About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 185 results reviewed clear search
Peer reviewed The foraging potential of the Holocene Cape South Coast of South Africa without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain
Marco Janssen Colin Wren | Published Monday, August 12, 2019The Palaeo-Agulhas Plain formed an important habitat exploited by Pleistocene hunter-gatherer populations during periods of lower sea level. This productive, grassy habitat would have supported numerous large-bodied ungulates accessible to a population of skilled hunters with the right hunting technology. It also provided a potentially rich location for plant food collection, and along its shores a coastline that moved with the rise and fall of sea levels. The rich archaeological and paleontological records of Pleistocene sites along the modern Cape south coast of South Africa, which would have overlooked the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain during Pleistocene times of lower sea level, provides a paleoarchive of this extinct ecosystem. In this paper, we present a first order illustration of the “palaeoscape modeling” approach advocated by Marean et al. (2015). We use a resourcescape model created from modern studies of habitat productivity without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain. This is equivalent to predominant Holocene conditions. We then run an agent-based model of the human foraging system to investigate several research questions. Our agent-based approach uses the theoretical framework of optimal foraging theory to model human foraging decisions designed to optimize the net caloric gains within a complex landscape of spatially and temporally variable resources. We find that during the high sea-levels of MIS 5e (+5-6 m asl) and the Holocene, the absence of the Plain left a relatively poor food base supporting a much smaller population relying heavily on edible plant resources from the current Cape flora. Despite high species diversity of plants with edible storage organs, and marine invertebrates, encounter rates with highly profitable resources were low. We demonstrate that without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain, human populations must have been small and low density, and exploited plant, mammal, and marine resources with relatively low caloric returns. The exposure and contraction of the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain was likely the single biggest driver of behavioral change during periods of climate change through the Pleistocene and into the transition to the Holocene.
Peer reviewed Organizational behavior in the hierarchy model
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, July 31, 2019In a two-level hierarchical structure (consisting of the positions of managers and operators), persons holding these positions have a certain performance and the value of their own (personal perception in this, simplified, version of the model) perception of each other. The value of the perception of each other by agents is defined as a random variable that has a normal distribution (distribution parameters are set by the control elements of the interface).
In the world of the model, which is the space of perceptions, agents implement two strategies: rapprochement with agents that perceive positively and distance from agents that perceive negatively (both can be implemented, one of these strategies, or neither, the other strategy, which makes the agent stationary). Strategies are implemented in relation to those agents that are in the radius of perception (PerRadius).
The manager (Head) forms a team of agents. The performance of the group (the sum of the individual productivities of subordinates, weighted by the distance from the leader) varies depending on the position of the agents in space and the values of their individual productivities. Individual productivities, in the current version of the model, are set as a random variable distributed evenly on a numerical segment from 0 to 100. The manager forms the team 1) from agents that are in (organizational) radius (Op_Radius), 2) among agents that the manager perceives positively and / or negatively (both can be implemented, one of the specified rules, or neither, which means the refusal of the command formation).
Agents can (with a certain probability, given by the variable PrbltyOfDecisn%), in case of a negative perception of the manager, leave his group permanently.
It is possible in the model to change on the fly radii values, update the perception value across the entire population and the perception of an individual agent by its neighbors within the perception radius, and the probability values for a subordinate to make a decision about leaving the group.
You can also change the set of strategies for moving agents and strategies for recruiting a team manager. It is possible to add a randomness factor to the movement of agents (Stoch_Motion_Speed, the default is set to 0, that is, there are no random movements).
…
Peer reviewed Charging behaviour of electric vehicle drivers
Wilfried van Sark Annemijn Peters Floor Alkemade Mart van der Kam | Published Wednesday, May 08, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, April 14, 2020This model was developed to study the combination of electric vehicles (EVs) and intermitten renewable energy sources. The model presents an EV fleet in a fictional area, divided into a residential area, an office area and commercial area. The area has renewable energy sources: wind and PV solar panels. The agents can be encouraged to charge their electric vehicles at times of renewable energy surplus by introducing different policy interventions. Other interesting variables in the model are the installed renewable energy sources, EV fleet composition and available charging infrastructure. Where possible, use emperical data as input for our model. We expand upon previous models by incorporating environmental self-identity and range anxiety as agent variables.
Peer reviewed lgm_ecodynamics
Colin Wren | Published Monday, April 22, 2019This is a modification of a model published previous by Barton and Riel-Salvatore (2012). In this model, we simulate six regional populations within Last Glacial Maximum western Europe. Agents interact through reproduction and genetic markers attached to each of six regions mix through subsequent generations as a way to track population dynamics, mobility, and gene flow. In addition, the landscape is heterogeneous and affects agent mobility and, under certain scenarios, their odds of survival.
Peer reviewed Collectivities
Nigel Gilbert | Published Tuesday, April 09, 2019 | Last modified Thursday, August 22, 2019The model that simulates the dynamic creation and maintenance of knowledge-based formations such as communities of scientists, fashion movements, and subcultures. The model’s environment is a spatial one, representing not geographical space, but a “knowledge space” in which each point is a different collection of knowledge elements. Agents moving through this space represent people’s differing and changing knowledge and beliefs. The agents have only very simple behaviors: If they are “lonely,” that is, far from a local concentration of agents, they move toward the crowd; if they are crowded, they move away.
