About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 450 results agent-based model clear search
Peer Review Model
Flaminio Squazzoni Claudio Gandelli | Published Wednesday, September 05, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model looks at implications of author/referee interaction for quality and efficiency of peer review. It allows to investigate the importance of various reciprocity motives to ensure cooperation. Peer review is modelled as a process based on knowledge asymmetries and subject to evaluation bias. The model includes various simulation scenarios to test different interaction conditions and author and referee behaviour and various indexes that measure quality and efficiency of evaluation […]
Homophily and Distance Depending Network Generation for Modelling Opinion Dynamics
Sascha Holzhauer | Published Wednesday, August 22, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, June 18, 2013The model uses opinion dynamics to test a simple and ecient but empirically based approach for generating social networks in spatial agent-based models which explicitly takes into account restrictions and opportunities imposed by effects of baseline homophily and considers the probability of links that depends on geographical distance between potential partners.
An agent-based model of adaptive cycles of the spruce budworm
Julia Schindler | Published Saturday, August 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is an empirically calibrated agent-based model that replicates spruce-budworm outbreaks, one of the most cited adaptive cycles reported. The adaptive-cycle metaphor by L. H. Gunderson and C. S. Holling posits the cross-case existence of repeating cycles of growth, conservation, collapse, and renewal in many complex systems, triggered by loss of resilience. This model is one of the first agent-based models of such cycles, with the novelty that adaptive cycles are not defined by system- […]
Irrigation game
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, July 23, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Irrigation game calibrated on experimental data
MayaSim: An agent-based model of the ancient Maya social-ecological system
Scott Heckbert | Published Wednesday, July 11, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, July 02, 2013MayaSim is an agent-based, cellular automata and network model of the ancient Maya. Biophysical and anthropogenic processes interact to grow a complex social ecological system.
A simple Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of the Commons (MASTOC-s)
Julia Schindler | Published Friday, June 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a simple model replicating Hardin’s Tragedy of the Commons using reactive agents that have psychological behavioral and social preferences.
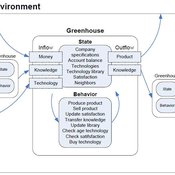
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
An Agent-Based Model of Internet Diffusion Under General and Specific Network Externalities
Filiz Garip | Published Friday, April 27, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Using nodes from the 2002 General Social Survey sample, the code establishes a network of ties with a given homophily bias, and simulates Internet adoption rates in that network under three conditions: (i) no network externalities, (ii) general network externalities, where an individual’s reservation price is a function of the overall adoption rate in the network, (iii) specific network externalities, where reservation price is a function of the adoption rate in individual’s personal […]
Agent-Based Model for the Evolution of Ethnocentrism
Max Hartshorn | Published Saturday, March 24, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is an implementation of an agent based model for the evolution of ethnocentrism. While based off a model published by Hammond and Axelrod (2006), the code has been modified to allow for a more fine-grained analysis of evolutionary dynamics.
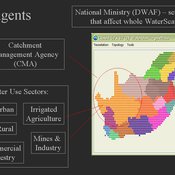
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Displaying 10 of 450 results agent-based model clear search