About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 647 results agent based clear search
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Dilemma
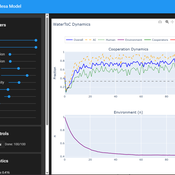
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. Although its original use was to simulate a ToC scenario with water as the shared resource, it can be applicable for a variety of scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour. The primary goal of the model is to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. It was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation of this model is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, this ABM serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
The model is built using Mesa 1.2.1 for the model and Solara for the interactive web-based dashboard. While Mesa version 3.0 was available at the time of this project’s finalization, version 1.2.1 was used to ensure functional correctness and maintain compatibility. Initial testing with Mesa 3.0 revealed significant, non-backward-compatible API changes relative to the 1.x series, which would have required a substantial rewrite of the existing, validated codebase. Therefore, to guarantee the stability and reproducibility of the results based on the original model implementation, version 1.2.1 was retained as the foundational dependency for this research.
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
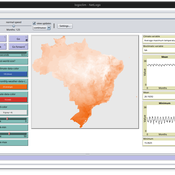
Leandro Garcia Daniel Vartanian Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, July 03, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental science, and other fields that rely on climate data integration.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) (O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017), available for academic and other non-commercial use.
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub.
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
This agent-based model (ABM), developed in NetLogo and available on the COMSES repository, simulates a stylized, competitive electricity market to explore the effects of carbon pricing policies under conditions of technological innovation. Unlike traditional models that treat innovation as exogenous, this ABM incorporates endogenous innovation dynamics, allowing clean technology costs to evolve based on cumulative deployment (Wright’s Law) or time (Moore’s Law). Electricity generation companies act as agents, making investment decisions across coal, gas, wind, and solar PV technologies based on expected returns and market conditions. The model evaluates three policy scenarios—No Policy, Emissions Trading System (ETS), and Carbon Tax—within a merit-order market framework. It is partially empirically grounded, using real-world data for technology costs and emissions caps. By capturing emergent system behavior, this model offers a flexible and transparent tool for analyzing the transition to low-carbon electricity systems.
The SAFIRe model : Simulation of Agents for Fertility, Integrated Energy, Food security, and Reforestation
Etienne DELAY Lucas Broutin | Published Thursday, June 12, 2025The SAFIRe model (Simulation of Agents for Fertility, Integrated Energy, Food Security, and Reforestation) is an agent-based model co-developed with rural communities in Senegal’s Groundnut Basin. Its purpose is to explore how local farming and pastoral practices affect the regeneration of Faidherbia albida trees, which are essential for maintaining soil fertility and supporting food security through improved millet production. The model supports collective reflection on how different social and ecological factors interact, particularly around firewood demand, livestock pressure, and agricultural intensification.
The model simulates a 100-hectare agricultural landscape where agents (farmers, shepherds, woodcutters, and supervisors) interact with trees, land parcels, and each other. It incorporates seasonality, crop rotation, tree growth and cutting, livestock feeding behaviors, and farmers’ engagement in sapling protection through Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR). Two types of surveillance strategies are compared: community-led monitoring and delegated surveillance by forestry authorities. Farmer engagement evolves over time based on peer influence, meeting participation, and the success of visible tree regeneration efforts.
SAFIRe integrates participatory modeling (ComMod and ComExp) and a backcasting approach (ACARDI) to co-produce scenarios rooted in local aspirations. It was explored using the OpenMole platform, allowing stakeholders to test a wide range of future trajectories and analyze the sensitivity of key parameters (e.g., discussion frequency, time in fields). The model’s outcomes not only revealed unexpected insights—such as the hidden role of farmers in tree loss—but also led to real-world actions, including community nursery creation and behavioral shifts toward tree care. SAFIRe illustrates how agent-based modeling can become a tool for social learning and collective action in socio-ecological systems.
