About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 185 results reviewed clear search
Peer reviewed MigrAgent
Wander Jager Rocco Paolillo | Published Friday, October 05, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, November 28, 2018MigrAgent simulates migration flows of a population from a home country to a host country and mutual adaptation of a migrant and local population post-migration. Agents accept interactions in intercultural networks depending on their degree of conservatism. Conservatism is a group-level parameter normally distributed within each ethnic group. Individual conservatism changes as function of reciprocity of interaction in intergroup experiences of acceptance or rejection.
The aim of MigrAgent is to unfold different outcomes of integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization in terms of networks as effect of different degrees of conservatism in each group and speed of migration flows.
Peer reviewed Ants Digging Networks
Elske van der Vaart | Published Friday, September 14, 2018This is a NetLogo version of Buhl et al.’s (2005) model of self-organised digging activity in ant colonies. It was built for a master’s course on self-organisation and its intended use is still educational. The ants’ behavior can easily be changed by toggling switches on the interface, or, for more advanced students, there is R code included allowing the model to be run and analysed through RNetLogo.
Peer reviewed Emergent Firms Model
J M Applegate | Published Friday, July 13, 2018The Emergent Firm (EF) model is based on the premise that firms arise out of individuals choosing to work together to advantage themselves of the benefits of returns-to-scale and coordination. The Emergent Firm (EF) model is a new implementation and extension of Rob Axtell’s Endogenous Dynamics of Multi-Agent Firms model. Like the Axtell model, the EF model describes how economies, composed of firms, form and evolve out of the utility maximizing activity on the part of individual agents. The EF model includes a cash-in-advance constraint on agents changing employment, as well as a universal credit-creating lender to explore how costs and access to capital affect the emergent economy and its macroeconomic characteristics such as firm size distributions, wealth, debt, wages and productivity.
Peer reviewed Zimbabwe Agro-Pastoral Management Model (ZAPMM): Musimboti wevanhu, zvipfuo nezvirimwa
MV Eitzel Solera Kleber Tulio Neves Jon Solera Kenneth B Wilson Abraham Mawere Ndlovu Aaron C Fisher André Veski Oluwasola E Omoju Emmanuel Mhike Hove | Published Tuesday, June 19, 2018This model has been created with and for the researcher-farmers of the Muonde Trust (http://www.muonde.org/), a registered Zimbabwean non-governmental organization dedicated to fostering indigenous innovation. Model behaviors and parameters (mashandiro nemisiyano nedzimwe model) derive from a combination of literature review and the collected datasets from Muonde’s long-term (over 30 years) community-based research. The goals of this model are three-fold (muzvikamu zvitatu):
A) To represent three components of a Zimbabwean agro-pastoral system (crops, woodland grazing area, and livestock) along with their key interactions and feedbacks and some of the human management decisions that may affect these components and their interactions.
B) To assess how climate variation (implemented in several different ways) and human management may affect the sustainability of the system as measured by the continued provisioning of crops, livestock, and woodland grazing area.
C) To provide a discussion tool for the community and local leaders to explore different management strategies for the agro-pastoral system (hwaro/nzira yekudyidzana kwavanhu, zvipfuo nezvirimwa), particularly in the face of climate change.
Peer reviewed Population Genetics
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, September 09, 2020This model simulates the mechanisms of evolution, or how allele frequencies change in a population over time.
Peer reviewed Dawkins Weasel
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, January 28, 2026Dawkins’ Weasel is a NetLogo model that illustrates the principle of evolution by natural selection. It is inspired by a thought experiment presented by Richard Dawkins in his book The Blind Watchmaker (1996).
Peer reviewed Strategy with Externalities
J M Applegate Glenn Hoetker | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017The SWE models firms search behaviour as the performance landscape shifts. The shift represents society’s pricing of negative externalities, and the performance landscape is an NK structure. The model is written in NetLogo.
Peer reviewed Agent-based Renewables model for Integrated Sustainable Energy (ARISE)
Anthony Halog Muhammad Indra Al Irsyad Rabindra Nepal | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2017 | Last modified Friday, October 05, 2018ARISE is a hybrid energy model incorporating macroeconomic data, micro socio-economic data, engineering data and environmental data. This version of ARISE can simulate scenarios of solar energy policy for Indonesia case.
Peer reviewed Empathy & Power
J M Applegate Ned Wellman | Published Monday, November 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, December 21, 2017The purpose of this model is to explore the effects of different power structures on a cross-functional team’s prosocial decision making. Are certain power distributions more conducive to the team making prosocial decisions?
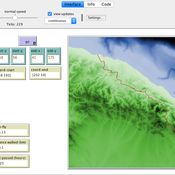
Peer reviewed Least cost path mobility
Colin Wren Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Saturday, September 02, 2017 | Last modified Monday, October 04, 2021This model aims to mimic human movement on a realistic topographical surface. The agent does not have a perfect knowledge of the whole surface, but rather evaluates the best path locally, at each step, thus mimicking imperfect human behavior.
Displaying 10 of 185 results reviewed clear search