About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 60 results food clear search
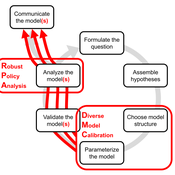
DMC-RPA: Diverse Model Calibration for Robust Policy Analysis (applied to an ABM of smallholder farmer resilience)
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, August 30, 2020This repository contains: (1) a model calibration procedure that identifies a set of diverse, plausible models; and (2) an ABM of smallholder agriculture, which is used as a case study application for the calibration method. By identifying a set of diverse models, the calibration method attends to the issue of “equifinality” prevalent in complex systems, which is a situation where multiple plausible process descriptions exist for a single outcome.
Peer reviewed Vigilant sharing in a small-scale society
Marcos Pinheiro | Published Wednesday, July 22, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, July 29, 2020The model explores food distribution patterns that emerge in a small-scale non-agricultural group when sharing individuals engage in intentional consumption leveling with a given probability.
Peer reviewed Lethal Geometry
Kristin Crouse | Published Friday, February 21, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, December 15, 2021LethalGeometry was developed to examine whether territory size influences the mortality risk for individuals within that territory. For animals who live in territoral groups and are lethally aggressive, we can expect that most aggression occurs along the periphery (or border) between two adjacent territories. For territories that are relatively large, the periphery makes up a proportionately small amount of the of the total territory size, suggesting that individuals in these territories might be less likely to die from these territorial skirmishes. LethalGeometry examines this geometric relationship between territory size and mortality risk under realistic assumptions of variable territory size and shape, variable border width, and stochastic interactions and movement.
The individuals (agents) are programmed to walk randomly about their environment, search for and eat food to obtain energy, reproduce if they can, and act aggressively toward individuals of other groups. During each simulation step, individuals analyze their environment and internal state to determine which actions to take. The actions available to individuals include moving, fighting, and giving birth.
Peer reviewed B3GET
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, November 14, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, September 20, 2022B3GET simulates populations of virtual organisms evolving over generations, whose evolutionary outcomes reflect the selection pressures of their environment. The model simulates several factors considered important in biology, including life history trade-offs, investment in fighting ability and aggression, sperm competition, infanticide, and competition over access to food and mates. Downloaded materials include starting genotype and population files. Edit the these files and see what changes occur in the behavior of virtual populations!
View the B3GET user manual here.
An agent-based model to simulate meat consumption behaviour of consumers in Britain
Andrea Scalco | Published Friday, October 18, 2019The current rate of production and consumption of meat poses a problem both to peoples’ health and to the environment. This work aims to develop a simulation of peoples’ meat consumption behaviour in Britain using agent-based modelling. The agents represent individual consumers. The key variables that characterise agents include sex, age, monthly income, perception of the living cost, and concerns about the impact of meat on the environment, health, and animal welfare. A process of peer influence is modelled with respect to the agents’ concerns. Influence spreads across two eating networks (i.e. co-workers and household members) depending on the time of day, day of the week, and agents’ employment status. Data from a representative sample of British consumers is used to empirically ground the model. Different experiments are run simulating interventions of application of social marketing campaigns and a rise in price of meat. The main outcome is the average weekly consumption of meat per consumer. A secondary outcome is the likelihood of eating meat.
07 EffLab_V5.07 NL
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, October 07, 2019EffLab was built to support the study of the efficiency of agents in an evolving complex adaptive system. In particular:
- There is a definition of efficiency used in ecology, and an analogous definition widely used in business. In ecological studies it is called EROEI (energy returned on energy invested), or, more briefly, EROI (pronounced E-Roy). In business it is called ROI (dollars returned on dollars invested).
- In addition, there is the more well-known definition of efficiency first described by Sadi Carnot, and widely used by engineers. It is usually represented by the Greek letter ‘h’ (pronounced as ETA). These two measures of efficiency bear a peculiar relationship to each other: EROI = 1 / ( 1 - ETA )
In EffLab, blind seekers wander through a forest looking for energy-rich food. In this multi-generational world, they live and reproduce, or die, depending on whether they can find food more effectively than their contemporaries. Data is collected to measure their efficiency as they evolve more effective search patterns.
