About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 113 results for "Sharona T Levy" clear search
Location Analysis Hybrid ABM
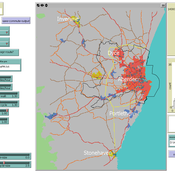
Lukasz Kowalski | Published Friday, February 08, 2019The purpose of this hybrid ABM is to answer the question: where is the best place for a new swimming pool in a region of Krakow (in Poland)?
The model is well described in ODD protocol, that can be found in the end of my article published in JASSS journal (available online: http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/22/1/1.html ). Comparison of this kind of models with spatial interaction ones, is presented in the article. Before developing the model for different purposes, area of interest or services, I recommend reading ODD protocol and the article.
I published two films on YouTube that present the model: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iFWG2Xv20Ss , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tDTtcscyTdI&t=1s
…
Transport simulation in a real road network
Gary Polhill Jiaqi Ge | Published Tuesday, April 17, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, April 17, 2018Ge, J., & Polhill, G. (2016). Exploring the Combined Impact of Factors Influencing Commuting Patterns and CO2 Emission in Aberdeen Using an Agent-Based Model. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 19(3). http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/19/3/11.html
We develop an agent-based transport model using a realistic GIS-enabled road network and the car following method. The model can be used to study the impact of social interventions such as flexi-time and workplace sharing, as well as large infrastructure such as the construction of a bypass or highway. The model is developed in Netlogo version 5 and requires road network data in GIS format to run.
Agent-Based Model for the Evolution of Ethnocentrism
Max Hartshorn | Published Saturday, March 24, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is an implementation of an agent based model for the evolution of ethnocentrism. While based off a model published by Hammond and Axelrod (2006), the code has been modified to allow for a more fine-grained analysis of evolutionary dynamics.
Peer reviewed A dynamic identity model for misinformation in social networks
emdhar | Published Friday, February 27, 2026A dynamic identity model for misinformation in social networks, an agent-based model of social identity and misinformation dynamics.
I developed this model as a part of my master’s thesis, “Does social identity drive belief and persistence in online misinformation? An agent-based modelling approach” at University College Dublin, Ireland (2024-2025).
The purpose of this model is to further understand the dynamics of misinformation sharing as an expression of social identity. I introduce a framework to understand the influence of self-categorisation on misinformation persistence in social network. It integrates a social learning model with the Dynamic Identity Model for Agents (DIMA) using simple logic to simulate the social trade-offs driving misinformation and observe the effects on misinformation spread.
Peer reviewed The dynamical relationship between individual needs and group performance: A simulation of the self-organising task allocation process
Shaoni Wang | Published Tuesday, October 05, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the dynamical relationship between individual needs and group performance when focusing on self-organizing task allocation. For this, we develop a model that formalizes Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) theory into an ABM creating a framework to study the social dynamics that pertain to the mutual relations between the individual and group level of team performance. Specifically, it aims to answer how the three individual motivations of autonomy, competence, and belonging affect team performance.
Peer reviewed A Computational Simulation for Task Allocation Influencing Performance in the Team System
Shaoni Wang | Published Friday, November 11, 2022 | Last modified Thursday, April 06, 2023This model system aims to simulate the whole process of task allocation, task execution and evaluation in the team system through a feasible method. On the basis of Complex Adaptive Systems (CAS) theory and Agent-based Modelling (ABM) technologies and tools, this simulation system attempts to abstract real-world teams into MAS models. The author designs various task allocation strategies according to different perspectives, and the interaction among members is concerned during the task-performing process. Additionally, knowledge can be acquired by such an interaction process if members encounter tasks they cannot handle directly. An artificial computational team is constructed through ABM in this simulation system, to replace real teams and carry out computational experiments. In all, this model system has great potential for studying team dynamics, and model explorers are encouraged to expand on this to develop richer models for research.
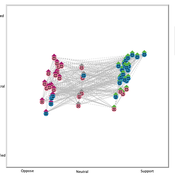
Gaming Polarisation: Using Agent-Based Simulations as A Dialogue Tool
Shaoni Wang | Published Friday, May 09, 2025This model aims to replicate the evolution of opinions and behaviours on a communal plan over time. It also aims to foster community dialogue on simulation outcomes, promoting inclusivity and engagement. Individuals (referred to as agents), grouped based on Sinus Milieus (Groh-Samberg et al., 2023), face a binary choice: support or oppose the plan. Motivated by experiential, social, and value needs (Antosz et al., 2019), their decision is influenced by how well the plan aligns with these fundamental needs.
Autonomy or control? An agent-based study of self-organising versus centralised task allocation
Shaoni Wang | Published Wednesday, January 29, 2025The aim of our model is to investigate the team dynamics through two types of task allocation strategies, with a focus on the dynamic interplay between individual needs and group performance. To achieve this goal, we have formulated an agent-based model (ABM) to formalize Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) and explore the social dynamics that govern the relationship between individual and group levels of team performance.
Industrial Cooperation and the Hydrogen Transition
Amineh Ghorbani Renske van 't Veer Emre Ates Zofia Lukszo | Published Tuesday, September 23, 2025An Agent Based Model that explores the deployment of hydrogen among a regional industrial cluster in the Netherlands, consisting of 15 companies. The companies seek to decarbonize by replacing their natural gas by hydrogen.
The model integrates technical characteristics as well as company motivations to transition to hydrogen. The baseline model only considers individual investments where company can locally produce hydrogen. If they reach the backbone threshold, companies can also consider buying hydrogen through a connection to the national hydrogen network. The second scenario considers that companies can participate in a joint investment to get an electrolyzer to locally produce the hydrogen.
Two experiments look at the impact of the sectoral configuration and at the impact of subsidy conditions on the region’s hydrogen transition
MERCURY extension: population
Tom Brughmans | Published Thursday, May 23, 2019This model is an extended version of the original MERCURY model (https://www.comses.net/codebases/4347/releases/1.1.0/ ) . It allows for experiments to be performed in which empirically informed population sizes of sites are included, that allow for the scaling of the number of tableware traders with the population of settlements, and for hypothesised production centres of four tablewares to be used in experiments.
Experiments performed with this population extension and substantive interpretations derived from them are published in:
Hanson, J.W. & T. Brughmans. In press. Settlement scale and economic networks in the Roman Empire, in T. Brughmans & A.I. Wilson (ed.) Simulating Roman Economies. Theories, Methods and Computational Models. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
…
Displaying 10 of 113 results for "Sharona T Levy" clear search