About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1252 results Sort by: Recently modified clear search
Selene ABM Suite
ihctdy-f | Published Sunday, January 11, 2026Project Selene ABM Suite
Agent-Based Scenario Exploration for Consortium Cooperation Dynamics
Version: 2.1 (Revised)
Date: January 2026
Status: Exploratory Analysis Tool
A model of opinion dynamics based on formal argumentation: application to the diffusion of the vegetarian diet
Patrick Taillandier Nicolas Salliou Rallou Thomopoulos | Published Monday, March 15, 2021 | Last modified Wednesday, January 07, 2026This generic agent-based model simulates the evolution of agent’s opinions through their exchange of arguments.
The idea behind this model is to explicitly represent the process of mental deliberation of agents from arguments to an opinion, through the use of Dung’s argumentation framework complemented by a structured description of arguments. An application of the model on the diffusion of vegetarian diets is proposed.
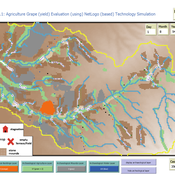
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
Non-attentional visual information transmission in groups under predation
J. Fransje Weerden, van | Published Wednesday, March 25, 2020Our aim is to show effects of group living when only low-level cognition is assumed, such as pattern recognition needed for normal functioning, without assuming individuals have knowledge about others around them or warn them actively.
The model is of a group of vigilant foragers staying within a patch, under attack by a predator. The foragers use attentional scanning for predator detection, and flee after detection. This fleeing action constitutes a visual cue to danger, and can be received non-attentionally by others if it occurs within their limited visual field. The focus of this model is on the effectiveness of this non-attentional visual information reception.
A blind angle obstructing cue reception caused by behaviour can exist in front, morphology causes a blind angle in the back. These limitations are represented by two visual field shapes. The scan for predators is all-around, with distance-dependent detection; reception of flight cues is limited by visual field shape.
Initial parameters for instance: group sizes, movement, vision characteristics for predator detection and for cue reception. Captures (failure), number of times the information reached all individuals at the same time (All-fled, success), and several other effects of the visual settings are recorded.
Consumer diets and values ABM
Natalie Davis Merlin Radbruch Dean Bucciarelli | Published Thursday, December 22, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, March 05, 2025An agent-based model of individual consumers making choices between five possible diets: omnivore, flexitarian, pescatarian, vegetarian, or vegan. Each consumer makes decisions based on personal constraints and values, and their perceptions of how well each diet matches with those values. Consumers can also be influenced by each other’s perceptions via interaction across three social networks: household members, friends, and acquaintances.
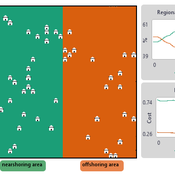
NOMAD: Near–Off Mobility under Aspiration Dynamics
Alejandro Platas López | Published Wednesday, December 17, 2025NOMAD is an agent-based model of firm location choice between two aggregate regions (“near” and “off”) under logistics uncertainty. Firms occupy sites characterised by attractiveness and logistics risk, earn a risk-adjusted payoff that depends on regional costs (wages plus congestion) and an individual risk-tolerance trait, and update location choices using aspiration-based satisficing rules with switching frictions. Logistics risk evolves endogenously on occupied sites through a region-specific absorption mechanism (good/bad events that reduce/increase risk), while congestion feeds back into regional costs via regional shares and local crowding. Runs stop endogenously once the near-region share becomes quasi-stable after burn-in, and the model records time series and quasi-stable outcomes such as near/off composition, switching intensity, costs, average risk, and average risk tolerance.
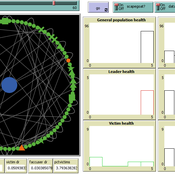
An agent-based model of scapegoating
Carlos Paes | Published Thursday, August 28, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, August 28, 2025This agent-based model investigates scapegoating as a social mechanism of crisis management. Inspired by René Girard’s mimetic theory, it simulates how individual tension accumulates and spreads across a small-world network. When tension exceeds certain thresholds, leaders emerge and accuse marginalized agents, who may attempt to transfer blame to substitutes. If scapegoating occurs, collective tension decreases, but victims become isolated while leaders consolidate temporary authority. This simulation provides a conceptual and methodological framework for exploring how collective blame, crisis contagion, and leadership paradoxes emerge in complex networks. It can also be extended with empirical data, such as social media dynamics of online harassment and virtual lynching, offering potential applications for both theoretical research and practical crisis monitoring.
Wolf-sheep predation Netlogo model, extended, with foresight
Guido Fioretti Andrea Policarpi | Published Wednesday, September 16, 2020 | Last modified Tuesday, April 13, 2021This model is an extension of the Netlogo Wolf-sheep predation model by U.Wilensky (1997). This extended model studies several different behavioural mechanisms that wolves and sheep could adopt in order to enhance their survivability, and their overall impact on global equilibrium of the system.
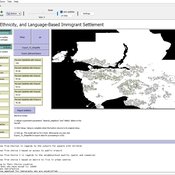
Geospatial Agent-Based Model of Immigrant Settlement Dynamics in Metro Vancouver
Liliana Perez Navid Mahdizadeh Gharakhanlou Maryam Yousefi | Published Wednesday, December 03, 2025This agent-based model simulates how new immigrant households choose where to live in Metro Vancouver under the origins diversity scenario. The model begins with 16,000 household agents, reflecting an expected annual population increase of about 42,500 people based on an average household size of 2.56. Each agent is assigned four characteristics: one of ten origin categories, income level (adjusted using NOC data and recent immigrant earnings), likelihood of having children, and preferred mode of commuting. The ten origin groups are drawn from Census patterns, including six subgroups within the broader Asian category (China, India, the Philippines, Iran, South Korea, and Other Asian countries) and two categories for immigrants from the Americas. This refined classification better captures the diversity of newcomers arriving in the region.
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
Displaying 10 of 1252 results Sort by: Recently modified clear search