About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search
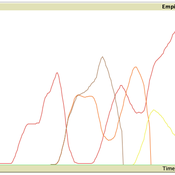
Replica of Turchin's (2003) Metaethnic Frontier model
Paul Smaldino | Published Sunday, February 15, 2026In his 2003 book, Historical Dynamics (ch. 4), Turchin describes and briefly analyzes a spatial ABM of his metaethnic frontier theory, which is essentially a formalization of a theory by Ibn Khaldun in the 14th century. In the model, polities compete with neighboring polities and can absorb them into an empire. Groups possess “asabiya”, a measure of social solidarity and a sense of shared purpose. Regions that share borders with other groups will have increased asabiya do to salient us vs. them competition. High asabiya enhances the ability to grow, work together, and hence wage war on neighboring groups and assimilate them into an empire. The larger the frontier, the higher the empire’s asabiya.
As an empire expands, (1) increased access to resources drives further growth; (2) internal conflict decreases asabiya among those who live far from the frontier; and (3) expanded size of the frontier decreases ability to wage war along all frontiers. When an empire’s asabiya decreases too much, it collapses. Another group with more compelling asabiya eventually helps establish a new empire.
Forest Logging and Ecosystem Degradation
Carla Guerrero | Published Sunday, February 15, 2026This model simulates a forest ecosystem affected by human logging. We explore different kind of approaches and their possible consequences for the ecosystem. Loggers can either be responsible or irresponsible, they will either take care to cut trees or not. In turn their actions will have consequences on the quality of the soil, the atmosphere as well as their profit made from logging. In this model we see that even careful management cannot prevent the degradation of the forest ecosystem.
Peer reviewed The Andean Resource Management Model (ARMM)
Olga Palacios | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2026ARMM is a theoretical agent-based model that formalizes Murra’s Theory of Verticality (Murra, 1972) to explore how multi-zonal resource management systems emerge in mountain landscapes. The model identifies the social, political, and economic mechanisms that enable vertical complementarity across ecological gradients.
Built in NetLogo, ARMM employs an abstract 111×111 grid divided into four Andean ecological zones (Altiplano, Highland, Lowland, Coast), each containing up to 18 resource types distributed according to ecological suitability. To test general theoretical principles rather than replicate specific geography, resource locations are randomized at each model initialization.
Settlement agents pursue one of two economic strategies: diversification (seeking resource variety, maximum 2 units per type) or accumulation (maximising total quantity, maximum 30 units). Agents move between adjacent zones through hierarchical decision-making, first attempting peaceful interactions—coexistence (governed by tolerance) and trading (governed by cooperation)—before resorting to conflict (theft or takeover, governed by belligerence).
The model demonstrates that vertical complementarity can emerge through fundamentally different mechanisms: either through autonomous mobility under political decentralization or through state-coordinated redistribution under centralization. Sensitivity analysis reveals that belligerence and economic strategy explain approximately 25% of outcome variance, confirming that structural inequalities between zones result from political-economic organization rather than environmental constraints alone.
As a preliminary theoretical model, ARMM intentionally maintains simplicity to isolate core mechanisms and generate testable hypotheses. This foundational framework will guide future empirically-calibrated versions that incorporate specific archaeological settlement data and geographic features from the Carangas region (Bolivia-Chile border), enabling direct comparison between theoretical predictions and observed historical patterns.
Peer reviewed Boyds (NetLogo): Boids That Fight
Oliver M. Haynold | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2026Boyds (Boids that Fight) is an agent-based model in NetLogo that extends the classic Flocking model with multi-faction competition, a local fight–flight heuristic, and a target locking/“taking” mechanism. The model separates perception (vision) from engagement range (lock distance) and uses per-faction steering bounds to explore how local numerical superiority, sensing, and bounded turning affect victory, losses, and emergent formations.
Software for an agent-based game-theoretic model of the contact hypothesis of prejudice reduction, to accompany “Modeling Prejudice Reduction,” in the Handbook of Computational Social Psychology, adapted from Public Affairs Quarterly 19 (2) 2005.
