About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 79 results for "Guillermo P Podestá" clear search
Behavioural parallel trading systems
Marcin Czupryna | Published Friday, June 26, 2020This model simulates the behaviour of the agents in 3 wine markets parallel trading systems: Liv-ex, Auctions and additionally OTC market (finally not used). Behavioural aspects (impatience) is additionally modeled. This is an extention of parallel trading systems model with technical trading (momentum and contrarian) and noise trading.
Peer reviewed Personnel decisions in the hierarchy
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Friday, August 19, 2022This is a model of organizational behavior in the hierarchy in which personnel decisions are made.
The idea of the model is that the hierarchy, busy with operations, is described by such characteristics as structure (number and interrelation of positions) and material, filling these positions (persons with their individual performance). A particular hierarchy is under certain external pressure (performance level requirement) and is characterized by the internal state of the material (the distribution of the perceptions of others over the ensemble of persons).
The World of the model is a four-level hierarchical structure, consisting of shuff positions of the top manager (zero level of the hierarchy), first-level managers who are subordinate to the top manager, second-level managers (subordinate to the first-level managers) and positions of employees (the third level of the hierarchy). ) subordinated to the second-level managers. Such a hierarchy is a tree, i.e. each position, with the exception of the position of top manager, has a single boss.
Agents in the model are persons occupying the specified positions, the number of persons is set by the slider (HumansQty). Personas have some operational performance (harisma, an unfortunate attribute name left over from the first edition of the model)) and a sense of other personas’ own perceptions. Performance values are distributed over the ensemble of persons according to the normal law with some mean value and variance.
The value of perception by agents of each other is positive or negative (implemented in the model as numerical values equal to +1 and -1). The distribution of perceptions over an ensemble of persons is implemented as a random variable specified by the probability of negative perception, the value of which is set by the control elements of the model interface. The numerical value of the probability equal to 0 corresponds to the case in which all persons positively perceive each other (the numerical value of the random variable is equal to 1, which corresponds to the positive perception of the other person by the individual).
The hierarchy is occupied with operational activity, the degree of intensity of which is set by the external parameter Difficulty. The level of productivity of each manager OAIndex is equal to the level of productivity of the department he leads and is the ratio of the sum of productivity of employees subordinate to the head to the level of complexity of the work Difficulty. An increase in the numerical value of Difficulty leads to a decrease in the OAIndex for all subdivisions of the hierarchy. The managerial meaning of the OAIndex indicator is the percentage of completion of the load specified for the hierarchy as a whole, i.e. the ratio of the actual performance of the structural subdivisions of the hierarchy to the required performance, the level of which is specified by the value of the Difficulty parameter.
…
Peer reviewed ABM to create populations with realistic Big Five Personality Trait Expressions
Michael Vogrin | Published Tuesday, May 30, 2023This model aims at creating agent populations that have “personalities”, as described by the Big Five Model of Personality. The expression of the Big Five in the agent population has the following properties, so that they resemble real life populations as closely as possible:
-The population mean of each trait is 0.5 on a scale from 0 to 1.
-The population-wide distribution of each trait approximates a normal distribution.
-The intercorrelations of the Big Five are close to those observed in the Literature.
The literature used to fit the model was a publication by Dimitri van der Linden, Jan te Nijenhuis, and Arnold B. Bakker:
…
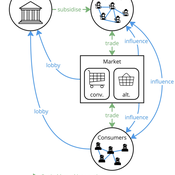
Agent-based model of power dynamics in agri-food systems
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, October 27, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, June 12, 2025This is a stylised agent-based model designed to explore the conditions that lead to lock-ins and transitions in agri-food systems.
The model represents interactions between four different types of agents: farmers, consumers, markets, and the state. Farmers and consumers are heterogeneous, and at each time step decide whether to trade with one of two market agents: the conventional or alternative. The state agent provides subsidies to the farmers at each time step.
The key emergent outcome is the fraction of trade in each time step that flows through the alternative market agent. This arises from the distributed decisions of farmer and consumer agents. A “sustainability transition” is defined as a shift in the dominant practices (and associated balance of power) towards the alternative paradigm.
…
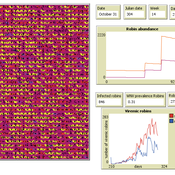
Peer reviewed AMRO_CULEX_WNV
Aniruddha Belsare Jennifer Owen | Published Saturday, February 27, 2021 | Last modified Thursday, March 11, 2021An agent-based model simulating West Nile Virus dynamics in a one host (American robin)-one vector (Culex spp. mosquito) system. ODD improved and code cleaned.
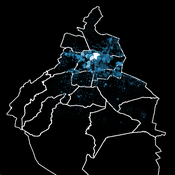
Socio-hydrologicalModel_version_SESMO
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Paola Gomez Luis Bojorquez Fidel Serrano-Candela Hallie Eakin Yosune Miquelajauregui Rodrigo Garcia-Herrera | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We present here MEGADAPT_SESMO model. A hybrid, dynamic, spatially explicit, integrated model to simulate the vulnerability of urban coupled socio-ecological systems – in our case, the vulnerability of Mexico City to socio-hydrological risk.
Success bias imitation increases the probability of effectively dealing with ecological disturbances
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018This model aims to investigate how different type of learning (social system) and disturbance specific attributes (ecological system) influence adoption of treatment strategies to treat the effects of ecological disturbances.
Individual bias and organizational objectivity
Bo Xu | Published Monday, April 15, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model introduces individual bias to the model of exploration and exploitation, simulates knowledge diffusion within organizations, aiming to investigate the effect of individual bias and other related factors on organizational objectivity.
REHAB: A Role Playing Game to Explore the Influence of Knowledge and Communication on Natural Resources Management
Christophe Le Page Anne Dray Pascal Perez Claude Garcia | Published Monday, July 13, 2015 | Last modified Monday, July 13, 2015REHAB has been designed as an ice-breaker in courses dealing with ecosystem management and participatory modelling. It helps introducing the two main tools used by the Companion Modelling approach, namely role-playing games and agent-based models.
MayaSim: An agent-based model of the ancient Maya social-ecological system
Scott Heckbert | Published Wednesday, July 11, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, July 02, 2013MayaSim is an agent-based, cellular automata and network model of the ancient Maya. Biophysical and anthropogenic processes interact to grow a complex social ecological system.
Displaying 10 of 79 results for "Guillermo P Podestá" clear search