About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 358 results for "Emmanuel Mhike Hove" clear search
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
Peer reviewed Axelrod_Cultural_Dissemination
Arezky Hernández | Published Wednesday, March 27, 2013 | Last modified Sunday, May 05, 2013The Axelrod’s model of cultural dissemination is an agent-model designed to investigate the dissemination of culture among interacting agents on a society.
PSMED - Patagonia Simple Model of Ethnic Differentiation
Xavier Vilà Joan A Barceló J A Cuesta Florencia Del Castillo Ricardo Del Olmo José M Galán Laura Mameli Francisco J Miguel David Poza José I Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2013Patagonia PSMED is an agent-based model designed to study a simple case of Evolution of Ethnic Differentiation. It replicates how can hunter-gatherer societies evolve and built cultural identities as a consequence of the way they interacted.
Political Participation
Didier Ruedin | Published Saturday, April 12, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, November 18, 2023Implementation of Milbrath’s (1965) model of political participation. Individual participation is determined by stimuli from the political environment, interpersonal interaction, as well as individual characteristics.
Peer reviewed Ideal Free Distribution of Mobile Pastoralists in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon
Jeff Cronley Andrew Yoak Mark Moritz Hongyang Pi Ian M Hamilton Paul Maddock | Published Thursday, June 19, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, January 06, 2018The purpose of the model is to examine whether and how mobile pastoralists are able to achieve an Ideal Free Distribution (IFD).
A preliminary extension of the Hemelrijk 1996 model of reciprocal behavior to include feeding
Sean Barton | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A more complete description of the model can be found in Appendix I as an ODD protocol. This model is an expansion of the Hemelrijk (1996) that was expanded to include a simple food seeking behavior.
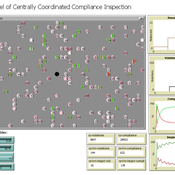
ICARUS - a multi-agent compliance inspection model
Slaven Smojver | Published Monday, May 09, 2022ICARUS is a multi-agent compliance inspection model (ICARUS - Inspecting Compliance to mAny RUleS). The model is applicable to environments where an inspection agency, via centrally coordinated inspections, examines compliance in organizations which must comply with multiple provisions (rules). The model (ICARUS) contains 3 types of agents: entities, inspection agency and inspectors / inspections. ICARUS describes a repeated, simultaneous, non-cooperative game of pure competition. Agents have imperfect, incomplete, asymmetric information. Entities in each move (tick) choose a pure strategy (comply/violate) for each rule, depending on their own subjective assessment of the probability of the inspection. The Inspection Agency carries out the given inspection strategy.
A more detailed description of the model is available in the .nlogo file.
Full description of the model (in line with the ODD+D protocol) and the analysis of the model (including verification, validation and sensitivity analysis) can be found in the attached documentation.
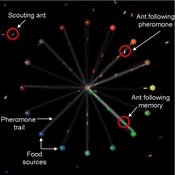
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
MoPAgrIB: simulating savannah landscape mosaic under shifting cultivation
Nicolas Becu Marc Deconchat Eric Garine Kouami Kokou Christine Raimond | Published Monday, May 27, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2014MoPAgrIB model simulates the movement of cultivated patches in a savannah vegetation mosaic ; how they move and relocate through the landscape, depending on farming practices, population growth, social rules and vegetation growth.
Replication of ECEC model: Environmental Feedback and the Evolution of Cooperation
Pierre Bommel | Published Tuesday, April 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model, presented here, is a re-implementation of the Pepper and Smuts’ model : - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2000. “The evolution of cooperation in an ecological context: an agent-based model”. Pp. 45-76 in T.A. Kohler and G.J. Gumerman, eds. Dynamics of human and primate societies: agent-based modeling of social and spatial processes. Oxford University Press, Oxford. - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2002. “Assortment through Environmental Feedback”. American Naturalist, 160: 205-213 […]
Displaying 10 of 358 results for "Emmanuel Mhike Hove" clear search