About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 93 results framework clear search
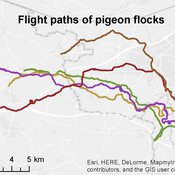
Homing pigeon model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016This model represents the flight paths of a flock of homing pigeons according to their flocking-, orientation- and leadership behaviour.
Multi Asset Variable Network Stock Market Model
Matthew Oldham | Published Monday, September 12, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, October 10, 2017An artifcal stock market model that allows users to vary the number of risky assets as well as the network topology that investors forms in an attempt to understand the dynamics of the market.
An Agent-Based DSS for Word-of-Mouth Programs in Freemium Apps
Manuel Chica | Published Monday, September 05, 2016An agent-based framework that aggregates social network-level individual interactions to run targeting and rewarding programs for a freemium social app. Git source code in https://bitbucket.org/mchserrano/socialdynamicsfreemiumapps
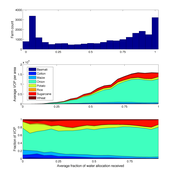
Irrigation Equity and Efficiency
Andrew Bell | Published Tuesday, August 30, 2016The purpose of this model is to examine equity and efficiency in crop production across a system of irrigated farms, as a function of maintenance costs, assessed water fees, and the capacity of farmers to trade water rights among themselves.
A Model to Unravel the Complexity of Rural Food Security
Stefano Balbi Samantha Dobbie | Published Monday, August 22, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018An ABM to simulate the behaviour of households within a village and observe the emerging properties of the system in terms of food security. The model quantifies food availability, access, utilisation and stability.
Multistate modeling extended by behavioral rules
Frans Willekens Sabine Zinn Matthias Leuchter Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, August 03, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 13, 2018Toolkit to specify demographic multistate model with a behavioural element linking intentions to behaviour
A simple agent-based spatial model of the economy
Bernardo Alves Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Thursday, March 10, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 22, 2016The modeling includes citizens, bounded into families; firms and governments; all of them interacting in markets for goods, labor and real estate. The model is spatial and dynamic.
A Model of Making
Bruce Edmonds | Published Friday, January 29, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, December 07, 2016This models provides the infrastructure to model the activity of making. Individuals use resources they find in their environment plus those they buy, to design, construct and deconstruct items. It represents plans and complex objects explicitly.
STECCAR: a simulation of the diffusion of electric cars
A Kangur Lc Verbrugge W Jager M Bockarjova | Published Sunday, November 29, 2015In this Repast model the ‘Consumat’ cognitive framework is applied to an ABM of the Dutch car market. Different policy scenarios can be selected or created to examine their effect on the diffusion of EVs.
Peer reviewed PPHPC - Predator-Prey for High-Performance Computing
Nuno Fachada | Published Saturday, August 08, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, November 25, 2015PPHPC is a conceptual model for studying and evaluating implementation strategies for spatial agent-based models (SABMs). It is a realization of a predator-prey dynamic system, and captures important SABMs characteristics.
Displaying 10 of 93 results framework clear search