About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 959 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search
ForagerNet3_Demography: A Non-Spatial Model of Hunter-Gatherer Demography
Andrew White | Published Thursday, October 17, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 17, 2013ForagerNet3_Demography is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. Key methods represent birth, death, and marriage. The dependency ratio is an imporant variable in many economic decisions embedded in the methods.
ForagerNet3_Demography_V2
Andrew White | Published Thursday, February 13, 2014ForagerNet3_Demography_V2 is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. This version (developed from FN3D_V1) contains code for calculating the ratio of old to young adults (the “OY ratio”) in the living and dead populations.
Spatio-Temporal Dynamic of Risk Model
J Jumadi | Published Tuesday, October 22, 2019 | Last modified Sunday, January 05, 2020This model aims to simlulate the dynamic of risk over time and space.
Linear Threshold
Kaushik Sarkar | Published Saturday, November 03, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetLogo implementation of Linear Threshold model of influence propagation.
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
Growing Unpopular Norms. A Network-Situated ABM of Norm Choice.
C Merdes | Published Tuesday, November 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, March 17, 2018The model’s purpose is to provide a potential explanation for the emergence, sustenance and decline of unpopular norms based on pluralistic ignorance on a social network.
A model to explore the link between the gender-gap reversal in education and relative divorce risks
Jan Van Bavel Christine Schnor André Grow | Published Thursday, June 30, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 13, 2017This model explores a social mechanism that links the reversal of the gender gap in education with changing patterns in relative divorce risks in 12 European countries.
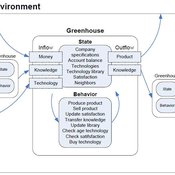
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Peer reviewed Emergent Firms Model
J M Applegate | Published Friday, July 13, 2018The Emergent Firm (EF) model is based on the premise that firms arise out of individuals choosing to work together to advantage themselves of the benefits of returns-to-scale and coordination. The Emergent Firm (EF) model is a new implementation and extension of Rob Axtell’s Endogenous Dynamics of Multi-Agent Firms model. Like the Axtell model, the EF model describes how economies, composed of firms, form and evolve out of the utility maximizing activity on the part of individual agents. The EF model includes a cash-in-advance constraint on agents changing employment, as well as a universal credit-creating lender to explore how costs and access to capital affect the emergent economy and its macroeconomic characteristics such as firm size distributions, wealth, debt, wages and productivity.
Peer reviewed General Housing Model
J M Applegate | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020The General Housing Model demonstrates a basic housing market with bank lending, renters, owners and landlords. This model was developed as a base to which students contributed additional functions during Arizona State University’s 2020 Winter School: Agent-Based Modeling of Social-Ecological Systems.
Displaying 10 of 959 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search