…
00b SimEvo_V5.08 NetLogo
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, October 05, 2019In 1985 Dr Michael Palmiter, a high school teacher, first built a very innovative agent-based model called “Simulated Evolution” which he used for teaching the dynamics of evolution. In his model, students can see the visual effects of evolution as it proceeds right in front of their eyes. Using his schema, small linear changes in the agent’s genotype have an exponential effect on the agent’s phenotype. Natural selection therefore happens quickly and effectively. I have used his approach to managing the evolution of competing agents in a variety of models that I have used to study the fundamental dynamics of sustainable economic systems. For example, here is a brief list of some of my models that use “Palmiter Genes”:
- ModEco - Palmiter genes are used to encode negotiation strategies for setting prices;
- PSoup - Palmiter genes are used to control both motion and metabolic evolution;
- TpLab - Palmiter genes are used to study the evolution of belief systems;
- EffLab - Palmiter genes are used to study Jevon’s Paradox, EROI and other things.
…
Local soy value chains in northern Ghana
Tim Verwaart | Published Thursday, August 29, 2019The purpose of the simulation is to evaluate alternative interventions by a value chain development program, aiming to improve rural livelihood and food and nutrition security. In northern Ghana, where distrust between the partners can be a problem in the functioning of value chains, the program supports the incorporation of smallholder farmers in soy clusters or agriculture APEX organization (farmers’ co-operatives) with a fair business environment. The goal is to to include the smallholder farmers in a strong value chain and reduce distrust.
Peer reviewed The foraging potential of the Holocene Cape South Coast of South Africa without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain
Marco Janssen Colin Wren | Published Monday, August 12, 2019The Palaeo-Agulhas Plain formed an important habitat exploited by Pleistocene hunter-gatherer populations during periods of lower sea level. This productive, grassy habitat would have supported numerous large-bodied ungulates accessible to a population of skilled hunters with the right hunting technology. It also provided a potentially rich location for plant food collection, and along its shores a coastline that moved with the rise and fall of sea levels. The rich archaeological and paleontological records of Pleistocene sites along the modern Cape south coast of South Africa, which would have overlooked the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain during Pleistocene times of lower sea level, provides a paleoarchive of this extinct ecosystem. In this paper, we present a first order illustration of the “palaeoscape modeling” approach advocated by Marean et al. (2015). We use a resourcescape model created from modern studies of habitat productivity without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain. This is equivalent to predominant Holocene conditions. We then run an agent-based model of the human foraging system to investigate several research questions. Our agent-based approach uses the theoretical framework of optimal foraging theory to model human foraging decisions designed to optimize the net caloric gains within a complex landscape of spatially and temporally variable resources. We find that during the high sea-levels of MIS 5e (+5-6 m asl) and the Holocene, the absence of the Plain left a relatively poor food base supporting a much smaller population relying heavily on edible plant resources from the current Cape flora. Despite high species diversity of plants with edible storage organs, and marine invertebrates, encounter rates with highly profitable resources were low. We demonstrate that without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain, human populations must have been small and low density, and exploited plant, mammal, and marine resources with relatively low caloric returns. The exposure and contraction of the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain was likely the single biggest driver of behavioral change during periods of climate change through the Pleistocene and into the transition to the Holocene.
Samambaia Basin - Hydro-ABM
Pedro Phelipe Gonçalves Porto | Published Sunday, April 07, 2019 | Last modified Monday, May 06, 2019This model is a tool to support water management on Samambaia Basin. On it you can explore different scenarios of policy, management and externalities that could influence the water uses. (Scenarios already tested include less rain and payment on water use)
Displaying 10 of 60 results food clear search