About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search
Wildlife-Human Interactions in Shared Landscapes (WHISL)
Nicholas Magliocca Neil Carter Andres Baeza-Castro | Published Friday, May 22, 2020This model simulates a group of farmers that have encounters with individuals of a wildlife population. Each farmer owns a set of cells that represent their farm. Each farmer must decide what cells inside their farm will be used to produce an agricultural good that is self in an external market at a given price. The farmer must decide to protect the farm from potential encounters with individuals of the wildlife population. This decision in the model is called “fencing”. Each time that a cell is fenced, the chances of a wildlife individual to move to that cell is reduced. Each encounter reduces the productive outcome obtained of the affected cell. Farmers, therefore, can reduce the risk of encounters by exclusion. The decision of excluding wildlife is made considering the perception of risk of encounters. In the model, the perception of risk is subjective, as it depends on past encounters and on the perception of risk from other farmers in the community. The community of farmers passes information about this risk perception through a social network. The user (observer) of the model can control the importance of the social network on the individual perception of risk.
Evolution of cooperation with strangers
Marco Janssen | Published Friday, October 15, 2010 | Last modified Wednesday, November 13, 2013The model is used to study the conditions under which agents will cooperate in one-shot two-player Prisoner’s Dilemma games if they are able to withdraw from playing the game and can learn to recogniz
Peer reviewed Evolution of Cooperation in Asymmetric Commons Dilemmas
Marco Janssen Nathan Rollins | Published Friday, August 20, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model can be used to explore under which conditions agents behave as observed in field experiments on irrigation games.
Multi-level model of attitudinal dynamics
Ingo Wolf | Published Wednesday, April 06, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, May 04, 2016A model of attitudinal dynamics based on the cognitive mechanism of emotional coherence. The code is written in Java. For initialization an additional dataset is required.
Hybrid traffic model
Patrick Taillandier Arnaud Banos Nathalie Corson | Published Thursday, March 16, 2017The model aims at simulating the car traffic. It allows to use either a macro or a micro sub-model for the simulation of the flow on the roads.
Peer reviewed Ants Digging Networks
Elske van der Vaart | Published Friday, September 14, 2018This is a NetLogo version of Buhl et al.’s (2005) model of self-organised digging activity in ant colonies. It was built for a master’s course on self-organisation and its intended use is still educational. The ants’ behavior can easily be changed by toggling switches on the interface, or, for more advanced students, there is R code included allowing the model to be run and analysed through RNetLogo.
An Agent-based Assessment of Health Vulnerability to Long-term particulate exposure in Seoul Districts
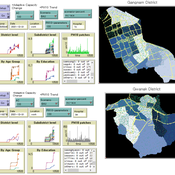
Hyesop Shin Mike Bithell | Published Monday, November 05, 2018 | Last modified Monday, December 03, 2018This model aims to understand the cumulative effects on the population’s vulnerability as represented by exposure to PM10 (particulate matter with diameter less than 10 micrometres) by different age and educational groups in two Seoul districts, Gangnam and Gwanak. Using this model, readers can explore individual’s daily commuting routine, and its health loss when the PM10 concentration of the current patch breaches the national limit of 100µg/m3.
Game of Thrones model
Sean Bergin Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, January 03, 2021 | Last modified Sunday, January 03, 2021This model slowly evolves to become Westeros, with houses fighting for the thrones, and whitewalkers trying to kill all living things. You can download each version to see the evolution of the code, from the Wolf Sheep Predation model to the Game of Thrones model. If you are only interested in the end product, simply download the latest version.
For instructions on each step, see: https://claudinegravelmigu.wixsite.com/got-abm
An Agent-Based Model of Indirect Minority Influence on Social Change
Jiin Jung | Published Wednesday, February 05, 2025This model demonstrates how different psychological mechanisms and network structures generate various patterns of cultural dynamics including cultural diversity, polarization, and majority dominance, as explored by Jung, Bramson, Crano, Page, and Miller (2021). It focuses particularly on the psychological mechanisms of indirect minority influence, a concept introduced by Serge Moscovici (1976, 1980)’s genetic model of social influence, and validates how such influence can lead to social change.
MIXTRUST - crop-livestock interactions at regional level
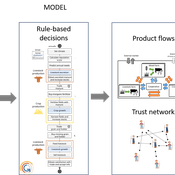
Myriam Grillot Aurélien Peter | Published Tuesday, February 25, 2025 | Last modified Monday, September 01, 2025The basic idea behind developing MIXTRUST was to represent a network of agricultural stakeholders composed of farmers and a cooperative in a mixed landscape to test its performances in response to risks. A mixed landscape here is a landscape where crop and livestock systems interact by the intermediary of material flows of agricultural products. It can be within mixed farms, or between farms, often specialized, (e.g. straw-manure).
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search