About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1260 results
An agent-based model to simulate field-specific nitrogen fertilizer applications in grasslands
Maria Haensel Thomas Schmitt Andrea Kaim Sylvia Helena Annuth Thomas Koellner | Published Sunday, February 09, 2025Grasslands have a large share of the world’s land cover and their sustainable management is important for the protection and provisioning of grassland ecosystem services. The question of how to manage grassland sustainably is becoming increasingly important, especially in view of climate change, which on the one hand extends the vegetation period (and thus potentially allows use intensification) and on the other hand causes yield losses due to droughts. Fertilization plays an important role in grassland management and decisions are usually made at farm level. Data on fertilizer application rates are crucial for an accurate assessment of the effects of grassland management on ecosystem services. However, these are generally not available on farm/field scale. To close this gap, we present an agent-based model for Fertilization In Grasslands (FertIG). Based on animal, land-use, and cutting data, the model estimates grassland yields and calculates field-specific amounts of applied organic and mineral nitrogen on grassland (and partly cropland). Furthermore, the model considers different legal requirements (including fertilization ordinances) and nutrient trade among farms. FertIG was applied to a grassland-dominated region in Bavaria, Germany comparing the effects of changes in the fertilization ordinance as well as nutrient trade. The results show that the consideration of nutrient trade improves organic fertilizer distribution and leads to slightly lower Nmin applications. On a regional scale, recent legal changes (fertilization ordinance) had limited impacts. Limiting the maximum applicable amount of Norg to 170 kg N/ha fertilized area instead of farm area as of 2020 hardly changed fertilizer application rates. No longer considering application losses in the calculation of fertilizer requirements had the strongest effects, leading to lower supplementary Nmin applications. The model can be applied to other regions in Germany and, with respective adjustments, in Europe. Generally, it allows comparing the effects of policy changes on fertilization management at regional, farm and field scale.
An Agent-Based Model of Indirect Minority Influence on Social Change
Jiin Jung | Published Wednesday, February 05, 2025This model demonstrates how different psychological mechanisms and network structures generate various patterns of cultural dynamics including cultural diversity, polarization, and majority dominance, as explored by Jung, Bramson, Crano, Page, and Miller (2021). It focuses particularly on the psychological mechanisms of indirect minority influence, a concept introduced by Serge Moscovici (1976, 1980)’s genetic model of social influence, and validates how such influence can lead to social change.
Autonomy or control? An agent-based study of self-organising versus centralised task allocation
Shaoni Wang | Published Wednesday, January 29, 2025The aim of our model is to investigate the team dynamics through two types of task allocation strategies, with a focus on the dynamic interplay between individual needs and group performance. To achieve this goal, we have formulated an agent-based model (ABM) to formalize Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) and explore the social dynamics that govern the relationship between individual and group levels of team performance.
Timing and certainty in evidence-based decision-making
Sacha Ferrari | Published Saturday, January 25, 2025Model implemented in Lammers, W., Pattyn, V., Ferrari, S. et al. Evidence for policy-makers: A matter of timing and certainty?. Policy Sci 57, 171–191 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11077-024-09526-9
The impact of scientific networks, affinity bias and scientific uncertainty on the public uptake of science
Sacha Ferrari | Published Thursday, January 23, 2025Ferrari, S., Lammers, W., Wenmackers, S. (forthcoming) How the structure of scientific communities could impact the public uptake of uncertain science. Philosophy of Science.
ABM Code: Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries
Diego Leal | Published Thursday, January 23, 2025The code and data in this repository are associated with the article titled: “Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries.” The NetLogo code (version 6.4.0) is designed to be a standalone piece of code although it uses the ‘nw’ and ‘matrix’ extensions that come integrated with NetLogo 6.4.0. The code was ran on a Windows 10 x 64 machine.
