About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 113 results random clear search
Peer Review Model
Flaminio Squazzoni Claudio Gandelli | Published Wednesday, September 05, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model looks at implications of author/referee interaction for quality and efficiency of peer review. It allows to investigate the importance of various reciprocity motives to ensure cooperation. Peer review is modelled as a process based on knowledge asymmetries and subject to evaluation bias. The model includes various simulation scenarios to test different interaction conditions and author and referee behaviour and various indexes that measure quality and efficiency of evaluation […]
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
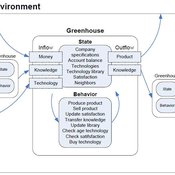
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
SearchResource
Romulus-Catalin Damaceanu | Published Friday, May 04, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An algorithm implemented in NetLogo that can be used for searching resources.
9 Maturity levels in Empirical Validation - An innovation diffusion example
Martin Rixin | Published Wednesday, October 19, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Several taxonomies for empirical validation have been published. Our model integrates different methods to calibrate an innovation diffusion model, ranging from simple randomized input validation to complex calibration with the use of microdata.
Income and Expenditure
Tony Lawson | Published Thursday, October 06, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013How do households alter their spending patterns when they experience changes in income? This model answers this question using a random assignment scheme where spending patterns are copied from a household in the new income bracket.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
The Evolution of Multiple Resistant Strains: An Abstract Model of Systemic Treatment and Accumulated Resistance
Benjamin Nye | Published Wednesday, August 31, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is intended to explore the effectiveness of different courses of interventions on an abstract population of infections. Illustrative findings highlight the importance of the mechanisms for variability and mutation on the effectiveness of different interventions.
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
Displaying 10 of 113 results random clear search