About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1113 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
The simulation on the study of the optimal business strategy with the interaction between technologies and consumers.
sej-yoo | Published Monday, June 27, 2022 | Last modified Monday, July 04, 2022HOW IT WORKS
This model consists of three agents, and each agent type operates per business theories as below.
a. New technologies(Tech): It evolves per sustaining or disruptive technology trajectory with the constraint of project management triangle (Scope, Time, Quality, and Cost).
b. Entrepreneurs(Entre): It builds up the solution by combining Tech components per its own strategy (Exploration, Exploitation, or Ambidex).
c. Consumer(Consumer): It selects the solution per its own preference due to Diffusion of innovation theory (Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards)
…
HomininSpace
Fulco Scherjon | Published Friday, November 25, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, October 06, 2020A modelling system to simulate Neanderthal demography and distribution in a reconstructed Western Europe for the late Middle Paleolithic.
Firm explore-exploit of knowledge
Rosanna Garcia | Published Monday, March 28, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The basic premise of the model is to simulate several ‘agents’ going through build-buy cycles: Build: Factories follow simple rules of strategy in the allocation of resources between making exploration and exploitation type products. Buy: Each of two types of Consumers, early-adopters and late adopters, follow simple purchase decision rules in deciding to purchase a product from one of two randomly chosen factories. Thus, the two working ‘agents’ of the model are ‘factories’ and […]
Agent-based model of risk behavior in adolescence
N Schuhmacher P Van Geert L Ballato | Published Monday, June 24, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The computer model simulates the development of a social network (i.e. formation of friendships and cliques), the (dyadic) interactions between pupils and the development of similarities and differences in their behavioral profiles.
ForagerNet3_Demography: A Non-Spatial Model of Hunter-Gatherer Demography
Andrew White | Published Thursday, October 17, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 17, 2013ForagerNet3_Demography is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. Key methods represent birth, death, and marriage. The dependency ratio is an imporant variable in many economic decisions embedded in the methods.
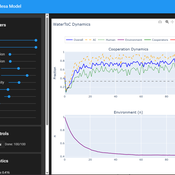
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Water Dilemma
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025 | Last modified Sunday, July 06, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. The primary function of this model was to test how resource-use among AI and human agents degrades the environment, and to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. We implemented a classic game theoretic matrix which decides agents´ strategies, and added a feedback loop which switches between strategies in pristine vs degraded environments. This leads to cooperation in bad environments, and defection in good ones.
Despite this use, it can be applicable for a variety of other scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour.
The ABM was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, it serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
…
SMILI: Small-scale fisheries Institutions and Local Interactions
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017The model represents an archetypical fishery in a co-evolutionary social-ecological environment, capturing different dimensions of trust between fishers and fish buyers for the establishment and persistence of self-governance arrangements.
Policy Formulation for Public Administration - Innovation
Bashar Ourabi | Published Tuesday, August 29, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, August 29, 2017Innovation a byproduct of the intellectual capital, requires a new paradigm for the production constituents. Human Capital HC,Structural capital SC and relational capital RC become key for intellectual capital and consequently for innovation.
Modeling a Victim-Centered Approach for Detection of Human Trafficking Victims within Migration Flows
Kyle Ballard Brant M Horio | Published Saturday, September 23, 2017The model employs an agent-based model for exploring the victim-centered approach to identifying human trafficking and the approach’s effectiveness in an abstract representation of migrant flows.
TIMELY Model
Pia Backmann | Published Thursday, September 19, 2019An individual-based model to evaluate, whether time delays in plant responses to insect herbivory can be beneficial for the plant.
Displaying 10 of 1113 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search