About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 853 results for "Jes%C3%BAs M Zamarre%C3%B1o" clear search
ABM for Underwater optical wireless communication in a water tank
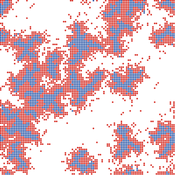
Mohamed ABID | Published Sunday, May 29, 2022This model simulates the propagation of photons in a water tank. A source of light emits an impulse of photons with equal energy represented by yellow dots. These photons are then scattered by water particles before possibly reaching the photo-detector represented by a gray line. Different types of water are considered. For each one of them we calculate the total received energy.
The water tank is represented by a blue rectangle with fixed dimensions. It’s exposed to the air interface and has totally absorbent barriers. Four types of water are supported. Each one is characterized by its absorption and scattering coefficients.
At the source, the photons are generated uniformly with a random direction within the beamwidth. Each photon travels a random distance drawn from a distribution depending on the water characteristics before encountering a water particle.
Based on the updated position of the photon, three situations may occur:
-The photon hits the barrier of the tank on its trajectory. In this case it’s considered as lost since the barriers are assumed totally absorbent.
…
Policy Formulation for Public Administration - Innovation
Bashar Ourabi | Published Tuesday, August 29, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, August 29, 2017Innovation a byproduct of the intellectual capital, requires a new paradigm for the production constituents. Human Capital HC,Structural capital SC and relational capital RC become key for intellectual capital and consequently for innovation.
Nice Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Friday, February 05, 2016 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2017The Nice Musical Chairs (NMC) model represent the competition for space between groups of stakeholders of farming and herding activities in the arid Afro-Eurasia.
Socio-hydrologicalModel_version_SESMO
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Paola Gomez Luis Bojorquez Fidel Serrano-Candela Hallie Eakin Yosune Miquelajauregui Rodrigo Garcia-Herrera | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We present here MEGADAPT_SESMO model. A hybrid, dynamic, spatially explicit, integrated model to simulate the vulnerability of urban coupled socio-ecological systems – in our case, the vulnerability of Mexico City to socio-hydrological risk.
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
Evaluate government policies for farmers’ adoption and synergy in improving irrigation systems
Amir Hajimirzajan | Published Sunday, February 25, 2024The ABM model is designed to model the adaptability of farmers in DTIM. This model includes two groups of farmers and local government admins agents. Farmers with different levels, with low WP of DTIM, are looking for economic benefits and reduced irrigation and production costs. Meanwhile, the government is looking for strategic goals to maintain water resources’ sustainability. The local government admins employ incentives (subsidies in this study) to encourage farmers to DTIM. In addition, it is used as a tool for supervision and training farmers’ performance. Farmers are currently harvesting water resources with irrigation systems and different levels of technology, and they intend to provide short-term benefits. Farmers adjust the existing approach based on their knowledge of the importance of DTIM and propensity to increase WP and cost-benefit evaluation. DTIM has an initial implementation fee. Every farmer can increase WP by using government subsidies. If none of the farmers create optimal use of water resources, access to water resources will be threatened in the long term. This is considered a hypothetical cost for farmers who do not participate in DTIM. With DTIM, considering that local government admins’ facilities cover an essential part of implementation costs, farmers may think of profiting from local government admins’ facilities by selling that equipment, especially if the farmers in the following conditions may consider selling their developed irrigation equipment. In this case, the technology of their irrigation system will return to the state before development.
- When the threshold of farmers’ propensity to DTIM is low (for example, in the conditions of scarcity of access to sufficient training about the new irrigation system or its role in reducing the cost and sustainability of water resources)
- When the share of government subsidy is high, and as a result, the profit from the sale of equipment is attractive, especially in conditions of inflation.
- Finally, farmers’ honesty threshold should be reduced based on the positive experience of profit-seeking and deception among neighbors.
Increasing the share of government subsidies can encourage farmers to earn profits. Therefore, the government can help increase farmers’ profits by considering the assessment teams at different levels with DTIM training . local government admins evaluations monitor the behavior of farmers. If farmers sell their improved irrigation system for profit, they may be deprived of some local government admins’ services and the possibility of receiving subsidies again. Assessments The local government admins can increase farmers’ honesty. Next, the ABM model evaluates local government admins policies to achieve a suitable framework for water resources management in the Miandoab region.
Increased costs of cooperation help cooperators in the long run
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, March 01, 2017A spatial prisoner’s dilemma model with mobile agents, de-coupled birth-death events, and harsh environments.
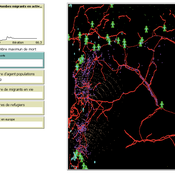
RefugeePathSIM Model
Liliana Perez Saeed Harati Guillaume Arnoux Hébert | Published Thursday, October 11, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, October 16, 2018RefugeePathSIM is an agent-based model to simulate the movement behavior of refugees in order to identify pathways of forced migration under crisis. The model generates migrants and lets them leave conflict areas for a destination that they choose based on their characteristics and desires. RefugeePathSIM has been developed and applied in a study of the Syrian war, using monthly data in years 2011-2015.
RobbyGA modified 2019
Timothy Gooding | Published Sunday, February 24, 2019This is a modification of the RobbyGA model by the Santa Fe Institute (see model Info tab for full information). The basic idea is that the GA has been changed to one where the agents have a set lifetime, anyone can reproduce with anyone, but where there is a user-set amount of ‘starvation’ that kills the agents that have a too low fitness.
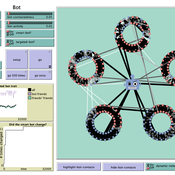
How do bots influence beliefs on social media? Why do beliefs propagated by social bots spread far and wide, yet does their direct influence appear to be limited?
This model extends Axelrod’s model for the dissemination of culture (1997), with a social bot agent–an agent who only sends information and cannot be influenced themselves. The basic network is a ring network with N agents connected to k nearest neighbors. The agents have a cultural profile with F features and Q traits per feature. When two agents interact, the sending agent sends the trait of a randomly chosen feature to the receiving agent, who adopts this trait with a probability equal to their similarity. To this network, we add a bot agents who is given a unique trait on the first feature and is connected to a proportion of the agents in the model equal to ‘bot-connectedness’. At each timestep, the bot is chosen to spread one of its traits to its neighbors with a probility equal to ‘bot-activity’.
The main finding in this model is that, generally, bot activity and bot connectedness are both negatively related to the success of the bot in spreading its unique message, in equilibrium. The mechanism is that very active and well connected bots quickly influence their direct contacts, who then grow too dissimilar from the bot’s indirect contacts to quickly, preventing indirect influence. A less active and less connected bot leaves more space for indirect influence to occur, and is therefore more successful in the long run.
Displaying 10 of 853 results for "Jes%C3%BAs M Zamarre%C3%B1o" clear search