Running the model shows that the initial uniform random distribution of agents separates into “clumps,” in which some agents are central and others are distributed around them. The central agents are crowded, and so move. In doing so, they shift the centroid of the clump slightly and may make other agents either crowded or lonely, and they too will move. Thus, the clump of agents, although remaining together for long durations (as measured in time steps), drifts across the view. Lonely agents move toward the clump, sometimes joining it and sometimes continuing to trail behind it. The clumps never merge.
The model is written in NetLogo (v6). It is used as a demonstration of agent-based modelling in Gilbert, N. (2008) Agent-Based Models (Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences). Sage Publications, Inc. and described in detail in Gilbert, N. (2007) “A generic model of collectivities,” Cybernetics and Systems. European Meeting on Cybernetic Science and Systems Research, 38(7), pp. 695–706.
Peer reviewed Applying Brantingham’s Neutral Model of Stone Raw Material Procurement to the Pinnacle Point Middle Stone Age Record, Western Cape, South Africa
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Sunday, March 10, 2019This model is an application of Brantingham’s neutral model to a real landscape with real locations of potential sources. The sources are represented as their sizes during current conditions, and from marine geophysics surveys, and the agent starts at a random location in Mossel Bay Region (MBR) surrounding the Archaeological Pinnacle Point (PP) locality, Western Cape, South Africa. The agent moves at random on the landscape, picks up and discards raw materials based only upon space in toolkit and probability of discard. If the agent happens to encounter the PP locality while moving at random the agent may discard raw materials at it based on the discard probability.
Peer reviewed From Individual Fuzzy Cognitive Maps to Agent Based Models: Modeling Multi-Factorial and Multi-stakeholder Decision-Making for Water Scarcity
Sara Mehryar | Published Monday, March 04, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, August 28, 2019This model simulates different farmers’ decisions and actions to adapt to the water scarce situation. This simulation helps to investigate how farmers’ strategies may impact macro-behavior of the social-ecological system i.e. overall groundwater use change and emigration of farmers. The environmental variables’ behavior and behavioral rules of stakeholders are captured with Fuzzy Cognitive Map (FCM) that is developed with both qualitative and quantitative data, i.e. stakeholders’ knowledge and empirical data from studies. This model have been used to compare the impact of different water scarcity policies on overall groundwater use in a farming community facing water scarcity.
Peer reviewed Gender desegregation in German high schools
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019 | Last modified Sunday, November 08, 2020The study goes back to a model created in the 1990s which successfully tried to replicate the changes of the percentages of female teachers among the teaching staff in high schools (“Gymnasien”) in the German federal state of Rheinland-Pfalz. The current version allows for additional validation and calibration of the model and is accompanied with the empirical data against which the model is tested and with an analysis program especially designed to perform the analyses in the most recent journal article.
Peer reviewed MHMSLeptoDy (Multi-host, multi-serovar Leptospira Dynamics Model)
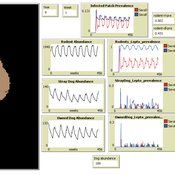
Aniruddha Belsare Matthew Gompper Meghan Mason Claudia Munoz-Zanzi | Published Tuesday, January 29, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, March 12, 2019Leptospirosis is a neglected, bacterial zoonosis with worldwide distribution, primarily a disease of poverty. More than 200 pathogenic serovars of Leptospira bacteria exist, and a variety of species may act as reservoirs for these serovars. Human infection is the result of direct or indirect contact with Leptospira bacteria in the urine of infected animal hosts, primarily livestock, dogs, and rodents. There is increasing evidence that dogs and dog-adapted serovar Canicola play an important role in the burden of leptospirosis in humans in marginalized urban communities. What is needed is a more thorough understanding of the transmission dynamics of Leptospira in these marginalized urban communities, specifically the relative importance of dogs and rodents in the transmission of Leptospira to humans. This understanding will be vital for identifying meaningful intervention strategies.
One of the main objectives of MHMSLeptoDy is to elucidate transmission dynamics of host-adapted Leptospira strains in multi-host system. The model can also be used to evaluate alternate interventions aimed at reducing human infection risk in small-scale communities like urban slums.
Peer reviewed ELTAP-Egy model (Energy Landscape Transition Analysis and Planning in Egypt)
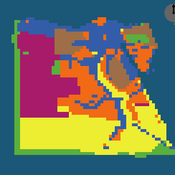
Mostafa Shaaban Jürgen Scheffran Jürgen Böhner Mohamed Salah Elsobki | Published Saturday, December 29, 2018The model investigates conditions, scenarios and strategies for future planning of energy in Egypt, with an emphasis on alternative energy pathways and a sustainable electricity supply mix as part of an energy roadmap till the year 2100. It combines the multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) with agent-based modeling (ABM) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) visualization to integrate the interactions of the decisions of multi-agents, the multi-criteria evaluation of sustainability, the time factor and the site factors to assess the transformation of energy landscapes.
Displaying 10 of 185 results reviewed clear search