About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search
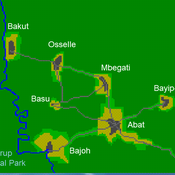
A stylized scale model to codesign with villagers an agent-based model of bushmeat hunting in the periphery of Korup National Park (Cameroon)
A Complex Model of Voter Turnout
Bruce Edmonds Laurence Lessard-Phillips Ed Fieldhouse | Published Monday, October 13, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, August 18, 2015This is a complex “Data Integration Model”, following a “KIDS” rather than a “KISS” methodology - guided by the available evidence. It looks at the complex mix of social processes that may determine why people vote or not.
Simulation model for compliance behaviour
Esther Van Asselt Sjoukje A Osinga | Published Friday, October 03, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, December 08, 2015This model can be used to optimize intervention strategies for inspection services.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
IDEAL
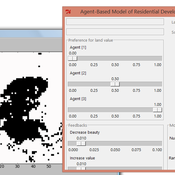
Arika Ligmann-Zielinska | Published Thursday, August 07, 2014IDEAL: Agent-Based Model of Residential Land Use Change where the choice of new residential development in based on the Ideal-point decision rule.
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
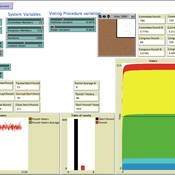
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Agent-based Simulation Models of the College Sorting Process
Rachel Baker Sean F Reardon Matt Kasman Daniel Klasik | Published Friday, May 23, 2014We explore how dynamic processes related to socioeconomic inequality operate to sort students into, and create stratification among, colleges.
Peer reviewed An Agent-Based Model of Status Construction in Task Focused Groups
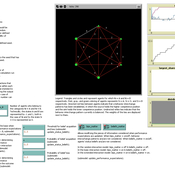
Andreas Flache Rafael Wittek André Grow | Published Sunday, May 18, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, June 16, 2015The model simulates interactions in small, task focused groups that might lead to the emergence of status beliefs among group members.
Quality uncertainty and market failure
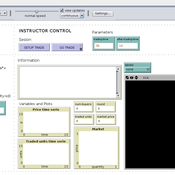
David Poza José Manuel Galán María Pereda José Santos | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018Quality uncertainty and market failure: an interactive model to conduct classroom experiments
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search