About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 133 results for "José I Santos" clear search
06 EiLab V1.36 – Entropic Index Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 14, 2017EiLab explores the role of entropy in simple economic models. EiLab is one of several models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, and CmLab.
04 TpLab V2.08 – Teleological Pruning Laboratory
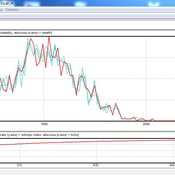
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Our societal belief systems are pruned by evolution, informing our unsustainable economies. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
COOPER - Flood impacts over Cooperative Winemaking Systems
David Nortes Martinez David Nortes-Martinez | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 22, 2019The model simulates flood damages and its propagation through a cooperative, productive, farming system, characterized as a star-type network, where all elements in the system are connected one to each other through a central element.
06 EiLab V1.40 – Entropic Index Laboratory
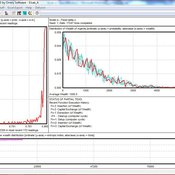
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, March 19, 2018There is a new type of economic model called a capital exchange model, in which the biophysical economy is abstracted away, and the interaction of units of money is studied. Benatti, Drăgulescu and Yakovenko described at least eight capital exchange models – now referred to collectively as the BDY models – which are replicated as models A through H in EiLab. In recent writings, Yakovenko goes on to show that the entropy of these monetarily isolated systems rises to a maximal possible value as the model approaches steady state, and remains there, in analogy of the 2nd law of thermodynamics. EiLab demonstrates this behaviour. However, it must be noted that we are NOT talking about thermodynamic entropy. Heat is not being modeled – only simple exchanges of cash. But the same statistical formulae apply.
In three unpublished papers and a collection of diary notes and conference presentations (all available with this model), the concept of “entropic index” is defined for use in agent-based models (ABMs), with a particular interest in sustainable economics. Models I and J of EiLab are variations of the BDY model especially designed to study the Maximum Entropy Principle (MEP – model I) and the Maximum Entropy Production Principle (MEPP – model J) in ABMs. Both the MEPP and H.T. Odum’s Maximum Power Principle (MPP) have been proposed as organizing principles for complex adaptive systems. The MEPP and the MPP are two sides of the same coin, and an understanding of their implications is key, I believe, to understanding economic sustainability. Both of these proposed (and not widely accepted) principles describe the role of entropy in non-isolated systems in which complexity is generated and flourishes, such as ecosystems, and economies.
EiLab is one of several models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, and CmLab.
CA-MRSA Demonstration Model
Jonathan Ozik Charles Macal Kenneth Letendre Irene Lee | Published Tuesday, January 06, 2015We demonstrate how a simple model of community associated Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) can be easily constructed by leveraging the statecharts and ReLogo capabilities in Repast Simphony.
A model of the emergence of intersectional life course inequalities through transitions in the workplace. It explores LGBTQ citizens’ career outcomes and trajectories in relation to several mediating factors: (i) workplace discrimination; (ii) social capital; (iii) policy interventions (i.e., workplace equality, diversity, and inclusion policies); (iv) and LGBTQ employees’ behaviours in response to discrimination (i.e., moving workplaces and/or different strategies for managing the visibility of their identity).
Linear recruitment leads to allocation and flexibility in collective foraging by ants
Takao Sasaki Zachary Joseph Shaffer Stephen Pratt | Published Thursday, July 11, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, September 05, 2013Ants in the genus Temnothorax use tandem runs (rather than pheromone trails) to recruit to food sources. This model explores the collective consequences of this linear recruitment (as opposed to highly nonlinear pheromone trails).
The purpose of the AdaptPumpa model is to analyze the robustness of the Pumpa irrigation system in Nepal to climate change.
Social Identity Model of Protest Emergence (SIMPE)
Cristina Chueca Del Cerro | Published Friday, March 17, 2023The Social Identity Model of Protest Emergence (SIMPE), an agent-based model of national identity and protest mobilisations.
I developed this model for my PhD project, “Polarisation and Protest Mobilisation Around Secessionist Movements: an Agent-Based Model of Online and Offline Social Networks”, at the University of Glasgow (2019-2023).
The purpose of this model is to simulate protest emergence in a given country where there is an independence movement, fostering the self-categorisation process of national identification. In order to contextualised SIMPE, I have used Catalonia, where an ongoing secessionist movement since 2011 has been present, national identity has shown signs of polarisation, and where numerous mobilisations have taken place over the last decade. Data from the Catalan Centre of Opinion Studies (CEO) has been used to inform some of the model parameters.
…
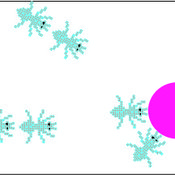
Ant Colony Optimization for infrastructure routing
Igor Nikolic Emile Chappin P W Heijnen | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, March 24, 2018The mode implements a variant of Ant Colony Optimization to explore routing on infrastructures through a landscape with forbidden zones, connecting multiple sinks to one source.
Displaying 10 of 133 results for "José I Santos" clear search