About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 92 results for "Caroline Schill" clear search
00b SimEvo_V5.08 NetLogo
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, October 05, 2019In 1985 Dr Michael Palmiter, a high school teacher, first built a very innovative agent-based model called “Simulated Evolution” which he used for teaching the dynamics of evolution. In his model, students can see the visual effects of evolution as it proceeds right in front of their eyes. Using his schema, small linear changes in the agent’s genotype have an exponential effect on the agent’s phenotype. Natural selection therefore happens quickly and effectively. I have used his approach to managing the evolution of competing agents in a variety of models that I have used to study the fundamental dynamics of sustainable economic systems. For example, here is a brief list of some of my models that use “Palmiter Genes”:
- ModEco - Palmiter genes are used to encode negotiation strategies for setting prices;
- PSoup - Palmiter genes are used to control both motion and metabolic evolution;
- TpLab - Palmiter genes are used to study the evolution of belief systems;
- EffLab - Palmiter genes are used to study Jevon’s Paradox, EROI and other things.
…
Comparing agent-based models on experimental data of irrigation games
Marco Janssen Jacopo A. Baggio | Published Tuesday, July 02, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 03, 2013Comparing 7 alternative models of human behavior and assess their performance on a high resolution dataset based on individual behavior performance in laboratory experiments.
Peer reviewed COMMONSIM: Simulating the utopia of COMMONISM
Lena Gerdes Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle Ernest Aigner Stefan Meretz Jens Schröter Hanno Pahl Annette Schlemm Simon Sutterlütti | Published Sunday, November 05, 2023This research article presents an agent-based simulation hereinafter called COMMONSIM. It builds on COMMONISM, i.e. a large-scale commons-based vision for a utopian society. In this society, production and distribution of means are not coordinated via markets, exchange, and money, or a central polity, but via bottom-up signalling and polycentric networks, i.e. ex-ante coordination via needs. Heterogeneous agents care for each other in life groups and produce in different groups care, environmental as well as intermediate and final means to satisfy sensual-vital needs. Productive needs decide on the magnitude of activity in groups for a common interest, e.g. the production of means in a multi-sectoral artificial economy. Agents share cultural traits identified by different behaviour: a propensity for egoism, leisure, environmentalism, and productivity. The narrative of this utopian society follows principles of critical psychology and sociology, complexity and evolution, the theory of commons, and critical political economy. The article presents the utopia and an agent-based study of it, with emphasis on culture-dependent allocation mechanisms and their social and economic implications for agents and groups.
An agent-based approach to weighted decision making in the spatially and temporally variable South African Paleoscape
Colin Wren | Published Thursday, December 29, 2016This model simulates a foraging system based on Middle Stone Age plant and shellfish foraging in South Africa.
NarrABS
Tilman Schenk | Published Thursday, September 20, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent based simulation of a political process based on stakeholder narratives
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
AIforGoodSimulator - Modeling Covid-19 Spread and Potential Interventions in Refugee Camps
Shyaam Ramkumar Woi Sok Oh | Published Thursday, March 18, 2021The Netlogo model is a conceptualization of the Moria refugee camp, capturing the household demographics of refugees in the camp, a theoretical friendship network based on values, and an abstraction of their daily activities. The model then simulates how Covid-19 could spread through the camp if one refugee is exposed to the virus, utilizing transmission probabilities and the stages of disease progression of Covid-19 from susceptible to exposed to asymptomatic / symptomatic to mild / severe to recovered from literature. The model also incorporates various interventions - PPE, lockdown, isolation of symptomatic refugees - to analyze how they could mitigate the spread of the virus through the camp.
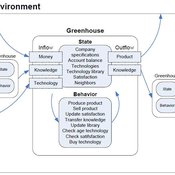
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
MiniDemographicABM.jl: A simplified agent-based demographic model of the UK
Atiyah Elsheikh | Published Friday, July 28, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 12, 2023This package implements a simplified artificial agent-based demographic model of the UK. Individuals of an initial population are subject to ageing, deaths, births, divorces and marriages. A specific case-study simulation is progressed with a user-defined simulation fixed step size on a hourly, daily, weekly, monthly basis or even an arbitrary user-defined clock rate. While the model can serve as a base model to be adjusted to realistic large-scale socio-economics, pandemics or social interactions-based studies mainly within a demographic context, the main purpose of the model is to explore and exploit capabilities of the state-of-the-art Agents.jl Julia package as well as other ecosystem of Julia packages like GlobalSensitivity.jl. Code includes examples for evaluating global sensitivity analysis using Morris and Sobol methods and local sensitivity analysis using OFAT and OAT methods. Multi-threaded parallelization is enabled for improved runtime performance.
Displaying 10 of 92 results for "Caroline Schill" clear search