Bargaining with misvaluation
Marcin Czupryna | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2026Subjective biases and errors systematically affect market equilibria, whether at the population level or in bilateral trading. Here, we consider the possibility that an agent engaged in bilateral trading is mistaken about her own valuation of the good she expects to trade, that has not been explicitly incorporated into the existing bilateral trade literature. Although it may sound paradoxical that a subjective private valuation is something an agent can be mistaken about, as it is up to her to fix it, we consider the case in which that agent, seller or buyer, consciously or not, given the structure of a market, a type of good, and a temporary lack of information, may arrive at an erroneous valuation. The typical context through which this possibility may arise is in relation with so-called experience goods, which are sold while all their intrinsic qualities are still unknown (such as untasted bottled fine wines). We model this “private misvaluation” phenomenon in our study. The agents may also be mistaken about how their exchange counterparties are themselves mistaken. Formally, they attribute a certain margin of error to the other agent, which can differ from the actual way that another agent misvalues the good under consideration. This can constitute the source of a second-order misvaluation. We model different attitudes and situations in which agents face unexpected signals from their counterparties and the manner and extent to which they revise their initial beliefs. We analyse and simulate numerically the consequences of first-order and second-order misvaluation on market equilibria.
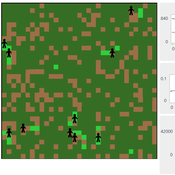
Geospatial Agent-Based Model of Immigrant Settlement Dynamics in Metro Vancouver
Liliana Perez Navid Mahdizadeh Gharakhanlou Maryam Yousefi | Published Wednesday, December 03, 2025This agent-based model simulates how new immigrant households choose where to live in Metro Vancouver under the origins diversity scenario. The model begins with 16,000 household agents, reflecting an expected annual population increase of about 42,500 people based on an average household size of 2.56. Each agent is assigned four characteristics: one of ten origin categories, income level (adjusted using NOC data and recent immigrant earnings), likelihood of having children, and preferred mode of commuting. The ten origin groups are drawn from Census patterns, including six subgroups within the broader Asian category (China, India, the Philippines, Iran, South Korea, and Other Asian countries) and two categories for immigrants from the Americas. This refined classification better captures the diversity of newcomers arriving in the region.
FRAMe (Flood Resilience Agent-Based Model)
Wenhan Feng | Published Wednesday, October 22, 2025The FRAMe (Flood Resilience Agent-Based Model) serves as a framework designed to simulate flood resilience dynamics at the community level, focusing on a rural settlement in the Mekong River Basin. Integrating empirical data from extensive surveys, Bayesian networks, and hydrological simulations, the framework quantifies resilience as a trade-off between robustness (resistance to damage) and adaptability (capacity for dynamic response). Agents include households, governments, and other actors, linked by social and governance networks that facilitate knowledge transfer, resource distribution, and risk communication. FRAMe incorporates mechanisms for flood forecasting, policy interventions (education, aid, insurance), and individual and collective decision-making, grounded in Protection Motivation Theory and MoHuB frameworks. The framework’s spatially explicit design leverages GIS data, which supports scenario testing of governance structures and stakeholder interactions. By examining policy scenarios and agent behavior, FRAMe aims to inform adaptive flood management strategies and enhance community resilience.
Peer reviewed The effect of homophily on co-offending outcomes
Ruslan Klymentiev Christophe Vandeviver Luis E. C. Rocha | Published Friday, September 26, 2025This Agent-Based Model is designed to simulate how similarity-based partner selection (homophily) shapes the formation of co-offending networks and the diffusion of skills within those networks. Its purpose is to isolate and test the effects of offenders’ preference for similar partners on network structure and information flow, under controlled conditions.
In the model, offenders are represented as agents with an individual attribute and a set of skills. At each time step, agents attempt to select partners based on similarity preference. When two agents mutually select each other, they commit a co-offense, forming a tie and exchanging a skill. The model tracks the evolution of network properties (e.g., density, clustering, and tie strength) as well as the spread of skills over time.
This simple and theoretical model does not aim to produce precise empirical predictions but rather to generate insights and test hypotheses about the trade-off between network stability and information diffusion. It provides a flexible framework for exploring how changes in partner selection preferences may lead to differences in criminal network dynamics. Although the model was developed to simulate offenders’ interactions, in principle, it could be applied to other social processes involving social learning and skills exchange.
…
Netlogo model ` Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations’
takuya nagura | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025This model was utilized for the simulation in the paper titled Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations. It allows you to examine whether oil spill polarization occurs through people’s communication under various conditions.
・Choose the network construction conditions you’d like to examine from the “rewire-style” chooser box.
・Select the desired strength of partisanship from the “partisanlevel” chooser box. You can also set the strength manually in the code tab.
・You can set the number of dynamic topics using the “number-of-topics” slider.
・Use the “divers-of-opinion” slider to set the number of preference types for each dynamic topic.
…
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search