About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 35 results agriculture clear search
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Friday, June 03, 2022ViSA simulates the decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. The lack of sufficient supply of ESSs triggers stakeholders to apply different management options to increase their supply. However, while attempting to reduce the supply-demand gap, conflicts arise among stakeholders due to the tradeoff nature of some ESS. ViSA investigates conditions and scenarios that can minimize such supply-demand gap while reducing the risk of conflicts by suggesting different mixes of management options and decision rules.
Large-scale land acqusitions and smallholder food security
Tim Williams | Published Thursday, September 16, 2021Large-scale land acquisitions (LSLAs) threaten smallholder livelihoods globally. Despite more than a decade of research on the LSLA phenomenon, it remains a challenge to identify governance conditions that may foster beneficial outcomes for both smallholders and investors. One potentially promising strategy toward this end is contract farming (CF), which more directly involves smallholder households in commodity production than conditions of acquisition and displacement.
To improve understanding of how CF may mediate the outcomes of LSLAs, we developed an agent-based model of smallholder livelihoods, which we used as a virtual laboratory to experiment on a range of hypothetical LSLA and CF implementation scenarios.
The model represents a community of smallholder households in a mixed crop-livestock system. Each agent farms their own land and manages a herd of livestock. Agents can also engage in off-farm employment, for which they earn a fixed wage and compete for a limited number of jobs. The principal model outputs include measures of household food security (representing access to a single, staple food crop) and agricultural production (of a single, staple food crop).
…
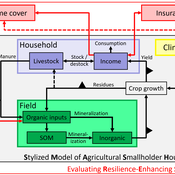
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
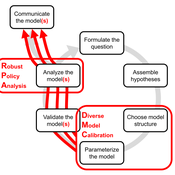
DMC-RPA: Diverse Model Calibration for Robust Policy Analysis (applied to an ABM of smallholder farmer resilience)
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, August 30, 2020This repository contains: (1) a model calibration procedure that identifies a set of diverse, plausible models; and (2) an ABM of smallholder agriculture, which is used as a case study application for the calibration method. By identifying a set of diverse models, the calibration method attends to the issue of “equifinality” prevalent in complex systems, which is a situation where multiple plausible process descriptions exist for a single outcome.
This model extends the original Artifical Anasazi (AA) model to include individual agents, who vary in age and sex, and are aggregated into households. This allows more realistic simulations of population dynamics within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350 than are possible in the original model. The parts of this model that are directly derived from the AA model are based on Janssen’s 1999 Netlogo implementation of the model; the code for all extensions and adaptations in the model described here (the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model) have been written by the authors. The AA model included only ideal and homogeneous “individuals” who do not participate in the population processes (e.g., birth and death)–these processes were assumed to act on entire households only. The ALHV model incorporates actual individual agents and all demographic processes affect these individuals. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. Thus, the ALHV model is a combination of individual processes (birth and death) and household-level processes (e.g., finding suitable agriculture plots).
As is the case for the AA model, the ALHV model makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original model (from Janssen’s Netlogo implementation) to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the valley. These estimates are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
Geographic Expansion Model (GEM)
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, February 28, 2020The purpose of this model is to explore the importance of geographic factors to the settlement choices of early Neolithic agriculturalists. In the model, each agriculturalist spreads to one of the best locations within a modeler specified radius. The best location is determined by choosing either one factor such as elevation or slope; or by ranking geographic factors in order of importance.
Local soy value chains in northern Ghana
Tim Verwaart | Published Thursday, August 29, 2019The purpose of the simulation is to evaluate alternative interventions by a value chain development program, aiming to improve rural livelihood and food and nutrition security. In northern Ghana, where distrust between the partners can be a problem in the functioning of value chains, the program supports the incorporation of smallholder farmers in soy clusters or agriculture APEX organization (farmers’ co-operatives) with a fair business environment. The goal is to to include the smallholder farmers in a strong value chain and reduce distrust.
Coastal Coupled Housing and Land Markets (C-CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca | Published Thursday, May 18, 2017Next generation of the CHALMS model applied to a coastal setting to investigate the effects of subjective risk perception and salience decision-making on adaptive behavior by residents.
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
A Model to Unravel the Complexity of Rural Food Security
Stefano Balbi Samantha Dobbie | Published Monday, August 22, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018An ABM to simulate the behaviour of households within a village and observe the emerging properties of the system in terms of food security. The model quantifies food availability, access, utilisation and stability.
Displaying 10 of 35 results agriculture clear search