About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 88 results for "Claude Garcia" clear search
Firm explore-exploit of knowledge
Rosanna Garcia | Published Monday, March 28, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The basic premise of the model is to simulate several ‘agents’ going through build-buy cycles: Build: Factories follow simple rules of strategy in the allocation of resources between making exploration and exploitation type products. Buy: Each of two types of Consumers, early-adopters and late adopters, follow simple purchase decision rules in deciding to purchase a product from one of two randomly chosen factories. Thus, the two working ‘agents’ of the model are ‘factories’ and […]
Spatial rangeland model
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 22, 2019 | Last modified Friday, March 04, 2022Spatial explicit model of a rangeland system, based on Australian conditions, where grass, woody shrubs and fire compete fore resources. Overgrazing can cause the system to flip from a healthy state to an unproductive shrub state. With the model one can explore the consequences of different movement rules of the livestock on the resilience of the system.
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/.
The AgriculTural LandscApe Simulator (ATLAS)
Hugo Thierry Claude Monteil Aude Vialatte Jean-Philippe Choisis Benoit Gaudou Hazel Parry | Published Monday, January 30, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, May 10, 2017The spatially-explicit AgriculTuralLandscApe Simulator (ATLAS) simulates realistic spatial-temporal crop availability at the landscape scale through crop rotations and crop phenology.
A Balance Model of Opinion Hyperpolarization
Simon Schweighofer Frank Schweitzer David Garcia Simon Schweighofer | Published Tuesday, December 17, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, December 17, 2019Contains python3 code to replicate the opinion dynamics model from our (so far unpublished) JASSS sumbission “A Balance Model of Opinion Hyperpolarization”. The main function is run_model(), which returns a dictionary object containing various outcome metrics.
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
Social norms and the dominance of Low-doers
Antonio Franco | Published Wednesday, July 13, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018The code for the paper “Social norms and the dominance of Low-doers”
From Cyber Space Opinion Leaders and the Spread of Anti-Vaccine Extremism to Physical Space Disease Outbreaks
Xiaoyi Yuan | Published Wednesday, March 08, 2017 | Last modified Friday, March 31, 2017This model simulates the spread of anti-vaccine sentiments in cyber and physical space and how it creates emergence of clusters of anti-vacciners, which eventually lead to higher probablity of disease outbreaks.
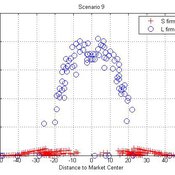
Micro-level Adaptation, Macro-level Selection, and the Dynamics of Market Partitioning
César García-Díaz | Published Monday, October 19, 2015 | Last modified Monday, October 19, 2015This model simulates the emergence of a dual market structure from firm-level interaction. Firms are profit-seeking, and demand is represented by a unimodal distribution of consumers along a set of taste positions.
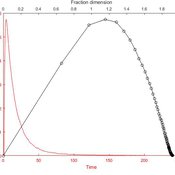
The Coevolution of the Firm and the Product Attribute Space
César García-Díaz | Published Friday, May 22, 2020This model inspects the performance of firms as the product attribute space changes, which evolves as a consequence of firms’ actions. Firms may create new product variants by dragging demand from other existing variants. Firms decide whether to open new product variants, to invade existing ones, or to keep their variant portfolio. At each variant there is a Cournot competition each round. Competition is nested since many firms compete at many variants simultaneously, affecting firm composition at each location (variant).
After the Cournot outcomes, at each round firms decide whether to (i) keep their existing product variant niche, (ii) invade an existing variant, (iii) create a new variant, or (iv) abandon a variant. Firms’ profits across their niche take into consideration the niche-width cost and the cost of opening a new variant.
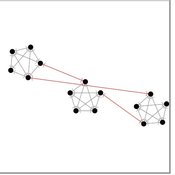
The influence of cognitive diversity on networked search and coordination
César García-Díaz | Published Wednesday, April 03, 2024Agent-based models of organizational search have long investigated how exploitative and exploratory behaviors shape and affect performance on complex landscapes. To explore this further, we build a series of models where agents have different levels of expertise and cognitive capabilities, so they must rely on each other’s knowledge to navigate the landscape. Model A investigates performance results for efficient and inefficient networks. Building on Model B, it adds individual-level cognitive diversity and interaction based on knowledge similarity. Model C then explores the performance implications of coordination spaces. Results show that totally connected networks outperform both hierarchical and clustered network structures when there are clear signals to detect neighbor performance. However, this pattern is reversed when agents must rely on experiential search and follow a path-dependent exploration pattern.
Displaying 10 of 88 results for "Claude Garcia" clear search