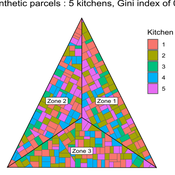
MeReDiem : Fallow Land Simulations to examine the conditions of sustainable village livelihood
Etienne DELAY Paul Chapron Mathieu | Published Monday, January 20, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2025The MeReDiem model aims to simulate the effect of socio-agricultural practices of farmers and pastors on the food sustainability and soil fertility of a serrer village, in Senegal. The model is a central part of a companion modeling and exploration approach, described in a paper, currently under review)
The village population is composed of families (kitchens). Kitchens cultivate their land parcels to feed their members, aiming for food security at the family level. On a global level , the village tries to preserve the community fallow land as long as possible.
Kitchens sizes vary depending on the kitchens food production, births and migration when food is insufficient.
…
Soy2Grow-ABM-V1
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Monday, January 20, 2025The Soy2Grow ABM aims to simulate the adoption of soybean production in Flanders, Belgium. The model primarily considers two types of agents as farmers: 1) arable and 2) dairy farmers. Each farmer, based on its type, assesses the feasibility of adopting soybean cultivation. The feasibility assessment depends on many interrelated factors, including price, production costs, yield, disease, drought (i.e., environmental stress), social pressure, group formations, learning and skills, risk-taking, subsidies, target profit margins, tolerance to bad experiences, etc. Moreover, after adopting soybean production, agents will reassess their performance. If their performance is unsatisfactory, an agent may opt out of soy production. Therefore, one of the main outcomes to look for in the model is the number of adopters over time.
The main agents are farmers. Generally, factors influencing farmers’ decision-making are divided into seven main areas: 1) external environmental factors, 2) cooperation and learning (with slight differences depending on whether they are arable or dairy farmers), 3) crop-specific factors, 4) economics, 5) support frameworks, 6) behavioral factors, and 7) the role of mobile toasters (applicable only to dairy farmers).
Moreover, factors not only influence decision-making but also interact with each other. Specifically, external environmental factors (i.e., stress) will result in lower yield and quality (protein content). The reducing effect, identified during participatory workshops, can reach 50 %. Skills can grow and improve yield; however, their growth has a limit and follows different learning curves depending on how individualistic a farmer is. During participatory workshops, it was identified that, contrary to cooperative farmers, individualistic farmers may learn faster and reach their limits more quickly. Furthermore, subsidies directly affect revenues and profit margins; however, their impact may disappear when they are removed. In the case of dairy farmers, mobile toasters play an important role, adding toasting and processing costs to those producing soy for their animal feed consumption.
Last but not least, behavioral factors directly influence the final adoption decision. For example, high risk-taking farmers may adopt faster, whereas more conservative farmers may wait for their neighbors to adopt first. Farmers may evaluate their success based on their own targets and may also consider other crops rather than soy.
The doctrinal paradox in deliberative process and in majority voting
Sacha Ferrari | Published Monday, January 13, 2025This model proposes a new approach analyzing to the doctrinal paradox by considering a deliberative process (which can be represented by an agent-based model) in comparison with classical (binary) majority voting and an aggregation of (continuous) degrees of belief prior to majority voting. This model is a multivariate extension of the Hegselmann–Krause opinion dynamics model.
On the liquidity of the illiquid (hard-to-trade) assets
Marcin Czupryna | Published Monday, January 13, 2025This paper investigates the impact of agents' trading decisions on market liquidity and transactional efficiency in markets for illiquid (hard-to-trade) assets. Drawing on a unique order book dataset from the fine wine exchange Liv-ex, we offer novel insights into liquidity dynamics in illiquid markets. Using an agent-based framework, we assess the adequacy of conventional liquidity measures in capturing market liquidity and transactional efficiency. Our main findings reveal that conventional liquidity measures, such as the number of bids, asks, new bids and new asks, may not accurately represent overall transactional efficiency. Instead, volume (measured by the number of trades) and relative spread measures may be more appropriate indicators of liquidity within the context of illiquid markets. Furthermore, our simulations demonstrate that a greater number of traders participating in the market correlates with an increased efficiency in trade execution, while wider trader-set margins may decrease the transactional efficiency. Interestingly, the trading period of the agents appears to have a significant impact on trade execution. This suggests that granting market participants additional time for trading (for example, through the support of automated trading systems) can enhance transactional efficiency within illiquid markets. These insights offer practical implications for market participants and policymakers aiming to optimise market functioning and liquidity.
Displaying 10 of 1260 results