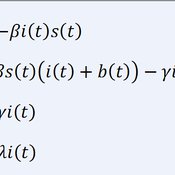About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 101 results r clear search
Peer reviewed Modelling the Social Complexity of Reputation and Status Dynamics
André Grow Andreas Flache | Published Wednesday, February 01, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, January 23, 2019The purpose of this model is to illustrate the use of agent-based computational modelling in the study of the emergence of reputation and status beliefs in a population.
LimnoSES - social-ecological lake management undergoing regime shifts
Romina Martin | Published Thursday, November 24, 2016 | Last modified Friday, January 18, 2019LimnoSES is a coupled system dynamics, agent-based model to simulate social-ecological feedbacks in shallow lake use and management.
Irrigation Equity and Efficiency
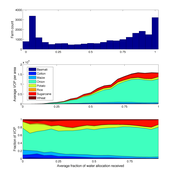
Andrew Bell | Published Tuesday, August 30, 2016The purpose of this model is to examine equity and efficiency in crop production across a system of irrigated farms, as a function of maintenance costs, assessed water fees, and the capacity of farmers to trade water rights among themselves.
Opinions on contested energy infrastructures
Annalisa Stefanelli | Published Thursday, June 23, 2016This ABM simulates opinions on a topic (originally contested infrastructures) through the interactions between paired agents and based on the sociopsychological assumptions of social judgment theory (SJT; Sherif & Hovland, 1961).
THE STATUS ARENA
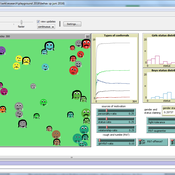
Gert Jan Hofstede Jillian Student Mark R Kramer | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 09, 2018Status-power dynamics on a playground, resulting in a status landscape with a gender status gap. Causal: individual (beauty, kindness, power), binary (rough-and-tumble; has-been-nice) or prior popularity (status). Cultural: acceptability of fighting.
Product Diffusion Model in an Advance Selling Strategy
Peng Shao | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 15, 2016the model can be used to describe the product diffusion in an Advance Selling Strategy. this model takes into account the consumers product adoption, and describe consumer’s online behavior based on four states.
The relationship between product information quantity and diversity of consumer decisions
Marco Janssen Takao Sasaki David Vaughn Becker Rebecca Neel | Published Tuesday, October 27, 2015We developed an agent-based model to explore underlying mechanisms of behavioral clustering that we observed in human online shopping experiments.
The emergence of tag-mediated altruism in structured societies
Shade Shutters David Hales | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, March 02, 2023This abstract model explores the emergence of altruistic behavior in networked societies. The model allows users to experiment with a number of population-level parameters to better understand what conditions contribute to the emergence of altruism.
DITCH --- A Model of Inter-Ethnic Partnership Formation
Ruth Meyer Laurence Lessard-Phillips Huw Vasey | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, February 02, 2016The DITCH model has been developed to investigate partner selection processes, focusing on individual preferences, opportunities for contact, and group size to uncover how these may lead to differential rates of inter-ethnic marriage.
This is the R code of the mathematical model that includes the decision making formulations for artificial agents. Plus, the code for graphical output is also added to the original code.
Displaying 10 of 101 results r clear search