About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 675 results agent based clear search
Spatiotemporal Visualization of Emotional and Emotional-related Mental States
Luis Macedo | Published Monday, November 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A system that receives from an agent-based social simulation the agent’s emotional data, their emotional-related data such as motivations and beliefs, as well as their location, and visualizes of all this information in a two dimensional map of the geographic region the agents inhabit as well as on graphs along the time dimension.
Will it spread or not? The effects of social influences and network topology on innovation diffusion
Sebastiano Delre | Published Monday, October 24, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This models simulates innovation diffusion curves and it tests the effects of the degree and the direction of social influences. This model replicates, extends and departs from classical percolation models.
Friendship Games Rev 1.0
David Dixon | Published Friday, October 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A friendship game is a kind of network game: a game theory model on a network. This is a NetLogo model of an agent-based adaptation of “‘Friendship-based’ Games” by PJ Lamberson. The agents reach an equilibrium that depends on the strategy played and the topology of the network.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
The Evolution of Multiple Resistant Strains: An Abstract Model of Systemic Treatment and Accumulated Resistance
Benjamin Nye | Published Wednesday, August 31, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is intended to explore the effectiveness of different courses of interventions on an abstract population of infections. Illustrative findings highlight the importance of the mechanisms for variability and mutation on the effectiveness of different interventions.
An agent-based model to study the effects of trust in coalition formation
Luis Gustavo Nardin | Published Wednesday, August 31, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is an agent-based simulation that consists of agents who play the spatial prisioner’s dilemma game with coalition formation. The coalition dynamics are mainly influenced by how much the agents trust their leaders. The main objective is provide a simulation model to enable the analysis of the impacts that the use of trust may cause in coalition formation.
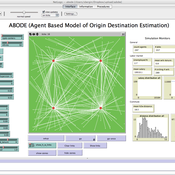
ABODE - Agent Based Model of Origin Destination Estimation
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The agent based model matches origins and destinations using employment search methods at the individual level.
ADAM: Agent-based Demand and Assignment Model
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The core algorithm is an agent-based model, which simulates travel patterns on a network based on microscopic decision-making by each traveler.
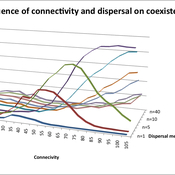
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
A consumer-demand simulation for Smart Metering tariffs (Innovation Diffusion)
Martin Rixin | Published Thursday, August 18, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An Agent-based model simulates consumer demand for Smart Metering tariffs. It utilizes the Bass Diffusion Model and Rogers´s adopter categories. Integration of empirical census microdata enables a validated socio-economic background for each consumer.
Displaying 10 of 675 results agent based clear search