About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search
Risk-Sharing under Heterogeneity: NetLogo simulation
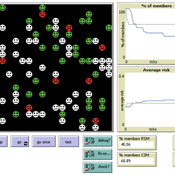
Eva Vriens | Published Monday, February 28, 2022Motivated by the emergence of new Peer-to-Peer insurance organizations that rethink how insurance is organized, we propose a theoretical model of decision-making in risk-sharing arrangements with risk heterogeneity and incomplete information about the risk distribution as core features. For these new, informal organisations, the available institutional solutions to heterogeneity (e.g., mandatory participation or price differentiation) are either impossible or undesirable. Hence, we need to understand the scope conditions under which individuals are motivated to participate in a bottom-up risk-sharing setting. The model puts forward participation as a utility maximizing alternative for agents with higher risk levels, who are more risk averse, are driven more by solidarity motives, and less susceptible to cost fluctuations. This basic micro-level model is used to simulate decision-making for agent populations in a dynamic, interdependent setting. Simulation results show that successful risk-sharing arrangements may work if participants are driven by motivations of solidarity or risk aversion, but this is less likely in populations more heterogeneous in risk, as the individual motivations can less often make up for the larger cost deficiencies. At the same time, more heterogeneous groups deal better with uncertainty and temporary cost fluctuations than more homogeneous populations do. In the latter, cascades following temporary peaks in support requests more often result in complete failure, while under full information about the risk distribution this would not have happened.
Large-scale land acqusitions and smallholder food security
Tim Williams | Published Thursday, September 16, 2021Large-scale land acquisitions (LSLAs) threaten smallholder livelihoods globally. Despite more than a decade of research on the LSLA phenomenon, it remains a challenge to identify governance conditions that may foster beneficial outcomes for both smallholders and investors. One potentially promising strategy toward this end is contract farming (CF), which more directly involves smallholder households in commodity production than conditions of acquisition and displacement.
To improve understanding of how CF may mediate the outcomes of LSLAs, we developed an agent-based model of smallholder livelihoods, which we used as a virtual laboratory to experiment on a range of hypothetical LSLA and CF implementation scenarios.
The model represents a community of smallholder households in a mixed crop-livestock system. Each agent farms their own land and manages a herd of livestock. Agents can also engage in off-farm employment, for which they earn a fixed wage and compete for a limited number of jobs. The principal model outputs include measures of household food security (representing access to a single, staple food crop) and agricultural production (of a single, staple food crop).
…
Peer reviewed LUCID: Land Use Competition In Drylands
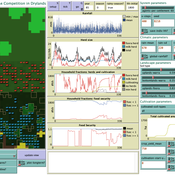
Birgit Müller Gunnar Dressler Lance Robinson | Published Wednesday, April 12, 2023The Land Use Competition in Drylands (LUCID) model is a stylized agent-based model of a smallholder farming system. Its main purpose is to illustrate how competition between pastoralism and crop cultivation can affect livelihoods of households, specifically their food security. In particular, the model analyzes whether the expansion of crop cultivation may contribute to a vicious circle where an increase in cultivated area leads to higher grazing pressure on the remaining pastureland, which in turn may cause forage shortages and livestock loss for households which are then forced to further expand their cultivated area in order to increase their food security. The model does not attempt to replicate a particular case study but to generate a general understanding of mechanisms and drivers of such vicious circles and to identify possible scenarios under which such circles may be prevented.
The model is inspired by observations of the Borana land use system in Southern Ethiopia. The climatic and ecological conditions of the Borana zone favor pastoralism, and traditionally livelihoods have been based mainly on livestock keeping. Recent years, however, have seen an advancement of crop cultivation as a coping strategy, e.g., to compensate the loss of livestock, even though crop yields are low on average and successful harvests are infrequent.
In the model, it is possible to evaluate patterns of individual (single household) as well as overall (across all households) consumption and food security, depending on a range of ecological, climatic and management parameters.
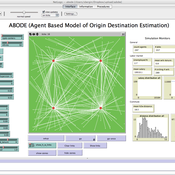
ABODE - Agent Based Model of Origin Destination Estimation
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The agent based model matches origins and destinations using employment search methods at the individual level.
Peer reviewed Swidden Farming Version 2.0
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, June 12, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, September 03, 2014Model of shifting cultivation. All parameters can be controlled by the user or the model can be run in adaptive mode, in which agents innovate and select parameters.
Peer Review with Multiple Reviewers
Flaminio Squazzoni Federico Bianchi | Published Thursday, September 10, 2015This ABM looks at the effect of multiple reviewers and their behavior on the quality and efficiency of peer review. It models a community of scientists who alternatively act as “author” or “reviewer” at each turn.
SimDrink: An agent-based NetLogo model of young, heavy drinkers for conducting alcohol policy experiments
Nick Scott James Wilson Michael Livingston Aaron Hart David Moore Paul Dietze | Published Friday, September 25, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, October 15, 2015A proof-of-concept agent-based model ‘SimDrink’, which simulates a population of 18-25 year old heavy alcohol drinkers on a night out in Melbourne to provide a means for conducting policy experiments to inform policy decisions.
Eliminating hepatitis C virus as a public health threat among HIV-positive men who have sex with men
Nick Scott Mark Stoove David P Wilson Olivia Keiser Carol El-Hayek Joseph Doyle Margaret Hellard | Published Wednesday, October 12, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 16, 2018We compare three model estimates for the time and treatment requirements to eliminate HCV among HIV-positive MSM in Victoria, Australia: a compartmental model; an ABM parametrized by surveillance data; and an ABM with a more heterogeneous population.
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
How does knowledge infrastructure mobilization influence the safe operating space of regulated exploited ecosystems?
Jean-Denis Mathias | Published Tuesday, July 17, 2018Decision-makers often have to act before critical times to avoid the collapse of ecosystems using knowledge \textcolor{red}{that can be incomplete or biased}. Adaptive management may help managers tackle such issues. However, because the knowledge infrastructure required for adaptive management may be mobilized in several ways, we study the quality and the quantity of knowledge provided by this knowledge infrastructure. In order to analyze the influence of mobilized knowledge, we study how the following typology of knowledge and its use may impact the safe operating space of exploited ecosystems: 1) knowledge of the past based on a time series distorted by measurement errors; 2) knowledge of the current systems’ dynamics based on the representativeness of the decision-makers’ mental models of the exploited ecosystem; 3) knowledge of future events based on decision-makers’ likelihood estimates of extreme events based on modeling infrastructure (models and experts to interpret them) they have at their disposal. We consider different adaptive management strategies of a general regulated exploited ecosystem model and we characterize the robustness of these strategies to biased knowledge. Our results show that even with significant mobilized knowledge and optimal strategies, imperfect knowledge may still shrink the safe operating space of the system leading to the collapse of the system. However, and perhaps more interestingly, we also show that in some cases imperfect knowledge may unexpectedly increase the safe operating space by suggesting cautious strategies.
The code enables to calculate the safe operating spaces of different managers in the case of biased and unbiased knowledge.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search