About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1190 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search
Peer reviewed Applying Brantingham’s Neutral Model of Stone Raw Material Procurement to the Pinnacle Point Middle Stone Age Record, Western Cape, South Africa
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Sunday, March 10, 2019This model is an application of Brantingham’s neutral model to a real landscape with real locations of potential sources. The sources are represented as their sizes during current conditions, and from marine geophysics surveys, and the agent starts at a random location in Mossel Bay Region (MBR) surrounding the Archaeological Pinnacle Point (PP) locality, Western Cape, South Africa. The agent moves at random on the landscape, picks up and discards raw materials based only upon space in toolkit and probability of discard. If the agent happens to encounter the PP locality while moving at random the agent may discard raw materials at it based on the discard probability.
The Opportunistic Acquisition Model of Stone Tool Raw Material Procurement
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Friday, April 21, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, March 10, 2019The Opportunistic Acquisition Model (OAM) posits that the archaeological lithic raw material frequencies are due to opportunistic encounters with sources while randomly walking in an environment.
While the world’s total urban population continues to grow, not all cities are witnessing such growth, some are actually shrinking. This shrinkage causes several problems to emerge including population loss, economic depression, vacant properties and the contraction of housing markets. Such problems challenge efforts to make cities sustainable. While there is a growing body of work on study shrinking cities, few explore such a phenomenon from the bottom up using dynamic computational models. To overcome this issue this paper presents an spatially explicit agent-based model stylized on the Detroit Tri-county area, an area witnessing shrinkage. Specifically, the model demonstrates how through the buying and selling of houses can lead to urban shrinkage from the bottom up. The model results indicate that along with the lower level housing transactions being captured, the aggregated level market conditions relating to urban shrinkage are also captured (i.e., the contraction of housing markets). As such, the paper demonstrates the potential of simulation to explore urban shrinkage and potentially offers a means to test polices to achieve urban sustainability.
CA-MRSA Demonstration Model
Jonathan Ozik Charles Macal Kenneth Letendre Irene Lee | Published Tuesday, January 06, 2015We demonstrate how a simple model of community associated Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) can be easily constructed by leveraging the statecharts and ReLogo capabilities in Repast Simphony.
Interplay between stakeholders of the management of a river
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Pascal Roggero Bertrand Baldet | Published Wednesday, November 12, 2014This model describes and analyses the outcomes of the confrontation of interests, some conflicting, some common, about the management of a small river in SW France
Peer reviewed Ache hunting
Kim Hill Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, August 13, 2013 | Last modified Friday, December 21, 2018Agent-based model of hunting behavior of Ache hunter-gatherers from Paraguay. We evaluate the effect of group size and cooperative hunting
Peninsula_Iberica 1.0
Carolina Cucart-Mora Sergi Lozano Javier Fernández-López De Pablo | Published Friday, November 04, 2016 | Last modified Monday, November 27, 2017This model was build to explore the bio-cultural interaction between AMH and Neanderthals during the Middle to Upper Paleolithic Transition in the Iberian Peninsula
Peer reviewed Urban Transport Mode Choices
Kathleen Salazar -Serna Lorena Cadavid Carlos Franco | Published Thursday, May 22, 2025The model represents urban commuters’ transport mode choices among cars, public transit, and motorcycles—a mode highly prevalent in developing countries. Using an agent-based modeling approach, it simulates transport dynamics and serves as a testbed for evaluating policies aimed at improving mobility.
The model simulates an ecosystem of human agents who decide, at each time step, which mode of transportation to use for commuting to work. Their decision is based on a combination of personal satisfaction with their most recent journey—evaluated across a vector of individual needs—the information they crowdsource from their social network, and their personal uncertainty regarding trying new transport options.
Agents are assigned demographic attributes such as sex, age, and income level, and are distributed across city neighborhoods according to their socioeconomic status. To represent social influence in decision-making, agents are connected via a scale-free social network topology, where connections are more likely among agents within the same socioeconomic group, reflecting the tendency of individuals to form social ties with similar others.
…
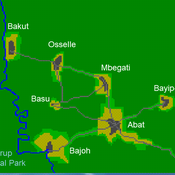
A stylized scale model to codesign with villagers an agent-based model of bushmeat hunting in the periphery of Korup National Park (Cameroon)
ABODE - Agent Based Model of Origin Destination Estimation
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The agent based model matches origins and destinations using employment search methods at the individual level.
Displaying 10 of 1190 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search