About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 17 results for "Taylor Anderson" clear search
A replication and extension of the Taylor's Simulation Model of Insurance Market Dynamics in C#
Rei England | Published Sunday, September 24, 2023A simple model is constructed using C# in order to to capture key features of market dynamics, while also producing reasonable results for the individual insurers. A replication of Taylor’s model is also constructed in order to compare results with the new premium setting mechanism. To enable the comparison of the two premium mechanisms, the rest of the model set-up is maintained as in the Taylor model. As in the Taylor example, homogeneous customers represented as a total market exposure which is allocated amongst the insurers.
In each time period, the model undergoes the following steps:
1. Insurers set competitive premiums per exposure unit
2. Losses are generated based on each insurer’s share of the market exposure
3. Accounting results are calculated for each insurer
…
Lake Anderson Revisited II
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Monday, June 28, 2021The purpose of this study is another agent-based replication of a System Dynamics model (Anderson,1973) where he analysed the dynamics of nutrient, biomass, oxygen and detritus in a model lake under conditions of artificial fertilising and policies to deal with the consequences of artificial fertilising.. A first replication (Möhring & Troitzsch,2001) added those agents to the original model that were necessary to move the role of the experimenter into the model, whereas this replication replaces the original lake with a collection of small elements between which biomass, nurtrents and oxygen are exchanged, adds rivers upstream and downstream as well as adjacent land divided into villages and populated with farms and industrial plants run by individual persons.
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
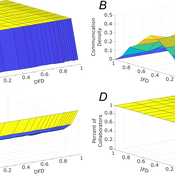
Role of Diversity in Team Performance: the Case of Missing Expertise, an Agent Based Simulations
Tamás Kiss | Published Friday, December 29, 2023This ABM simulates problem solving agents as they work on a set of tasks. Each agent has a trait vector describing their skills. Two agents might form a collaboration if their traits are similar enough. Tasks are defined by a component vector. Agents work on tasks by decreasing tasks’ component vectors towards zero.
The simulation generates agents with given intrapersonal functional diversity (IFD), and dominant function diversity (DFD), and a set of random tasks and evaluates how agents’ traits influence their level of communication and the performance of a team of agents.
Modeling results highlight the importance of the distributions of agents’ properties forming a team, and suggests that for a thorough description of management teams, not only diversity measures based on individual agents, but an aggregate measure is also required.
…
Stoplight parrotfish population model
Tyler Pavlowich | Published Monday, April 02, 2018This agent-based model simulates a stoplight parrotfish population in a heavily-fished Caribbean coral reef. The model allows for the simulation of various fishing regulations and observation of population and catch outcomes. It was built using the structure and equations from several previously published models, including the work of Bozec et al. (2016) and Alonzo and Mangel (2004 and 2005). The initial model conditions are parameterized to population and fishing data collected in Buen Hombre, Dominican Republic by Tyler Pavlowich.
Mobility, Ethnicity, and Language-Based Immigrant Settlement Model - MELBIS
Liliana Perez Jonathan Gaudreau Suzana Dragicevic Taylor Anderson Aaron Leung | Published Monday, June 14, 2021 | Last modified Monday, June 14, 2021MELBIS-V1 is a spatially explicit agent-based model that allows the geospatial simulation of the decision-making process of newcomers arriving in the bilingual cities and boroughs of the island of Montreal, Quebec in CANADA, and the resulting urban segregation spatial patterns. The model was implemented in NetLogo, using geospatial raster datasets of 120m spatial resolution.
MELBIS-V2 enhances MELBIS-V1 to implement and simulate the decision-making processes of incoming immigrants, and to analyze the resulting spatial patterns of segregation as immigrants arrive and settle in various cities in Canada. The arrival and segregation of immigrants is modeled with MELBIS-V2 and compared for three major Canadian immigration gateways, including the City of Toronto, Metro Vancouver, and the City of Calgary.
MixFarm ABM Model
Leigh Anderson | Published Thursday, March 03, 2016MixFarmABM Model examines the competitiveness of second-generation biofuel crops with existing crops and beef cows at the farm level and their impact on the farm structure.
Emerging innovation niches model
Antonio Lopolito Richard Taylor Piergiuseppe Morone | Published Monday, September 22, 2014Objective of our model is to simulate the emergence and operation of a technological niches (TN) in terms of actors’ interaction. A TN can be conceived as protected socio-economic space where radical innovations are developed and tested
Team Structure and Task Performance
Davide Secchi Martin Neumann | Published Monday, August 05, 2024This model was designed to study resilience in organizations. Inspired by ethnographic work, it follows the simple goal to understand whether team structure affects the way in which tasks are performed. In so doing, it compares the ‘hybrid’ data-inspired structure with three more traditional structures (i.e. hierarchy, flexible/relaxed hierarchy, and anarchy/disorganization).
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
Displaying 10 of 17 results for "Taylor Anderson" clear search