About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 232 results other clear search
THE STATUS ARENA
Gert Jan Hofstede Jillian Student Mark R Kramer | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 09, 2018Status-power dynamics on a playground, resulting in a status landscape with a gender status gap. Causal: individual (beauty, kindness, power), binary (rough-and-tumble; has-been-nice) or prior popularity (status). Cultural: acceptability of fighting.
An Agent-based model of the economy with consumer credit
Paola D'Orazio Gianfranco Giulioni | Published Friday, April 15, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, March 07, 2019The model was built to study the links between consumer credit, wealth distribution and aggregate demand in a complex macroeconomics system.
Food supply chain innovations under public pressure
Tim Verwaart Wil Hennen Jan Buurma | Published Friday, April 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 27, 2018Aroused public opinion has led to public debates on social responsibility issues in food supply chains. This model based op opinion dynamics and the linkages between involved actors simulates the public debate leading to the transitions.
Segregation and Opinion Polarization
Thomas Feliciani Andreas Flache Jochem Tolsma | Published Wednesday, April 13, 2016This is a tool to explore the effects of groups´ spatial segregation on the emergence of opinion polarization. It embeds two opinion formation models: a model of negative (and positive) social influence and a model of persuasive argument exchange.
Simulation of Self-enforcing Agreement in Cooperative Teams
Hang Xiong | Published Friday, April 01, 2016This is an agent-based model of the implementation of the self-enforcing agreement in cooperative teams.
A Model of Making
Bruce Edmonds | Published Friday, January 29, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, December 07, 2016This models provides the infrastructure to model the activity of making. Individuals use resources they find in their environment plus those they buy, to design, construct and deconstruct items. It represents plans and complex objects explicitly.
Affinity/Hostility in Divided Communities
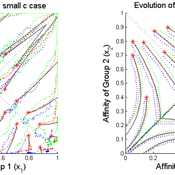
Christopher Thron | Published Friday, January 22, 2016Agent-based model of intergroup conflict in divided communities.
Influence with over-confident agents
Juliette Rouchier Emily Tanimura | Published Wednesday, October 21, 2015Agents can influence each other if they are close enough in knowledge. The probability to convince with good knowledge and number of agents have an impact on the dissemination of knowledge.
Inquisitiveness in ad hoc teams
Davide Secchi | Published Sunday, October 18, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, June 11, 2020This model builds on inquisitiveness as a key individual disposition to expand the bounds of their rationality. It represents a system where teams are formed around problems and inquisitive agents integrate competencies to find ‘emergent’ solutions.
Private forest owner management behavior using social interactions, information flow, and peer-to-peer n
Jessica Leahy Emily Silver Huff Aaron R Weiskittel Caroline L Noblet David Hiebeler | Published Tuesday, October 13, 2015This theoretical model includes forested polygons and three types of agents: forest landowners, foresters, and peer leaders. Agent rules and characteristics were parameterized from existing literature and an empirical survey of forest landowners.
Displaying 10 of 232 results other clear search