About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 201 results for "Francisco J V%C3%A1zquez" clear search
COMM-PDND: Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks
Lars Reinelt | Published Friday, September 08, 2023The Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks (COMM-PDND) is an agent-based model specifically created to examine the dynamics of perceived descriptive norms in the context of digital network structures. The model, developed as part of a master’s thesis titled “The Dynamics of Perceived Descriptive Norms in Digital Network Publics: An Agent-Based Simulation,” emphasizes the critical role of communication processes in norm formation. It focuses on the role of communicative interactions in shaping perceived descriptive norms.
The COMM-PDND is tuned to explore the effects of normative deviance in digital social networks. It provides functionalities for manipulating agents according to their network position, and has a versatile set of customizable parameters, making it adaptable to a wide range of research contexts.
Multi-level model of attitudinal dynamics
Ingo Wolf | Published Wednesday, April 06, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, May 04, 2016A model of attitudinal dynamics based on the cognitive mechanism of emotional coherence. The code is written in Java. For initialization an additional dataset is required.
Peer reviewed Emergence of Organizations out of Garbage Can Dynamics
Guido Fioretti | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 26, 2020The Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice (GCM) is a fundamental model of organizational decision-making originally propossed by J.D. Cohen, J.G. March and J.P. Olsen in 1972. In their model, decisions are made out of random meetings of decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems within an organization.
With this model, these very same agents are supposed to meet in society at large where they make decisions according to GCM rules. Furthermore, under certain additional conditions decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems form stable organizations. In this artificial ecology organizations are born, grow and eventually vanish with time.
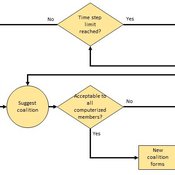
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
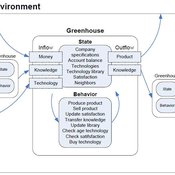
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
AMIRIS
Ulrich Frey Felix Nitsch Christoph Schimeczek Johannes Kochems Kristina Nienhaus Evelyn Sperber Aboubakr Achraf El Ghazi Seyedfarzad Sarfarazi | Published Thursday, February 03, 2022AMIRIS is the Agent-based Market model for the Investigation of Renewable and Integrated energy Systems.
It is an agent-based simulation of electricity markets and their actors.
AMIRIS enables researches to analyse and evaluate energy policy instruments and their impact on the actors involved in the simulation context.
Different prototypical agents on the electricity market interact with each other, each employing complex decision strategies.
AMIRIS allows to calculate the impact of policy instruments on economic performance of power plant operators and marketers.
…
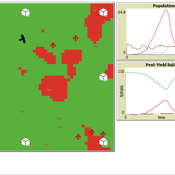
Peer reviewed Avian pest control: Yield outcome due to insectivorous birds, falconry, and integration of nest boxes.
David Jung | Published Monday, November 13, 2023 | Last modified Sunday, November 19, 2023The model aims to simulate predator-prey relationships in an agricultural setting. The focus lies on avian communities and their effect on different pest organisms (here: pest birds, rodents, and arthropod pests). Since most case studies focused on the impact on arthropod pests (AP) alone, this model attempts to include effects on yield outcome. By incorporating three treatments with different factor levels (insectivorous bird species, falconry, nest box density) an experimental setup is given that allows for further statistical analysis to identify an optimal combination of the treatments.
In light of a global decline of birds, insects, and many other groups of organisms, alternative practices of pest management are heavily needed to reduce the input of pesticides. Avian pest control therefore poses an opportunity to bridge the disconnect between humans and nature by realizing ecosystem services and emphasizing sustainable social ecological systems.
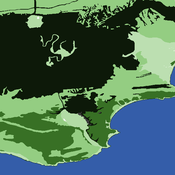
An agent-based approach to weighted decision making in the spatially and temporally variable South African Paleoscape
Colin Wren | Published Thursday, December 29, 2016This model simulates a foraging system based on Middle Stone Age plant and shellfish foraging in South Africa.
Rangeland and evolution of management styles
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020Provided is a landscape of properties where pastoralists make decisions how much livestock they put on their property and how much to suppress fire from occuring. Rangelands can be grass dominated, or unproductive shrubb dominated. Overgrazing and fire suppresion lead to shrub dominated landscapes. What management strategies evolve, and how is this impacted by policies?
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/.
This model extends the original Artifical Anasazi (AA) model to include individual agents, who vary in age and sex, and are aggregated into households. This allows more realistic simulations of population dynamics within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350 than are possible in the original model. The parts of this model that are directly derived from the AA model are based on Janssen’s 1999 Netlogo implementation of the model; the code for all extensions and adaptations in the model described here (the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model) have been written by the authors. The AA model included only ideal and homogeneous “individuals” who do not participate in the population processes (e.g., birth and death)–these processes were assumed to act on entire households only. The ALHV model incorporates actual individual agents and all demographic processes affect these individuals. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. Thus, the ALHV model is a combination of individual processes (birth and death) and household-level processes (e.g., finding suitable agriculture plots).
As is the case for the AA model, the ALHV model makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original model (from Janssen’s Netlogo implementation) to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the valley. These estimates are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
Displaying 10 of 201 results for "Francisco J V%C3%A1zquez" clear search