About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1256 results
Peer reviewed Least cost path mobility
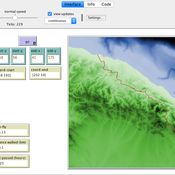
Colin Wren Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Saturday, September 02, 2017 | Last modified Monday, October 04, 2021This model aims to mimic human movement on a realistic topographical surface. The agent does not have a perfect knowledge of the whole surface, but rather evaluates the best path locally, at each step, thus mimicking imperfect human behavior.
Policy Formulation for Public Administration - Innovation
Bashar Ourabi | Published Tuesday, August 29, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, August 29, 2017Innovation a byproduct of the intellectual capital, requires a new paradigm for the production constituents. Human Capital HC,Structural capital SC and relational capital RC become key for intellectual capital and consequently for innovation.
InnovationGame
Madeline Tyson | Published Thursday, August 24, 2017This model includes an innovation search environment. Agents search and can share their findings. It’s implemented in Netlogo-Hubnet & a parallel Netlogo model. This allows for validation of search strategies against experimental findings.
Towards an Agent-Based Model for Civil Revolution: Modeling Emergence of Protesters, Military Decisions, and Resulting State of
Salwa Ismail | Published Friday, August 18, 2017This paper builds on a basic ABM for a revolution and adds a combination of behaviors to its agents such as military benefits, citizen’s grievances, geographic vision, empathy, personality type and media impact.
Extended Flache and Mas (2008)
Hadi Aliahmadi | Published Wednesday, August 16, 2017 | Last modified Monday, February 26, 2018We extend the Flache-Mäs model to incorporate the location and dyadic communication regime of the agents in the opinion formation process. We make spatially proximate agents more likely to interact with each other in a pairwise communication regime.
Team Problem Solving and Motivation under Disorganization
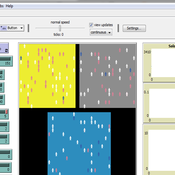
Dinuka Herath | Published Sunday, August 13, 2017The model combines the two elements of disorganization and motivation to explore their impact on teams. Effects of disorganization on team task performance (problem solving)
Simulation of the Effects of Disorganization on Goals and Problem Solving
Dinuka Herath | Published Sunday, August 13, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, August 13, 2017This is a model of the occurrence of disorganization and its impact on individual goal setting and problem-solving. This model therefore, explores the effects of disorganization on goal achievement.
The Li-BIM model aims at simulating the behavior of occupants in a building. It is structured around the numerical modeling of the building (IFC format) and a BDI cognitive architecture. The model has been implemented under the GAMA platform.
OMOLAND-CA: An Agent-Based Modeling of Rural Households’ Adaptation to Climate Change
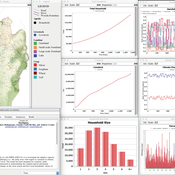
Atesmachew Hailegiorgis Andrew Crooks Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, July 25, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, July 10, 2018The purpose of the OMOLAND-CA is to investigate the adaptive capacity of rural households in the South Omo zone of Ethiopia with respect to variation in climate, socioeconomic factors, and land-use at the local level.
Harvesting daisies in Daisyworld
Marco Janssen | Published Saturday, July 22, 2017Comparing impact of alternative behavioral theories in a simple social-ecological system.
Displaying 10 of 1256 results