About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1259 results
Absorption of particulate matter by leafs
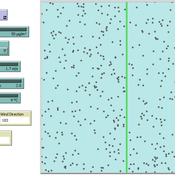
Georg Jäger Chiara Letter | Published Monday, November 12, 2018 | Last modified Monday, November 12, 2018This model aims to understand the interaction between particulate matter and leaves of trees. The particles collide with the leaf and can either be absorbed with a certain probability, otherwise they bounce off it. The absorptions are detected in a counter.
The movement of the particles depends mainly on the strength and direction of the wind and the air temperature. They also show a certain random movement, but the proportion is negligible.
In a collision with the leaf, the particles are absorbed with a certain probability (absorption-probability), otherwise repelled.
An Agent-based Assessment of Health Vulnerability to Long-term particulate exposure in Seoul Districts
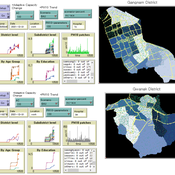
Hyesop Shin Mike Bithell | Published Monday, November 05, 2018 | Last modified Monday, December 03, 2018This model aims to understand the cumulative effects on the population’s vulnerability as represented by exposure to PM10 (particulate matter with diameter less than 10 micrometres) by different age and educational groups in two Seoul districts, Gangnam and Gwanak. Using this model, readers can explore individual’s daily commuting routine, and its health loss when the PM10 concentration of the current patch breaches the national limit of 100µg/m3.
word-of-mouth dynamics with information seeking
Samuel Thiriot | Published Wednesday, October 24, 2018Studies on word-of-mouth identify two behaviors leading to transmission of information between individuals: proactive transmission of information, and information seeking. Individuals who are aware might be curious of it and start seeking for information; they might find around them the expertise held by another individual. Field studies indicate individuals do not adopt an innovation if they don’t hold the corresponding expertise. This model describes this information seeking behavior, and enables the exploration of the dynamics which emerges out of it.
This program simulates a group of hunter-gatherer (households) moving randomly over an artificial landscapoe pulated with resources randomly distributed (a Gaussian distribution). To survive, agents hunt and gather using their own labor resources and available technology. When labor and technology is not enough to compensate the resource difficulty of access, they need to cooperate. The purpose of the model is to analyze the consequences of cooperation on cultural diversity: the more the agents cooperate, the more their culture (a 10 componenet vector) is updated to imitate the culture of cooperative agents. The less the agent cooperates, the more different its culture becomes.
Co-evolution of mental models among socially learning agents
Garry Sotnik | Published Sunday, October 14, 2018The model simulates seven agents engaging in collective action and inter-network social learning. The objective of the model is to demonstrate how mental models of agents can co-evolve through a complex relationship among factors influencing decision-making, such as access to knowledge and personal- and group-level constraints.
LaMEStModel
Ruth Meyer | Published Friday, October 12, 2018The Labour Markets and Ethnic Segmentation (LaMESt) Model is a model of a simplified labour market, where only jobs of the lowest skill level are considered. Immigrants of two different ethnicities (“Latino”, “Asian”) compete with a majority (“White”) and minority (“Black”) native population for these jobs. The model’s purpose is to investigate the effect of ethnically homogeneous social networks on the emergence of ethnic segmentation in such a labour market. It is inspired by Waldinger & Lichter’s study of immigration and the social organisation of labour in 1990’s Los Angeles.
RefugeePathSIM Model
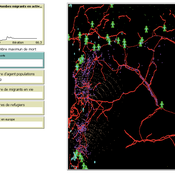
Liliana Perez Saeed Harati Guillaume Arnoux Hébert | Published Thursday, October 11, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, October 16, 2018RefugeePathSIM is an agent-based model to simulate the movement behavior of refugees in order to identify pathways of forced migration under crisis. The model generates migrants and lets them leave conflict areas for a destination that they choose based on their characteristics and desires. RefugeePathSIM has been developed and applied in a study of the Syrian war, using monthly data in years 2011-2015.
Peer reviewed MigrAgent
Wander Jager Rocco Paolillo | Published Friday, October 05, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, November 28, 2018MigrAgent simulates migration flows of a population from a home country to a host country and mutual adaptation of a migrant and local population post-migration. Agents accept interactions in intercultural networks depending on their degree of conservatism. Conservatism is a group-level parameter normally distributed within each ethnic group. Individual conservatism changes as function of reciprocity of interaction in intergroup experiences of acceptance or rejection.
The aim of MigrAgent is to unfold different outcomes of integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization in terms of networks as effect of different degrees of conservatism in each group and speed of migration flows.
Root disease model
Adam Bouche | Published Sunday, September 30, 2018This is a model of root disease spread between trees in the landscape. The disease spreads via two transmission processes: (a) root contact/root graft transmission between adjacent trees and (b) insect vectors that carry spores between trees. Full details can be found in the “Info” tab in the model and in the readme file in the GitHub repository.
Importing a Roman transport network
Tom Brughmans | Published Sunday, September 30, 2018A draft model teaching how a Roman transport model can be imported into Netlogo, and the issues confronted when importing and reusing open access Roman datasets. This model is used for the tutorial:
Brughmans, T. (2018). Importing a Roman Transport network with Netlogo, Tutorial, https://archaeologicalnetworks.wordpress.com/resources/#transport .
Displaying 10 of 1259 results