About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search
Mobility, Resource Harvesting and Robustness of Social-Ecological Systems
Irene Perez Ibarra | Published Monday, September 24, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model is a stylized representation of a social-ecological system of agents moving and harvesting a renewable resource. The purpose is to analyze how mobility affects sustainability. Experiments changing agents’ mobility, landscape and information governments have can be run.
NarrABS
Tilman Schenk | Published Thursday, September 20, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent based simulation of a political process based on stakeholder narratives
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
Peer reviewed Torsten Hägerstrand’s Spatial Innovation Diffusion Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a replication of Torsten Hägerstrand’s 1965 model–one of the earliest known calibrated and validated simulations with implicit “agent based” methodology.
Peer Review Model
Flaminio Squazzoni Claudio Gandelli | Published Wednesday, September 05, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model looks at implications of author/referee interaction for quality and efficiency of peer review. It allows to investigate the importance of various reciprocity motives to ensure cooperation. Peer review is modelled as a process based on knowledge asymmetries and subject to evaluation bias. The model includes various simulation scenarios to test different interaction conditions and author and referee behaviour and various indexes that measure quality and efficiency of evaluation […]
An agent-based model of adaptive cycles of the spruce budworm
Julia Schindler | Published Saturday, August 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is an empirically calibrated agent-based model that replicates spruce-budworm outbreaks, one of the most cited adaptive cycles reported. The adaptive-cycle metaphor by L. H. Gunderson and C. S. Holling posits the cross-case existence of repeating cycles of growth, conservation, collapse, and renewal in many complex systems, triggered by loss of resilience. This model is one of the first agent-based models of such cycles, with the novelty that adaptive cycles are not defined by system- […]
Irrigation game
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, July 23, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Irrigation game calibrated on experimental data
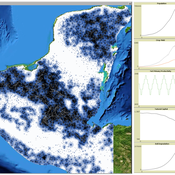
MayaSim: An agent-based model of the ancient Maya social-ecological system
Scott Heckbert | Published Wednesday, July 11, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, July 02, 2013MayaSim is an agent-based, cellular automata and network model of the ancient Maya. Biophysical and anthropogenic processes interact to grow a complex social ecological system.
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search