About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 988 results for "Rolf Anker Ims" clear search
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
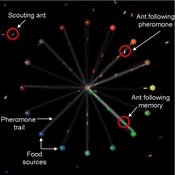
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
Bicycle encounter model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 29, 2019This Bicycle encounter model builds on the Salzburg Bicycle model (Wallentin & Loidl, 2015). It simulates cyclist flows and encounters, which are locations of potential accidents between cyclists.
The Opportunistic Acquisition Model of Stone Tool Raw Material Procurement
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Friday, April 21, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, March 10, 2019The Opportunistic Acquisition Model (OAM) posits that the archaeological lithic raw material frequencies are due to opportunistic encounters with sources while randomly walking in an environment.
SimPLS - The PLS Agent
Iris Lorscheid Sandra Schubring Matthias Meyer Christian Ringle | Published Monday, April 18, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, May 17, 2016The simulation model SimPLS shows an application of the PLS agent concept, using SEM as empirical basis for the definition of agent architectures. The simulation model implements the PLS path model TAM about the decision of using innovative products.
Hedonic and Eudaimonic Well-being Based Reward for Intrinsic Motivated Reinforcement Learning Agents
Yue Gao Shimon Edelman | Published Monday, March 21, 2016The code contains four experiments for well-being based IMRL reward features.
Human-in-the-loop Experiment of the Strategic Coalition Formation using the glove game
Andrew Collins | Published Monday, November 23, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 22, 2022The purpose of the model is to collect information on human decision-making in the context of coalition formation games. The model uses a human-in-the-loop approach, and a single human is involved in each trial. All other agents are controlled by the ABMSCORE algorithm (Vernon-Bido and Collins 2020), which is an extension of the algorithm created by Collins and Frydenlund (2018). The glove game, a standard cooperative game, is used as the model scenario.
The intent of the game is to collection information on the human players behavior and how that compares to the computerized agents behavior. The final coalition structure of the game is compared to an ideal output (the core of the games).
Peer reviewed BAMERS: Macroeconomic effect of extortion
Alejandro Platas López Alejandro Guerra-Hernández | Published Monday, March 23, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, July 26, 2020Inspired by the European project called GLODERS that thoroughly analyzed the dynamics of extortive systems, Bottom-up Adaptive Macroeconomics with Extortion (BAMERS) is a model to study the effect of extortion on macroeconomic aggregates through simulation. This methodology is adequate to cope with the scarce data associated to the hidden nature of extortion, which difficults analytical approaches. As a first approximation, a generic economy with healthy macroeconomics signals is modeled and validated, i.e., moderate inflation, as well as a reasonable unemployment rate are warranteed. Such economy is used to study the effect of extortion in such signals. It is worth mentioning that, as far as is known, there is no work that analyzes the effects of extortion on macroeconomic indicators from an agent-based perspective. Our results show that there is significant effects on some macroeconomics indicators, in particular, propensity to consume has a direct linear relationship with extortion, indicating that people become poorer, which impacts both the Gini Index and inflation. The GDP shows a marked contraction with the slightest presence of extortion in the economic system.
Agent-based simulation of small group decision-making under no communication
Christopher Poile | Published Thursday, May 26, 2016A computational model of a classic small group study by Alex Bavelas. This computational model was designed to explore the difficulty in translating a seemingly simple real-world experiment into a computational model.
Displaying 10 of 988 results for "Rolf Anker Ims" clear search