About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 195 results behavior clear search
This agent-based model (ABM), developed in NetLogo and available on the COMSES repository, simulates a stylized, competitive electricity market to explore the effects of carbon pricing policies under conditions of technological innovation. Unlike traditional models that treat innovation as exogenous, this ABM incorporates endogenous innovation dynamics, allowing clean technology costs to evolve based on cumulative deployment (Wright’s Law) or time (Moore’s Law). Electricity generation companies act as agents, making investment decisions across coal, gas, wind, and solar PV technologies based on expected returns and market conditions. The model evaluates three policy scenarios—No Policy, Emissions Trading System (ETS), and Carbon Tax—within a merit-order market framework. It is partially empirically grounded, using real-world data for technology costs and emissions caps. By capturing emergent system behavior, this model offers a flexible and transparent tool for analyzing the transition to low-carbon electricity systems.
Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) Simulation for Compact Urban Growth in Dublin: An Agent-Based Model in NetLogo
ajithvyas | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2025This agent-based model simulates the implementation of a Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) mechanism in a stylized urban environment inspired by Dublin. It explores how developer agents interact with land parcels under spatial zoning, conservation protections, and incentive-based policy rules. The model captures emergent outcomes such as compact growth, green and heritage zone preservation, and public cost-efficiency. Built in NetLogo, the model enables experimentation with variable FSI bonuses, developer behavior, and spatial alignment of sending/receiving zones. It is intended as a policy sandbox to test market-aligned planning tools under behavioral and spatial uncertainty.
Social Innovation Model
Jiin Jung | Published Monday, April 28, 2025This research aims to uncover the micro-mechanisms that drive the macro-level relationship between cultural tolerance and innovation. We focus on the indirect influence of minorities—specifically, workers with diverse domain expertise—within collaboration networks. We propose that minority influence from individuals with different expertise can serve as a key driver of organizational innovation, particularly in dynamic market environments, and that cultural tolerance is critical for enabling such minority-induced innovation. Our model demonstrates that seemingly conflicting empirical patterns between cultural tightness/looseness and innovation can emerge from the same underlying micro-mechanisms, depending on parameter values. A systematic simulation experiment revealed an optimal cultural configuration: a medium level of tolerance (t = 0.6) combined with low consistency (κ = 0.05) produced the fastest adaptation to abrupt market changes. These findings provide evidence that indirect minority influence is a core micro-mechanism linking cultural tolerance to innovation.
Environmental stochasticity, resource heterogeneity, and the evolution of cooperation
Colin Lynch Carl Lipo Terry Hunt Michaela Starkey | Published Friday, March 14, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, June 19, 2025The emergence of cooperation in human societies is often linked to environmental constraints, yet the specific conditions that promote cooperative behavior remain an open question. This study examines how resource unpredictability and spatial dispersion influence the evolution of cooperation using an agent-based model (ABM). Our simulations test the effects of rainfall variability and resource distribution on the survival of cooperative and non-cooperative strategies. The results show that cooperation is most likely to emerge when resources are patchy, widely spaced, and rainfall is unpredictable. In these environments, non-cooperators rapidly deplete local resources and face high mortality when forced to migrate between distant patches. In contrast, cooperators—who store and share resources—can better endure extended droughts and irregular resource availability. While rainfall stochasticity alone does not directly select for cooperation, its interaction with resource patchiness and spatial constraints creates conditions where cooperative strategies provide a survival advantage. These findings offer broader insights into how environmental uncertainty shapes social organization in resource-limited settings. By integrating ecological constraints into computational modeling, this study contributes to a deeper understanding of the conditions that drive cooperation across diverse human and animal systems.
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
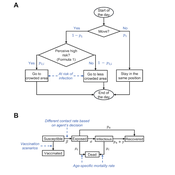
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
Retention in Higher Education: An Agent-Based Model of Social Interactions and Motivated Agent Behavior
Andrew Crooks Amira Al-Khulaidy Stine | Published Wednesday, October 23, 2024Educational attainment and student retention in higher education are two of the main focuses of higher education research. Institutions in the U.S. are constantly looking for ways to identify areas of improvement across different aspects of the student experience on university campuses. This paper combines Department of Education data, U.S. Census data, and higher education theory on student retention, to build an agent-based model of student behavior.
Agent-Based Model of a Circular Food Packaging Ecosystem to assess Packaging Waste Dynamics
Annoek Reitsema | Published Friday, October 11, 2024Reducing packaging waste is a critical challenge that requires organizations to collaborate within circular ecosystems, considering social, economic, and technical variables like decision-making behavior, material prices, and available technologies. Agent-Based Modeling (ABM) offers a valuable methodology for understanding these complex dynamics. In our research, we have developed an ABM to explore circular ecosystems’ potential in reducing packaging waste, using a case study of the Dutch food packaging ecosystem. The model incorporates three types of agents—beverage producers, packaging producers, and waste treaters—who can form closed-loop recycling systems.
Beverage Producer Agents: These agents represent the beverage company divided into five types based on packaging formats: cans, PET bottles, glass bottles, cartons, and bag-in-boxes. Each producer has specific packaging demands based on product volume, type, weight, and reuse potential. They select packaging suppliers annually, guided by deterministic decision styles: bargaining (seeking the lowest price) or problem-solving (prioritizing high recycled content).
Packaging Producer Agents: These agents are responsible for creating packaging using either recycled or virgin materials. The model assumes a mix of monopolistic and competitive market situations, with agents calculating annual material needs. Decision styles influence their choices: bargaining agents compare recycled and virgin material costs, while problem-solving agents prioritize maximum recycled content. They calculate recycled content in packaging and set prices accordingly, ensuring all produced packaging is sold within or outside the model.
…
Peer reviewed Behavior changes through influence
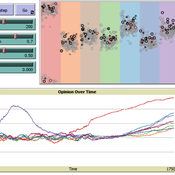
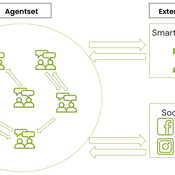
Daria Soboleva | Published Friday, August 30, 2024The model is designed to simulate the behavior and decision-making processes of individuals (agents) in a social network. It aims to represent the changes in individual probability to take any action based on changes in attributes. The action is anything that can be reasonably influenced by the three influencing methods implemented in this model: peer pressure, social media, and state campaigns, and for which the user has a decision-making model. The model is implemented in the multi-agent programmable environment NetLogo 6.3.0.
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Insight into Eco-Choices: Simulating the Fast Fashion Shift
Daria Soboleva Angel Sánchez | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2024 | Last modified Wednesday, June 11, 2025The present model was created and used for the study titled ``Agent-Based Insight into Eco-Choices: Simulating the Fast Fashion Shift.” The model is implemented in the multi-agent programmable environment NetLogo 6.3.0. The model is designed to simulate the behavior and decision-making processes of individuals (agents) in a social network. It focuses on how agents interact with their peers, social media, and government campaigns, specifically regarding their likelihood to purchase fast fashion.
Displaying 10 of 195 results behavior clear search