About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 86 results landscape clear
Potato late blight model
Francine Pacilly | Published Friday, April 13, 2018The purpose of the model is to simulate the spatial dynamics of potato late blight to analyse whether resistant varieties can be used effectively for sustainable disease control. The model represents an agricultural landscape with potato fields and data of a Dutch agricultural region is used as input for the model. We simulated potato production, disease spread and pathogen evolution during the growing season (April to September) for 36 years. Since late blight development and crop growth is weather dependent, measured weather data is used as model input. A susceptible and late blight resistant potato variety are distinguished. The resistant variety has a potentially lower yield but cannot get infected with the disease. However, during the growing season virulent spores can emerge as a result of mutations during spore production. This new virulent strain is able to infect the resistant fields, resulting in resistance breakdown. The model shows how disease severity, resistance durability and potato yield are affected by the fraction of fields across a landscape with a disease-resistant potato variety.
TRUE GRASP (Tree Recruitment Under Exotic GRAsses in a Savanna-Pineland)
is a socio-ecological agent-based model (ABM) and role playing game (RPG) for farmers and other stakeholders involved in rural landscape planning.
The purpose of this model is to allow actors to explore the individual and combined effects - as well as tradeoffs - of three methods of controlling exotic grasses in pine savannas: fire, weeding, and grazing cattle.
Design of TRUE GRASP is based on 3 years of socio-ecological fieldwork in a human-induced pine savanna in La Sepultura Biosphere Reserve (SBR) in the Mexican state of Chiapas. In this savanna, farmers harvest resin from Pinus oocarpa, which is used to produce turpentine and other products. However, long term persistence of this activity is jeopardized by low tree recruitment due to exotic tall grass cover in the forest understory (see Braasch et al., 2017). The TRUE GRASP model provides the user with different management strategies for controlling exotic grass cover and avoiding possible regime shifts, which in the case of the SBR would jeopardize resin harvesting.
A land-use model to illustrate ambiguity in design
Julia Schindler | Published Monday, October 15, 2012 | Last modified Friday, January 13, 2017This is an agent-based model that allows to test alternative designs for three model components. The model was built using the LUDAS design strategy, while each alternative is in line with the strategy. Using the model, it can be shown that alternative designs, though built on the same strategy, lead to different land-use patterns over time.
MoPAgrIB: simulating savannah landscape mosaic under shifting cultivation
Nicolas Becu Marc Deconchat Eric Garine Kouami Kokou Christine Raimond | Published Monday, May 27, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2014MoPAgrIB model simulates the movement of cultivated patches in a savannah vegetation mosaic ; how they move and relocate through the landscape, depending on farming practices, population growth, social rules and vegetation growth.
Population aggregation in ancient arid environments
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, May 04, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The purpose of this model is to help understand how prehistoric societies adapted to the prehistoric American southwest landscape. In the American southwest there is a high degree of environmental var
Peer reviewed Strategy with Externalities
J Applegate Glenn Hoetker | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017The SWE models firms search behaviour as the performance landscape shifts. The shift represents society’s pricing of negative externalities, and the performance landscape is an NK structure. The model is written in NetLogo.
Managing Connectivity: insights from modelling species interactions accross multiple scales in an idealized landscape
Jacopo Baggio Kehinde Salau Michael Schoon Marco Janssen | Published Monday, October 01, 2012 | Last modified Monday, January 20, 2014The model objective’s is to explore the management choice set to uncover which subsets of strategies are most effective at maximizing species coexistence on a fragmented landscape.
Mobility, Resource Harvesting and Robustness of Social-Ecological Systems
Irene Perez Ibarra | Published Monday, September 24, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model is a stylized representation of a social-ecological system of agents moving and harvesting a renewable resource. The purpose is to analyze how mobility affects sustainability. Experiments changing agents’ mobility, landscape and information governments have can be run.
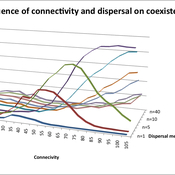
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
Model to simulation the landscape of possible shedding games
Marco Janssen | Published Sunday, May 16, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates 2048 versions of shedding games and evaluates the consequences on the average length and the difficulty of the game agents experience. The purpose of the model is to understand th
Displaying 10 of 86 results landscape clear