About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 788 results for "Blanca Gonzalez-Mon" clear search
Peer reviewed NoD-Neg: A Non-Deterministic model of affordable housing Negotiations
Aya Badawy Nuno Pinto Richard Kingston | Published Sunday, September 08, 2024The Non-Deterministic model of affordable housing Negotiations (NoD-Neg) is designed for generating hypotheses about the possible outcomes of negotiating affordable housing obligations in new developments in England. By outcomes we mean, the probabilities of failing the negotiation and/or the different possibilities of agreement.
The model focuses on two negotiations which are key in the provision of affordable housing. The first is between a developer (DEV) who is submitting a planning application for approval and the relevant Local Planning Authority (LPA) who is responsible for reviewing the application and enforcing the affordable housing obligations. The second negotiation is between the developer and a Registered Social Landlord (RSL) who buys the affordable units from the developer and rents them out. They can negotiate the price of selling the affordable units to the RSL.
The model runs the two negotiations on the same development project several times to enable agents representing stakeholders to apply different negotiation tactics (different agendas and concession-making tactics), hence, explore the different possibilities of outcomes.
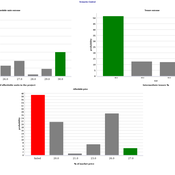
The model produces three types of outputs: (i) histograms showing the distribution of the negotiation outcomes in all the simulation runs and the probability of each outcome; (ii) a data file with the exact values shown in the histograms; and (iii) a conversation log detailing the exchange of messages between agents in each simulation run.
Opinions on contested energy infrastructures
Annalisa Stefanelli | Published Thursday, June 23, 2016This ABM simulates opinions on a topic (originally contested infrastructures) through the interactions between paired agents and based on the sociopsychological assumptions of social judgment theory (SJT; Sherif & Hovland, 1961).
Expectation-Based Bayesian Belief Revision
C Merdes Momme Von Sydow Ulrike Hahn | Published Monday, June 19, 2017 | Last modified Monday, August 06, 2018This model implements a Bayesian belief revision model that contrasts an ideal agent in possesion of true likelihoods, an agent using a fixed estimate of trusting its source of information, and an agent updating its trust estimate.
epiworldR Type: Fast Agent-Based Epi Models
George G. Vega Yon Derek Meyer | Published Monday, August 26, 2024A flexible framework for Agent-Based Models (ABM), the ‘epiworldR’ package provides methods for prototyping disease outbreaks and transmission models using a ‘C++’ backend, making it very fast. It supports multiple epidemiological models, including the Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible (SIS), Susceptible-Infected-Removed (SIR), Susceptible-Exposed-Infected-Removed (SEIR), and others, involving arbitrary mitigation policies and multiple-disease models. Users can specify infectiousness/susceptibility rates as a function of agents’ features, providing great complexity for the model dynamics. Furthermore, ‘epiworldR’ is ideal for simulation studies featuring large populations.
Diffusion of Innovations on Social Networks
Hang Xiong | Published Saturday, April 16, 2016This is model that simulates how multiple kinds of peer effects shape the diffusion of innovations through different types of social relationships.
Perspectives on the Information-Based Economy
Vladimir Gazda Jana Zausinova Marcel Volosin | Published Monday, October 24, 2022This is the agent-based model of information market evolution. It simulates the influences of the transition from material to electronic carriers of information, which is modelled by the falling price of variable production factor. It demonstrates that due to zero marginal production costs, the competition increases, the market becomes unstable, and experience various phases of evolution leading to market monopolization.
Space colonization
allagonne | Published Wednesday, January 05, 2022Agent-Based-Modeling - space colonization
ask me for the .nlogo model
WHAT IS IT?
The goal of this project is to simulate with NetLogo (v6.2) a space colonization of humans, starting from Earth, into the Milky Way.
HOW IT WORKS
…
Peer reviewed The Indus Village's Weather model: procedural generation of daily weather
Andreas Angourakis | Published Tuesday, May 13, 2025Overview
The Weather model is a procedural generation model designed to create realistic daily weather data for socioecological simulations. It generates synthetic weather time series for solar radiation, temperature, and precipitation using algorithms based on sinusoidal and double logistic functions. The model incorporates stochastic variation to mimic unpredictable weather patterns and aims to provide realistic yet flexible weather inputs for exploring diverse climate scenarios.
The Weather model can be used independently or integrated into larger models, providing realistic weather patterns without extensive coding or data collection. It can be customized to meet specific requirements, enabling users to gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and have greater confidence in their applications.
…
The effect of error on cultural transmission
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Thursday, November 01, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the replication of the experiment performed by Eerkens and Lipo (2005) to look at the effect of copying errors when specific traits are transferred from an individual to another.
Modeling financial networks based on interpersonal trust
Michael Roos Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, November 28, 2013We build a stylized model of a network of business angel investors and start-up entrepreneurs. Decisions are based on trust as a decision making tool under true uncertainty.
Displaying 10 of 788 results for "Blanca Gonzalez-Mon" clear search