About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search
REHAB: A Role Playing Game to Explore the Influence of Knowledge and Communication on Natural Resources Management
Christophe Le Page Anne Dray Pascal Perez Claude Garcia | Published Monday, July 13, 2015 | Last modified Monday, July 13, 2015REHAB has been designed as an ice-breaker in courses dealing with ecosystem management and participatory modelling. It helps introducing the two main tools used by the Companion Modelling approach, namely role-playing games and agent-based models.
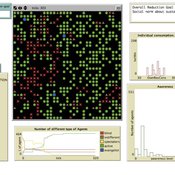
Peer reviewed A model of environmental awareness spread and its effect in resource consumption reduction
Giovanna Sissa | Published Sunday, June 21, 2015 | Last modified Monday, August 17, 2015The model reproduces the spread of environmental awareness among agents and the impact of awareness level of the agents on the consumption of a resource, like energy. An agent is a household with a set of available advanced smart metering functions.
Seasonal Social Networks and Learning Opportunities Under Unbiased Cultural Transmission
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Monday, May 18, 2015This agent-based model examines the impact of seasonal aggregation, dispersion, and learning opportunities on the richness and evenness of artifact styles under random social learning (unbiased transmission).
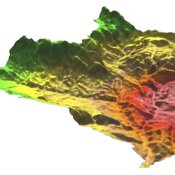
MedLanD Modeling Laboratory
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Isaac Ullah Gary Mayer Hessam Sarjoughian Helena Mitasova | Published Friday, May 08, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, December 14, 2017The MML is a hybrid modeling environment that couples an agent-based model of small-holder agropastoral households and a cellular landscape evolution model that simulates changes in erosion/deposition, soils, and vegetation.
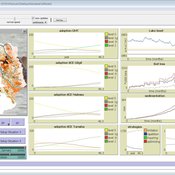
CONSERVAT
Pieter Van Oel | Published Monday, April 13, 2015The CONSERVAT model evaluates the effect of social influence among farmers in the Lake Naivasha basin (Kenya) on the spatiotemporal diffusion pattern of soil conservation effort levels and the resulting reduction in lake sedimentation.
A Multi-level Multi-model of Collective Motion
Benjamin Camus Christine Bourjot Vincent Chevrier | Published Wednesday, March 25, 2015This multi-model (i.e. a model composed of interacting submodels) is a multi-level representation of a collective motion phenomenon. It was designed to study the impact of the mutual influences between individuals and groups in collective motion.
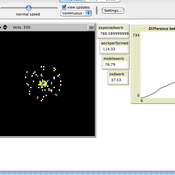
The Agent-Based Model of the Closed Market( similar to Stock Market) with One Commodity and with careful and risky mechanisms
Mark Voronovitsky | Published Sunday, March 15, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, March 22, 2015The model of market of one commodity , in which there are in each moment of time the same quantity and the same quantity of money was formulated and researched in this text. We also study this system as a game of automata.
Peer reviewed Lithic Raw Material Procurement and Provisioning
Jonathan Paige | Published Friday, March 06, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015This model simulates the lithic raw material use and provisioning behavior of a group that inhabits a permanent base camp, and uses stone tools.
Netlogo Profiler code example
Colin Wren | Published Wednesday, March 04, 2015This is a very simple foraging model used to illustrate the features of Netlogo’s Profiler extension.
A Model of Iterated Ultimatum game
Andrea Scalco | Published Tuesday, February 24, 2015 | Last modified Monday, March 09, 2015The simulation generates two kinds of agents, whose proposals are generated accordingly to their selfish or selfless behaviour. Then, agents compete in order to increase their portfolio playing the ultimatum game with a random-stranger matching.
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search