A language economics perspective on language spread: Simulating Language Dynamics in a Social Network
Marco Civico | Published Saturday, June 07, 2025This model examines language dynamics within a social network using simulation techniques to represent the interplay of language adoption, social influence, economic incentives, and language policies. The agent-based model (ABM) focuses on interactions between agents endowed with specific linguistic attributes, who engage in communication based on predefined rules. A key feature of our model is the incorporation of network analysis, structuring agent relationships as a dynamic network and leveraging network metrics to capture the evolving inter-agent connections over time. This integrative approach provides nuanced insights into emergent behaviors and system dynamics, offering an analytical framework that extends beyond traditional modeling approaches. By combining agent-based modeling with network analysis, the model sheds light on the underlying mechanisms governing complex language systems and can be effectively paired with sociolinguistic observational data.
Peer reviewed Urban Transport Mode Choices
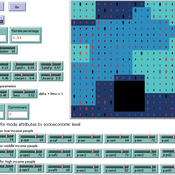
Kathleen Salazar -Serna Lorena Cadavid Carlos Franco | Published Thursday, May 22, 2025The model represents urban commuters’ transport mode choices among cars, public transit, and motorcycles—a mode highly prevalent in developing countries. Using an agent-based modeling approach, it simulates transport dynamics and serves as a testbed for evaluating policies aimed at improving mobility.
The model simulates an ecosystem of human agents who decide, at each time step, which mode of transportation to use for commuting to work. Their decision is based on a combination of personal satisfaction with their most recent journey—evaluated across a vector of individual needs—the information they crowdsource from their social network, and their personal uncertainty regarding trying new transport options.
Agents are assigned demographic attributes such as sex, age, and income level, and are distributed across city neighborhoods according to their socioeconomic status. To represent social influence in decision-making, agents are connected via a scale-free social network topology, where connections are more likely among agents within the same socioeconomic group, reflecting the tendency of individuals to form social ties with similar others.
…
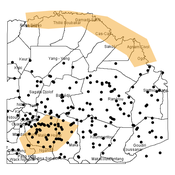
Agent-based modeling of the spatio-temporal distribution of Sahelian transhumant herds
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Tuesday, May 20, 2025Sahelian transhumance is a seasonal pastoral mobility between the transhumant’s terroir of origin and one or more host terroirs. Sahelian transhumance can last several months and extend over hundreds of kilometers. Its purpose is to ensure efficient and inexpensive feeding of the herd’s ruminants. This paper describes an agent-based model to determine the spatio-temporal distribution of Sahelian transhumant herds and their impact on vegetation. Three scenarios based on different values of rainfall and the proportion of vegetation that can be grazed by transhumant herds are simulated. The results of the simulations show that the impact of Sahelian transhumant herds on vegetation is not significant and that rainfall does not impact the alley phase of transhumance. The beginning of the rainy season has a strong temporal impact on the spatial distribution of transhumant herds during the return phase of transhumance.
Agent-based Simulation of Innovation Diffusion
Theresa Elbracht | Published Monday, May 19, 2025The agent-based simulation of innovation diffusion is based on the idea of the Bass model (1969).
The adoption of an agent is driven two parameters: its innovativess p and its prospensity to conform with others. The model is designed for a computational experiment building up on the following four model variations:
(i) the agent population it fully connected and all agents share the same parameter values for p and q
(ii) the agent population it fully connected and agents are heterogeneous, i.e. individual parameter values are drawn from a normal distribution
(iii) the agents population is embeded in a social network and all agents share the same parameter values for p and q
…
Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) Simulation for Compact Urban Growth in Dublin: An Agent-Based Model in NetLogo
ajithvyas | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2025This agent-based model simulates the implementation of a Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) mechanism in a stylized urban environment inspired by Dublin. It explores how developer agents interact with land parcels under spatial zoning, conservation protections, and incentive-based policy rules. The model captures emergent outcomes such as compact growth, green and heritage zone preservation, and public cost-efficiency. Built in NetLogo, the model enables experimentation with variable FSI bonuses, developer behavior, and spatial alignment of sending/receiving zones. It is intended as a policy sandbox to test market-aligned planning tools under behavioral and spatial uncertainty.
Displaying 10 of 647 results agent based clear search