constraints alone.
As a preliminary theoretical model, ARMM intentionally maintains simplicity to isolate core mechanisms and generate testable hypotheses. This foundational framework will guide future empirically-calibrated versions that incorporate specific archaeological settlement data and geographic features from the Carangas region (Bolivia-Chile border), enabling direct comparison between theoretical predictions and observed historical patterns.
Agent-Based Model for Multiple Team Membership (ABMMTM)
Andrew Collins | Published Thursday, April 03, 2025The Agent-Based Model for Multiple Team Membership (ABMMTM) simulates design teams searching for viable design solutions, for a large design project that requires multiple design teams that are working simultaneously, under different organizational structures; specifically, the impact of multiple team membership (MTM). The key mechanism under study is how individual agent-level decision-making impacts macro-level project performance, specifically, wage cost. Each agent follows a stochastic learning approach, akin to simulated annealing or reinforcement learning, where they iteratively explore potential design solutions. The agent evaluates new solutions based on a random-walk exploration, accepting improvements while rejecting inferior designs. This iterative process simulates real-world problem-solving dynamics where designers refine solutions based on feedback.
As a proof-of-concept demonstration of assessing the macro-level effects of MTM in organizational design, we developed this agent-based simulation model which was used in a simulation experiment. The scenario is a system design project involving multiple interdependent teams of engineering designers. In this scenario, the required system design is split into three separate but interdependent systems, e.g., the design of a satellite could (trivially) be split into three components: power source, control system, and communication systems; each of three design team is in charge of a design of one of these components. A design team is responsible for ensuring its proposed component’s design meets the design requirement; they are not responsible for the design requirements of the other components. If the design of a given component does not affect the design requirements of the other components, we call this the uncoupled scenario; otherwise, it is a coupled scenario.
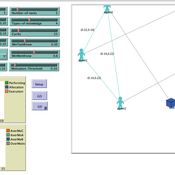
Autonomy or control? An agent-based study of self-organising versus centralised task allocation
Shaoni Wang | Published Wednesday, January 29, 2025The aim of our model is to investigate the team dynamics through two types of task allocation strategies, with a focus on the dynamic interplay between individual needs and group performance. To achieve this goal, we have formulated an agent-based model (ABM) to formalize Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) and explore the social dynamics that govern the relationship between individual and group levels of team performance.
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
An Agent-Based Model to Assess Possible Interventions for Large Shigellosis Outbreaks
Erez Hatna Jeewoen Shin Sharon Greene | Published Wednesday, June 12, 2024Large outbreaks of Shigella sonnei among children in Haredi Jewish (ultra-Orthodox) communities in Brooklyn, New York have occurred every 3–5 years since at least the mid-1980s. These outbreaks are partially attributable to large numbers of young children in these communities, with transmission highest in child care and school settings, and secondary transmission within households. As these outbreaks have been prolonged and difficult to control, we developed an agent-based model of shigellosis transmission among children in these communities to support New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene staff. Simulated children were assigned an initial susceptible, infectious, or recovered (immune) status and interacted and moved between their home, child care program or school, and a community site. We calibrated the model according to observed case counts as reported to the Health Department. Our goal was to better understand the efficacy of existing interventions and whether limited outreach resources could be focused more effectively.
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Monday, March 25, 2024ViSA 2.0.0 is an updated version of ViSA 1.0.0 aiming at integrating empirical data of a new use case that is much smaller than in the first version to include field scale analysis. Further, the code of the model is simplified to make the model easier and faster. Some features from the previous version have been removed.
It simulates decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. It investigates conditions and scenarios that can increase the supply of ecosystem services while keeping the viability of the social system by suggesting different mixes of initial unit utilities and decision rules.
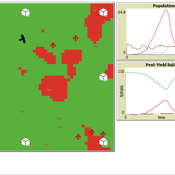
Peer reviewed Avian pest control: Yield outcome due to insectivorous birds, falconry, and integration of nest boxes.
David Jung | Published Monday, November 13, 2023 | Last modified Sunday, November 19, 2023The model aims to simulate predator-prey relationships in an agricultural setting. The focus lies on avian communities and their effect on different pest organisms (here: pest birds, rodents, and arthropod pests). Since most case studies focused on the impact on arthropod pests (AP) alone, this model attempts to include effects on yield outcome. By incorporating three treatments with different factor levels (insectivorous bird species, falconry, nest box density) an experimental setup is given that allows for further statistical analysis to identify an optimal combination of the treatments.
In light of a global decline of birds, insects, and many other groups of organisms, alternative practices of pest management are heavily needed to reduce the input of pesticides. Avian pest control therefore poses an opportunity to bridge the disconnect between humans and nature by realizing ecosystem services and emphasizing sustainable social ecological systems.
Controlling the misinformation diffusion in social media by the effect of different classes of agents
Ali Khodabandeh Yalabadi | Published Thursday, October 05, 2023An agent-based framework to simulate the diffusion process of a piece of misinformation according to the SBFC model in which the fake news and its debunking compete in a social network. Considering new classes of agents, this model is closer to reality and proposed different strategies how to mitigate and control misinformation.
Peer reviewed Street Dog Sim - An agent based model for investigating strategies of free roaming dog control.
Andrew Calinger-yoak | Published Wednesday, July 19, 2023This is an agent-based model constructed in Netlogo v6.2.2 which seeks to provide a simple but flexible tool for researchers and dog-population managers to help inform management decisions.
It replicates the basic demographic processes including:
* reproduction
* natural death
* dispersal
…
Peer reviewed SWIRS Spread of a woody invader in riparian systems
Moira Zellner Beatriz Sosa Carlos Andrés Chiale | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023Riparian forests are one of the most vulnerable ecosystems to the development of biological invasions, therefore limiting their spread is one of the main challenges for conservation. The main factors that explain plant invasions in these ecosystems are the capacity for both short- and long-distance seed dispersion, and the occurrence of suitable habitats that facilitate the establishment of the invasive species. Large floods constitute an abiotic filter for invasion.
This model simulates the spatio-temporal spread of the woody invader Gleditsia. triacanthos in the riparian forest of the National Park Esteros de Farrapos e Islas del Río Uruguay, a riparian system in the coast of the Uruguay river (South America). In this model, we represent different environmental conditions for the development of G. triacanthos, long- and short-distance spread of its fruits, and large floods as the main factor of mortality for fruit and early stages.
Field results show that the distribution pattern of this invasive species is limited by establishment, i.e. it spreads locally through the expansion of small areas, and remotely through new invasion foci. This model recreates this dispersion pattern. We use this model to derive management implications to control the spread of G. triacanthos
Displaying 10 of 61 results control clear search