About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 178 results information clear search
The Geography of Conflict Diamonds: The Case of Sierra Leone
Andrew Crooks Bianica Pires | Published Thursday, March 24, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, March 24, 2016Using Sierra Leone as a test case, the purpose of the model is to explore the role of geography in a resource-driven war. An ABM is integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) for this purpose.
Product Diffusion Model in an Advance Selling Strategy
Peng Shao | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 15, 2016the model can be used to describe the product diffusion in an Advance Selling Strategy. this model takes into account the consumers product adoption, and describe consumer’s online behavior based on four states.
Modeling the Emergence of Riots
Andrew Crooks Bianica Pires | Published Wednesday, January 20, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 21, 2016The purpose of the model is to explore how the unique socioeconomic variables underlying Kibera, local interactions, and the spread of a rumor, may trigger a riot.
A Consumer in the Jungle of Product Differentiation
Alessandro Pluchino Andrea Rapisarda Alessio Emanuele Biondo Alfio Giarlotta | Published Tuesday, December 22, 2015Building upon the distance-based Hotelling’s differentiation idea, we describe the behavioral experience of several prototypes of consumers, who walk a hypothetical cognitive path in an attempt to maximize their satisfaction.
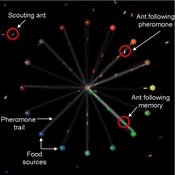
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
Health and social public information office (SPUN) simulation
Emilio Sulis Manuela Vinai | Published Friday, November 06, 2015 | Last modified Saturday, November 07, 2015The program simulate the functioning of an italian health and social public information office (SPUN) on the basis of the real data collected in the first five years of functioning.
Agent-based model for centralized student admission process
Connie Wang Shu-Heng Chen Bin-Tzong Chi | Published Wednesday, November 04, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, March 06, 2019This model is to match students and schools using real-world student admission mechanisms. The mechanisms in this model are serial dictatorship, deferred acceptance, the Boston mechanism, Chinese Parallel, and the Taipei mechanism.
The relationship between product information quantity and diversity of consumer decisions
Marco Janssen Takao Sasaki David Vaughn Becker Rebecca Neel | Published Tuesday, October 27, 2015We developed an agent-based model to explore underlying mechanisms of behavioral clustering that we observed in human online shopping experiments.
Inquisitiveness in ad hoc teams
Davide Secchi | Published Sunday, October 18, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, June 11, 2020This model builds on inquisitiveness as a key individual disposition to expand the bounds of their rationality. It represents a system where teams are formed around problems and inquisitive agents integrate competencies to find ‘emergent’ solutions.
Private forest owner management behavior using social interactions, information flow, and peer-to-peer n
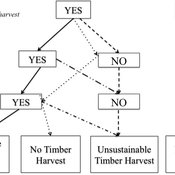
Jessica Leahy Emily Silver Huff Aaron R Weiskittel Caroline L Noblet David Hiebeler | Published Tuesday, October 13, 2015This theoretical model includes forested polygons and three types of agents: forest landowners, foresters, and peer leaders. Agent rules and characteristics were parameterized from existing literature and an empirical survey of forest landowners.
Displaying 10 of 178 results information clear search