About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 481 results social clear search
Peer reviewed MigrAgent
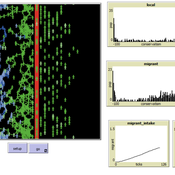
Wander Jager Rocco Paolillo | Published Friday, October 05, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, November 28, 2018MigrAgent simulates migration flows of a population from a home country to a host country and mutual adaptation of a migrant and local population post-migration. Agents accept interactions in intercultural networks depending on their degree of conservatism. Conservatism is a group-level parameter normally distributed within each ethnic group. Individual conservatism changes as function of reciprocity of interaction in intergroup experiences of acceptance or rejection.
The aim of MigrAgent is to unfold different outcomes of integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization in terms of networks as effect of different degrees of conservatism in each group and speed of migration flows.
Social Closure and the Evolution of Cooperation via Indirect Reciprocity
Károly Takács Simone Righi | Published Saturday, June 09, 2018 | Last modified Saturday, June 09, 2018Righi S., Takacs K., Social Closure and the Evolution of Cooperation via Indirect Reciprocity, Resubmitted after Revisions to Scientific Reports
The Regional Security Game: An Agent-based, Evolutionary Model of Strategic Evolution and Stability
Anthony Skews | Published Saturday, June 09, 2018The Regional Security Game is a iterated public goods game with punishement based on based on life sciences work by Boyd et al. (2003 ) and Hintze & Adami (2015 ), with modifications appropriate for an international relations setting. The game models a closed regional system in which states compete over the distribution of common security benefits. Drawing on recent work applying cultural evolutionary paradigms in the social sciences, states learn through imitation of successful strategies rather than making instrumentally rational choices. The model includes the option to fit empirical data to the model, with two case studies included: Europe in 1933 on the verge of war and south-east Asia in 2013.
Endogenous changes in public opinion dynamics
Francisco J. León-Medina | Published Tuesday, June 05, 2018The model formalizes a situation where agents embedded in different types of networks (random, small world and scale free networks) interact with their neighbors and express an opinion that is the result of different mechanisms: a coherence mechanism, in which agents try to stick to their previously expressed opinions; an assessment mechanism, in which agents consider available external information on the topic; and a social influence mechanism, in which agents tend to approach their neighbor’s opinions.
Model of a Socioterritorial complex system - The Southern Rural Territory of Sergipe
Marcos Aurélio Santos da Silva | Published Friday, May 18, 2018The model represents a set of social actors engaged into a collegiate (composed of representants of civil society and public sector) to manage the Southern Rural Territory of Sergipe (SRTS), created by two territorial public policies, the National Program for the Sustainable Development of Rural Territories (PRONAT) and the Program Territories of Citizenship (PTC) which aim at balancing power relations between social actors of Rural Territories. The main gola of these public policies is to empower the civil society engaged in the territory to enable them to negotiate with the traditional power (mainly majors). It was designed two models of the SRTS, one that represents the situation in 2012, and other that represents the social interdependencies in 2017. For each period it is possible to measure the capability and power of each modeled social actor and see whether it is observed the empowerment of the civil society or not.
An Agent-Based Simulation of Continuous-Time Public Goods Games
Tuong Manh Vu | Published Thursday, May 17, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, April 02, 2019To our knowledge, this is the first agent-based simulation of continuous-time PGGs (where participants can change contributions at any time) which are much harder to realise within both laboratory and simulation environments.
Work related to this simulation has been published in the following journal article:
Vu, Tuong Manh, Wagner, Christian and Siebers, Peer-Olaf (2019) ‘ABOOMS: Overcoming the Hurdles of Continuous-Time Public Goods Games with a Simulation-Based Approach’ Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 22 (2) 7 http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/22/2/7.html. doi: 10.18564/jasss.3995
Abstract:
…
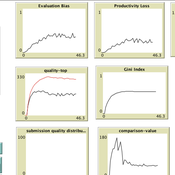
Peer Review Game
Giangiacomo Bravo Flaminio Squazzoni Francisco Grimaldo Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, April 30, 2018NetLogo software for the Peer Review Game model. It represents a population of scientists endowed with a proportion of a fixed pool of resources. At each step scientists decide how to allocate their resources between submitting manuscripts and reviewing others’ submissions. Quality of submissions and reviews depend on the amount of allocated resources and biased perception of submissions’ quality. Scientists can behave according to different allocation strategies by simply reacting to the outcome of their previous submission process or comparing their outcome with published papers’ quality. Overall bias of selected submissions and quality of published papers are computed at each step.
Kiss Nightclub simulation
Mathieu Bourgais | Published Friday, April 27, 2018 | Last modified Friday, April 05, 2019Model for the simulation of the Kiss Nightclub fevacuations with agents featring cognition, emotions, emotonal contagion, personality, social relations and norms.
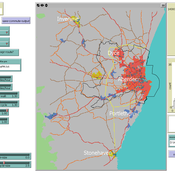
Transport simulation in a real road network
Gary Polhill Jiaqi Ge | Published Tuesday, April 17, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, April 17, 2018Ge, J., & Polhill, G. (2016). Exploring the Combined Impact of Factors Influencing Commuting Patterns and CO2 Emission in Aberdeen Using an Agent-Based Model. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 19(3). http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/19/3/11.html
We develop an agent-based transport model using a realistic GIS-enabled road network and the car following method. The model can be used to study the impact of social interventions such as flexi-time and workplace sharing, as well as large infrastructure such as the construction of a bypass or highway. The model is developed in Netlogo version 5 and requires road network data in GIS format to run.
The Thin Blue Line Between Protesters and Their Counter-Protesters
Tamsin Lee | Published Monday, March 26, 2018More frequently protests are accompanied by an opposing group performing a counter protest. This phenomenon can increase tension such that police must try to keep the two groups separated. However, what is the best strategy for police? This paper uses a simple agent-based model to determine the best strategy for keeping the two groups separated. The ‘thin blue line’ varies in density (number of police), width and the keenness of police to approach protesters. Three different groups of protesters are modelled to mimic peaceful, average and volatile protests. In most cases, a few police forming a single-file ‘thin blue line’ separating the groups is very effective. However, when the protests are more volatile, it is more effective to have many police occupying a wide ‘thin blue line’, and police being keen to approach protesters. To the authors knowledge, this is the first paper to model protests and counter-protests.
Displaying 10 of 481 results social clear search