About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 126 results for "Daniel G Brown" clear search
Agent-based Simulation Models of the College Sorting Process
Rachel Baker Sean F Reardon Matt Kasman Daniel Klasik | Published Friday, May 23, 2014We explore how dynamic processes related to socioeconomic inequality operate to sort students into, and create stratification among, colleges.
MarPEM: An Agent Based Model to Explore the Effects of Policy Instruments on the Transition of the Maritime Fuel System
G Bas I Nikolic K De Boo Am Vaes - Van De Hulsbeek | Published Thursday, June 15, 2017MarPEM is an agent-based model that can be used to study the effects of policy instruments on the transition away from HFO.
Scholars have written extensively about hierarchical international order, on the one hand, and war on the other, but surprisingly little work systematically explores the connection between the two. This disconnect is all the more striking given that empirical studies have found a strong relationship between the two. We provide a generative computational network model that explains hierarchy and war as two elements of a larger recursive process: The threat of war drives the formation of hierarchy, which in turn shapes states’ incentives for war. Grounded in canonical theories of hierarchy and war, the model explains an array of known regularities about hierarchical order and conflict. Surprisingly, we also find that many traditional results of the IR literature—including institutional persistence, balancing behavior, and systemic self-regulation—emerge from the interplay between hierarchy and war.
An Agent-Based DSS for Word-of-Mouth Programs in Freemium Apps
Manuel Chica | Published Monday, September 05, 2016An agent-based framework that aggregates social network-level individual interactions to run targeting and rewarding programs for a freemium social app. Git source code in https://bitbucket.org/mchserrano/socialdynamicsfreemiumapps
PolicySpace: agent-based modeling
Francisco Miguel Quesada Bernardo Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Tuesday, March 06, 2018PolicySpace models public policies within an empirical, spatial environment using data from 46 metropolitan regions in Brazil. The model contains citizens, markets, residences, municipalities, commuting and a the tax scheme. In the associated publications (book in press and https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.00259) we validate the model and demonstrate an application of the fiscal analysis. Besides providing the basics of the platform, our results indicate the relevance of the rules of taxes transfer for cities’ quality of life.
Peer reviewed Infectious diseases model for mixed-methods research chapter
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Sunday, January 30, 2022The purpose of this curricular model is to teach students the basics of modeling complex systems using agent-based modeling. It is a simple SIR model that simulates how a disease spreads through a population as its members change from susceptible to infected to recovered and then back to susceptible. The dynamics of the model are such that there are multiple emergent outcomes depending on the parameter settings, initial conditions, and chance.
The curricular model can be used with the chapter Agent-Based Modeling in Mixed Methods Research (Moritz et al. 2022) in the Handbook of Teaching Qualitative & Mixed Methods (Ruth et al. 2022).
The instructional videos can be accessed on YouTube: Video 1 (https://youtu.be/32_JIfBodWs); Video 2 (https://youtu.be/0PK_zVKNcp8); and Video 3 (https://youtu.be/0bT0_mYSAJ8).
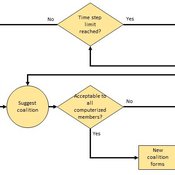
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
NetLogo-R-Example for the Inititialisation of Agents with Correlated Random Numbers
Danilo Saft | Published Friday, February 14, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This is a short NetLogo example demonstrating how to initialize 500 agents with 4 correlated parameters each with random values by doing the necessary calculations in the program “R” and retrieving the results.
HMODEL: an exploratory simulation of surface archaeological formation
Benjamin Davies Simon Holdaway Patricia Fanning | Published Thursday, November 30, 2017This model is used to simulate the influence of spatially and temporally variable sedimentary processes on the distribution of dated archaeological features in a surface context.
Logônia: Plant Growth Response Model in NetLogo
Leandro Garcia Daniel Vartanian Aline | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025Logônia is a NetLogo model that simulates the growth response of a fictional plant, logônia, under different climatic conditions. The model uses climate data from WorldClim 2.1 and demonstrates how to integrate the LogoClim model through the LevelSpace extension.
Logônia follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub.
Displaying 10 of 126 results for "Daniel G Brown" clear search