About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 73 results for "Alistair G Sutcliffe" clear search
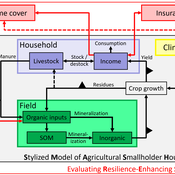
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
Mast seeding model
Giangiacomo Bravo Lucia Tamburino | Published Saturday, September 08, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Purpose of the model is to perform a “virtual experiment” to test the predator satiation hypothesis, advanced in literature to explain the mast seeding phenomenon.
Bicycle encounter model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 29, 2019This Bicycle encounter model builds on the Salzburg Bicycle model (Wallentin & Loidl, 2015). It simulates cyclist flows and encounters, which are locations of potential accidents between cyclists.
Traffic and Shipments out of Inter-Firm Communication in a Textile Industrial District
Guido Fioretti Guido Fioretti | Published Monday, April 27, 2020This article presents an agent-based model of an Italian textile district where thousands of small firms specialize in particular phases of fabrics production. It reconstructs the web of communication between firms as they arrange production chains. In turn, production chains result in road traffic between the geographical areas on which the district extends. The reconstructed traffic exhibits a pattern that has been observed, but not foreseen, by policy makers.
Peer reviewed Emergence of Organizations out of Garbage Can Dynamics
Guido Fioretti | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 26, 2020The Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice (GCM) is a fundamental model of organizational decision-making originally propossed by J.D. Cohen, J.G. March and J.P. Olsen in 1972. In their model, decisions are made out of random meetings of decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems within an organization.
With this model, these very same agents are supposed to meet in society at large where they make decisions according to GCM rules. Furthermore, under certain additional conditions decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems form stable organizations. In this artificial ecology organizations are born, grow and eventually vanish with time.
Knowledge Based Economy
Guido Fioretti Sirio Capizzi Ruggero Rossi Martina Casari Ala Jlif | Published Tuesday, May 18, 2021Knowledge Based Economy (KBE) is an artificial economy where firms placed in geographical space develop original knowledge, imitate one another and eventually recombine pieces of knowledge. In KBE, consumer value arises from the capability of certain pieces of knowledge to bridge between existing items (e.g., Steve Jobs illustrated the first smartphone explaining that you could make a call with it, but also listen to music and navigate the Internet). Since KBE includes a mechanism for the generation of value, it works without utility functions and does not need to model market exchanges.
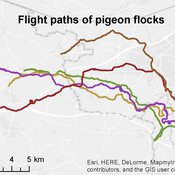
Homing pigeon model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016This model represents the flight paths of a flock of homing pigeons according to their flocking-, orientation- and leadership behaviour.
Salzburg Bicycle model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016An ABM to simulate the spatio-temporal distribution of cyclists across the road network of the city of Salzburg.
TREELIM
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Wednesday, November 30, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 10, 2017The model simulates the spatial patterns of secondary forest succession above the current alpine tree line in the context of land use and climate change. Three scenarios are offered: (1) climate change, (2) land use change, (3) species composition.
An adaptive model of homing pigeons: A genetic algorithm approach
Gudrun Wallentin Francis Oloo | Published Friday, January 27, 2017In this model, we simulate the navigation behavior of homing pigeons. Specifically we use genetic algorithms to optimize the navigation and flocking parameters of pigeon agents.
Displaying 10 of 73 results for "Alistair G Sutcliffe" clear search