About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 490 results for "Tim M Daw" clear search
Peer reviewed MigrAgent
Wander Jager Rocco Paolillo | Published Friday, October 05, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, November 28, 2018MigrAgent simulates migration flows of a population from a home country to a host country and mutual adaptation of a migrant and local population post-migration. Agents accept interactions in intercultural networks depending on their degree of conservatism. Conservatism is a group-level parameter normally distributed within each ethnic group. Individual conservatism changes as function of reciprocity of interaction in intergroup experiences of acceptance or rejection.
The aim of MigrAgent is to unfold different outcomes of integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization in terms of networks as effect of different degrees of conservatism in each group and speed of migration flows.
Peer reviewed Emergence of Organizations out of Garbage Can Dynamics
Guido Fioretti | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 26, 2020The Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice (GCM) is a fundamental model of organizational decision-making originally propossed by J.D. Cohen, J.G. March and J.P. Olsen in 1972. In their model, decisions are made out of random meetings of decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems within an organization.
With this model, these very same agents are supposed to meet in society at large where they make decisions according to GCM rules. Furthermore, under certain additional conditions decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems form stable organizations. In this artificial ecology organizations are born, grow and eventually vanish with time.
Individual-based model to "Intraspecific trait variation in personality‐related movement behavior promotes coexistence" (Milles et al., 2020)
Alexander Milles | Published Monday, June 22, 2020The community consequences of intra-specific trait variation (ITV) are a current topic in ecological research. The effects of ITV on species coexistence have, yet, not sufficiently been understood. With this individual-based model we analyzed the effect of intra-specific variation in movement by mimicking variation found in ground-dwelling rodents and analyzing how such variation affects inter-specific differences in competitive ability (i.e. foraging efficiency) and temporary coexistence. The movement algorithm and behavioral plasticity was adapted from existing algorithms and current ecological literature. As a measure for temporary coexistence, we analyzed the time until one of the species went extinct.
Peer reviewed CHIME ABM of Hurricane Evacuation
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Joshua Watts Joshua Alland Rebecca Morss | Published Monday, October 18, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, January 04, 2022The Communicating Hazard Information in the Modern Environment (CHIME) agent-based model (ABM) is a Netlogo program that facilitates the analysis of information flow and protective decisions across space and time during hazardous weather events. CHIME ABM provides a platform for testing hypotheses about collective human responses to weather forecasts and information flow, using empirical data from historical hurricanes. The model uses real world geographical and hurricane data to set the boundaries of the simulation, and it uses historical hurricane forecast information from the National Hurricane Center to initiate forecast information flow to citizen agents in the model.
Unification-Conditions-of-Civilization-Patterns-Multi-Agent-Modeling-of-Human-History
zhuo zhang | Published Friday, May 27, 2022 | Last modified Sunday, May 29, 2022The model of Chinese and Western civilization patterns can help understand how civilizations formed, how they evolved by themselves, and the difference between the unity of China and the disunity of the Western. The previous research had examined historical phenomena about civilization patterns with subjective, static, local, and inductive methods. Therefore, we propose a general model of history dynamics for civilizations pattern, which contains both China and the West, to improve our understanding of civilization formation and the factors influencing the pattern of civilization. And at the same time, the model is used to find the boundary conditions of two different patterns.
Incentives for data sharing
Flaminio Squazzoni Federico Bianchi Thomas Klebel Tony Ross-Hellauer | Published Thursday, October 02, 2025Although beneficial to scientific development, data sharing is still uncommon in many research areas. Various organisations, including funding agencies that endorse open science, aim to increase its uptake. However, estimating the large-scale implications of different policy interventions on data sharing by funding agencies, especially in the context of intense competition among academics, is difficult empirically. Here, we built an agent-based model to simulate the effect of different funding schemes (i.e., highly competitive large grants vs. distributive small grants), and varying intensity of incentives for data sharing on the uptake of data sharing by academic teams strategically adapting to the context.
AnimDens NetLogo
Miguel Pais Christine Ward-Paige | Published Friday, February 10, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, February 23, 2020The model demonstrates how non-instantaneous sampling techniques produce bias by overestimating the number of counted animals, when they move relative to the person counting them.
Kulayinjana
Christophe Le Page Arthur Perrotton Michel De Garine-Wichatitsky Barry Bitu Killion Koyisi Ferdinand Mwamba Cephus Ncube Victor Ncube Siphusisiwe Ndlovu Raphael Ngwenya Ambu Nyathi Fumbane Nyathi Patrick Sibanda Zenzo Sibanda | Published Monday, October 03, 2016a computer-based role-playing game simulating the interactions between farming activities, livestock herding and wildlife in a virtual landscape reproducing local socioecological dynamics at the periphery of Hwange National Park (Zimbabwe).
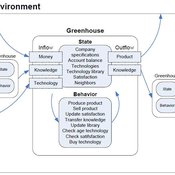
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
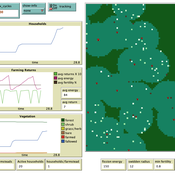
Swidden farming by individual households
C Michael Barton | Published Sunday, April 27, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Swidden Farming is designed to explore the dynamics of agricultural land management strategies.
Displaying 10 of 490 results for "Tim M Daw" clear search