About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 7 of 57 results income clear search
Income Model
Tony Lawson | Published Monday, August 26, 2013This is the code for the model described in an article in the International Journal of Microsimulation. Lawson (2013) ‘Modelling Household Spending Using a Random Assignment Scheme’, International Journal of Microsimulation, 6(2) Autumn 2013, 56-75.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
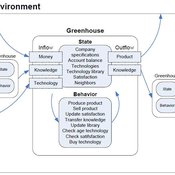
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
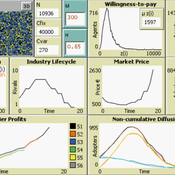
9 Maturity levels in Empirical Validation - An innovation diffusion example
Martin Rixin | Published Wednesday, October 19, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Several taxonomies for empirical validation have been published. Our model integrates different methods to calibrate an innovation diffusion model, ranging from simple randomized input validation to complex calibration with the use of microdata.
Income and Expenditure
Tony Lawson | Published Thursday, October 06, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013How do households alter their spending patterns when they experience changes in income? This model answers this question using a random assignment scheme where spending patterns are copied from a household in the new income bracket.
CITMOD A Tax-Benefit Modeling System for the average citizen
Philip Truscott | Published Monday, August 15, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Must tax-benefit policy making be limited to the ‘experts’?
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
Displaying 7 of 57 results income clear search