About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 6 of 6 results auction clear search
Auctionsimulation
Deniz Kayar | Published Wednesday, August 12, 2020This repository the multi-agent simulation software for the paper “Comparison of Competing Market Mechanisms with Reinforcement Learning in a CarPooling Scenario”. It’s a mutlithreaded Javaapplication.
Double Auction
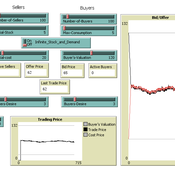
Timothy Gooding | Published Sunday, February 24, 2019This model reproduces the double auction experiments and explores the difference between short-term and long-term trading and pricing.
An Agent Based Model for implementing a double auction financial market
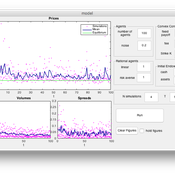
Annalisa Fabretti | Published Thursday, April 14, 2016The model implements a double auction financial markets with two types of agents: rational and noise. The model aims to study the impact of different compensation structure on the market stability and market quantities as prices, volumes, spreads.
An Agent-Based Model of Flood Risk and Insurance
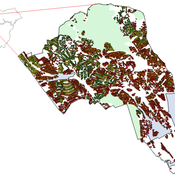
J Dubbelboer I Nikolic K Jenkins J Hall | Published Monday, July 27, 2015 | Last modified Monday, October 03, 2016A model to show the effects of flood risk on a housing market; the role of flood protection for risk reduction; the working of the existing public-private flood insurance partnership in the UK, and the proposed scheme ‘Flood Re’.
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
A Double-Auction Equity Market For a Single Firm with AR1 Earnings
Eric Weisbrod | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a final project for the class AML 591 at Arizona State University. I have done a small amount of bug-checking, but overall the project represents only a half of a semester’s work, so proceed w